Causes Of Deafness Before Birth
Permanent deafness in children is most commonly caused by genetics, passed down in families, even though there appears to be no family history of deafness.
Some of the most common syndromes associated with hearing loss are:
- Alport syndrome
- Usher syndrome Type 1 and Type 2
- Waardenburg syndrome
For detailed information on these syndromes, visit Contact.
Deafness