How The Newborn Hearing Screening Is Performed
The hearing screening is performed using an Automated Auditory Brainstem Response device.
The screening is quick, easy, painless and reliable. It usually takes only a few minutes. It must be done while your baby is asleep or in a very quiet, relaxed state.
How Is The Hearing Test Done
The hearing test is usually done at the bed side while you and your baby are still in hospital. The hearing screener will explain the test and ask you to sign a consent form.
Some Australian states use the automated auditory brainstem response screening test. For this test, the screener places ear cups on your babys ears that play a soft clicking noise. Sensors are placed on your babys forehead, neck and shoulder to measure how the auditory nerve responds to the sounds played. The auditory nerve transfers sound from the cochlea in the inner ear to the brain. The test is quick and painless. Your baby can sleep or feed during the test.
Other states use a different screening test, known as the TEOAE hearing test. This test is done by placing a probe in the ear canal that makes soft sounds. This test is also quick and painless.
Where Does Nbs Happen
All babies need NBS, regardless of where they are born.
If your baby is born at a hospital, screening will happen before you take your baby home. Usually, a health care provider performs NBS in your room or a newborn/nursery area.
If your baby has an out-of-hospital birth, screening can happen outside of the hospital like at your birth center or home. Many midwives are trained to complete NBS.
If you are planning an out-of-hospital birth, talk to your midwife about NBS before your baby is born. If your midwife cannot perform NBS, make other arrangements. Your babys health care provider can help arrange screening by another midwife, a hospital, clinic, or local health department. It is important that you make a plan so your baby completes screening near the recommended age.
Recommended Reading: How To Be The Best Dad To A Newborn
How Are Newborns Screened For Hearing Loss
Nearly every baby born in a hospital in the United States has a hearing screening before they go home. Hospitals use two types of newborn hearing screening tests:
- Auditory brainstem response testing uses earphones to send sounds to your babys ears. Sticker sensors on your babys head detect how the hearing nerve responds to sounds.
- Otoacoustic Emissions testing uses a tiny earphone and microphone placed in the babys ear. The earphone sends sounds to your babys ear. The microphone detects if there is a response from your babys inner ear.
These tests are quick and painless, and your baby needs to be quiet or asleep to get accurate results.
Have Your Baby Screened For Hearing Loss
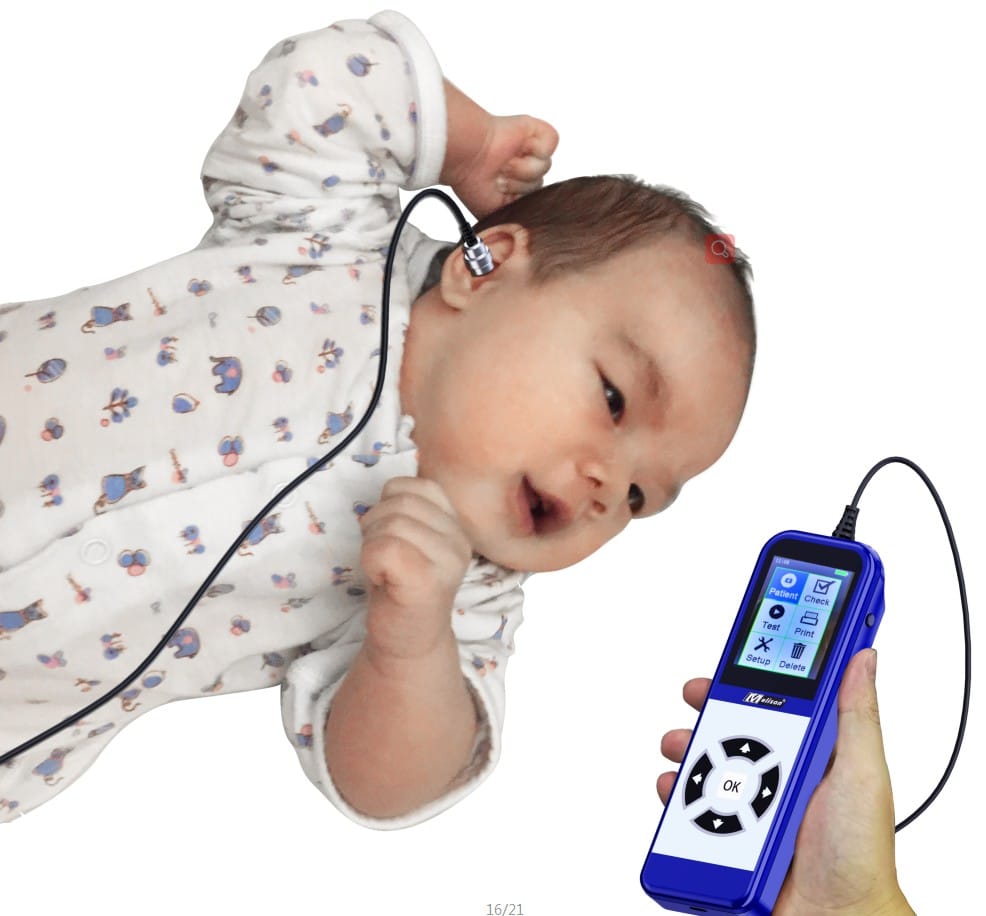

- All babies should be screened for hearing loss no later than one month of age. It is best if they are screened before leaving the hospital after birth.
- If your baby does not pass a hearing screening, it is very important to get a full hearing test as soon as possible, but no later than 3 months of age.
You May Like: What Do I Feed A Newborn Puppy
What If My Newborn Passes The Hearing Screening
Most newborns who pass the hearing screening have normal hearing. However, some newborns might hear well enough to pass a screening, even though their hearing is not perfectly normal. It is a screening and not a diagnostic test, and so the newborn hearing screening cannot properly identify 100 percent of babies with hearing loss.
Additionally, some newborns may pass the screening at birth, yet they can lose hearing from illness, medications, or genetic reasons. This hearing loss can come on suddenly or gradually over time.
Because of these factors, it is important that, even if your newborn passes the screening, you contact your childs pediatrician and get a referral to an audiologist for hearing testing if you have any concerns for your childs hearing.
When Does The Hearing Test Happen
The hearing test should ideally be performed before your baby leaves hospital after the birth. The test is usually done within 2 days and can be done as early as 6 hours after birth. If for some reason you go home before the test your baby can still have their hearing tested as an outpatient or during a home visit by an appropriately qualified early discharge nurse. The test should be done within 1 month of birth for healthy babies or by 3 months for sick or premature babies.
You May Like: How To Feed Newborn Baby With Bottle
Know The Signs Of Hearing Loss
The signs and symptoms of hearing loss are different for different children. If you see any of these signs, call your child’s doctor or nurse:
- Does not turn to the source of a sound from birth to 3-4 months of age.
- Does not say single words, such as “dada” or “mama”, by 1 year of age.
- Turns head when he or she sees you but not if you call out his or her name
- Hears some sounds but not others.
Automated Auditory Brainstem Response
If an infant cannot get a OAE or if an infant doesnt pass the OAE, they can get a different test an automated auditory brainstem response. For this test, small sensors are put on the babys head, and the baby will wear earphones. This test measures how the nerves that control hearing respond to sound. Small sensors are placed on the babys head and earphones are also used. Both of these tests are safe and do not hurt.
Both of these test must be done at the hospital your baby was born. If your baby was born at home, your midwife needs to give you a referral to one of these birthing hospitals.
Don’t Miss: What Items Do You Need For A Newborn Baby
Current Approaches To Newborn And Infant Hearing Screening In The World
Not only the exact data is unavailable in most of countries, the minimal level of hearing loss being taken in account and method of testing is different. Members of the International Association of Logopedics Audiology Committee recently reported on the activities of their newborn hearing screening programs during 2008. The data presented was either for the whole country or for specific regions . The detection threshold targeted by newborn hearing screening ranges from 20 dB HL to 40 dB HL and is performed bilaterally in all replying countries. The screening methods used in all replying countries are transient evoked otoacoustic emissions testing and automated auditory brainstem response , with distortion product otoacoustic emissions testing also used in some countries. Most countries use AABR in neonatal intensive care units or for babies at risk of early infant hearing loss. The protocols used in the first stage are TEOAE alone TEOAE/DPOAE TEOAE/AABR or AABR alone . In the second stage, TEOAE alone is used in India and Serbia TEOAE/AABR in Sweden and the United States and AABR alone in Germany. In India, AABR is also used for a third stage. The first and second stages of screening are performed mostly in hospitals , while the third stage screenings are performed in hospitals , in Hearing Health Care Services , or in pediatric-audiological or ENT departments and practices .
What Is Newborn Infant Hearing Screening
- Newborn infant hearing screening programs are designed to identify hearing loss in infants shortly after birth.
- All states have implemented these screening protocols within hospitals and birthing clinics.
- Most hearing screening tests are done prior to discharge from the hospital or birthing clinics.
- Typically, nurses or medical assistants are trained extensively on how to operate automated equipment for testing infants. Prior to discharge, each newborn has his/her hearing tested. If, for some reason, the newborn does not pass the screen, a rescreen is usually done. If the infant does not pass the second hearing test, he/she is referred to a specialist for further testing.
- Specialists who are experts at testing hearing are called audiologists. Audiologists have had training that emphasizes diagnostic hearing testing techniques as well as hearing rehabilitation of children and adults. Their postgraduate academic training requires a minimum of a masters degree.
You May Like: How Do You Get A Newborn Social Security Card
How The Test Is Done
The newborn hearing screening test checks your babys inner ear . When a healthy ear receives sound, the inner part produces an echo. Recording this tells us that the hearing is satisfactory.
This screening test can be repeated if a clear response is not achieved in either one or both ears.
You May Like: Can Newborns Have Acid Reflux
Importance Of Screening Your Newborn For Hearing Loss
Good hearing is essential for the normal development of speech and language. The ability to speak and understand language develops mainly between birth and age 3. Without a newborn hearing screening, hearing loss may go undetected for several years and may affect your childs speech and language skills.
Also Check: What Is The Best Similac Formula For Newborns
No Response In One Or Both Ears
If the hearing screen doesnt show a clear response from one or both ears, your baby may have hearing loss.
Other reasons your baby might not show a clear response are:
- they may have had fluid or a temporary blockage in the ears after birth
- they may have been unsettled during the screen
- there may have been background noise
Two to 3 babies in every 100 screened dont show a clear response.
Hearing Loss In Babies
1 to 2 babies in every 1,000 are born with permanent hearing loss in 1 or both ears.
This increases to about 1 in every 100 babies who have spent more than 48 hours in intensive care.
Most of these babies are born into families with no history of permanent hearing loss.
Permanent hearing loss can significantly affect babies’ development.
Finding out early can give these babies a better chance of developing language, speech and communication skills.
It will also help them make the most of relationships with their family or carers from an early age.
Read Also: How Much Enfamil Should A Newborn Drink
Reimbursement And Program Funding
Newborn hearing screening funding varies from state to state. States procure funds from fees, Medicaid, the Title V Maternal and Child Health Block Grant program, and state general revenues. The trend is to identify funding sources other than grants to ensure program continuity should grant support become unavailable. Costs associated with newborn hearing screening include those associated with the tests and those associated with program management .
Early Periodic Screening, Diagnostic, and Treatment Program
Through the EPSDT program, a set of services and benefits are mandated for all individuals under age 21 years who are enrolled in Medicaid. Federal rules encourage partnerships between state Medicaid and Title V agencies to ensure better access to and receipt of the full range of screening, diagnostic, and treatment services. EPSDT funds are an appropriate reimbursement source for screening and diagnostic services.
Current Procedural Terminology Codes
There are a number of CPT codes used to describe early hearing detection testing to a payer. Codes are defined by the payer or program. For specific instructions, see NCHAM State Contacts.
Alexander, D., & Van Dyck, P. C. . A vision of the future of newborn screening. Pediatrics, 117, S350-S354.
American Academy of Pediatrics. . Early Hearing Detection and Intervention . Retrieved from
Infants And Babies Hearing Can Be Checked
Do you know that your babys hearing can be checked even before leaving the birth hospital? Many states, communities, and hospitals offer hearing screening for babies. A babys hearing can be screened using Automated Auditory Brainstem Response , Otoacoustic Emissions , or both.
Babies usually have their hearing screened while still in the hospital, either in the nursery or in their mothers room.
You May Like: When A Newborn Baby Can See And Hear
What If My Newborn Does Not Pass The Hearing Screening
If your baby does not pass the newborn hearing screening, a follow-up screening or hearing test will be needed in the days or weeks after leaving the birthing hospital. This is a crucial step in determining whether your baby has hearing loss. Some newborns who need a follow-up hearing screening or a hearing test have normal hearingBUT some have hearing loss.
If your newborn does not pass the hearing screening, it is important to make an appointment with an audiologist for a complete infant hearing test.
Newborn Hearing Identifying Problems Early
South Carolina operates an early hearing detection and intervention program called First Sound. This is how it works:
- South Carolina hospitals that birth an average of 100 or more babies per year screen each newborn baby for hearing and send the results to DHEC.
- Infants who do not pass the initial hearing screening in the hospital are referred for rescreening this should be performed by the time the infant is one month old. The rescreening may be done at the birth hospital or at an audiologist’s office.
- Infants who do not pass the rescreening are referred to an audiologist for a diagnostic hearing evaluation. The evaluation should be performed before the baby is three months old..
- Infants who are confirmed as deaf or hard of hearing are referred to BabyNet for early intervention services. Deaf or hard of hearing infants should begin early intervention by six months old.
DHEC also tracks infants for three years if they pass their hospital screening but are at high risk for developing hearing loss.
If your infant has not been screened for hearing loss or if you are a health care provider wishing to refer an infant to First Sound, contact us at 898-0708. Fax: 803-898-4453
Recommended Reading: How To Care For A Newborn Belly Button
How Do You Treat Hearing Loss In Babies
The best treatment for hearing loss in babies is an early intervention plan that includes your pediatrician, an audiologist and a pediatric otolaryngologist. This medical team can help you determine which treatments or devices can aid your baby best based on the type and degree of hearing loss she’s experienced, such as hearing aids or cochlear implants .
With quick and consistent treatment, studies have shown that a babys spoken language development may match that of other babies her age if her hearing problems are discovered early and the intervention begins by 6 months of age or earlier if possible.
From the What to Expect editorial team and Heidi Murkoff, author of What to Expect When You’re Expecting. What to Expect follows strict reporting guidelines and uses only credible sources, such as peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions and highly respected health organizations. Learn how we keep our content accurate and up-to-date by reading our medical review and editorial policy.
Before Newborn Screening: Questions To Ask
Many parents have questions about NBS. Following is a list of questions that you may want to ask your health care provider or your babys health care provider before your babys birth, before your babys screening, or while your baby is being screened.
- Will I need to ask for my baby to be screened?
- When does NBS happen?
Also Check: How Warm Bath Water Newborn
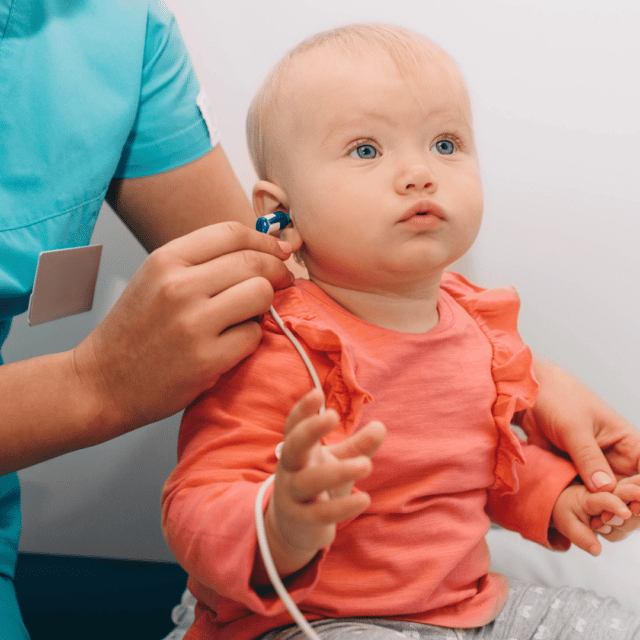
What Happens During The Hearing Test For Babies
- Small sensors are placed on your babys forehead, and below and above an ear.
- A cushioned earpiece is placed over one ear at a time and a chirping sound is played through this.
- The sensors on your babys head pick up the response from your babys hearing nerve.
- A computer measures the response and provides a result.
- The test takes about 1520 minutes and doesnt cause your baby any pain.
- A second test is offered if the results from the first test are unclear.
Why Is It Important To Have My Babys Hearing Screened Early
The most important time for a child to learn language is in the first 3 years of life, when the brain is developing and maturing. In fact, children with typical hearing begin learning speech and language in the first 6 months of life. This is why it is so important to screen and start interventions for hearing loss as early as possible. Research shows that children with hearing loss who get help early develop better language skills than those who dont.
Also Check: How Often To Bathe Newborn
Differences In The Newborn Screening Panel
The group of conditions that a state has chosen to detect with newborn blood spot screening is called its newborn screening panel. In the U.S., each state decides which conditions to include on its newborn screening panel. This means that babies in different states may be screened for slightly different panels of conditions.
States consider many things when deciding which conditions belong on their newborn screening panels. For example, all core conditions on state newborn screening panels:
- Have a low-cost screen
- Cannot be found just by looking at a baby
- Are serious and, without treatment, cause serious health problems early in life
- Have health care providers with the right expertise to diagnose, treat, and care for babies with the conditions
- Have an effective treatment
To help states decide which conditions to include on their newborn screening panels, the U.S. Secretary of Health and Human Services provides a list of conditions recommended for newborn screening. This list is called the Recommended Uniform Screening Panel .
To learn more about the RUSP, visit the Recommended Uniform Screening Panel page.
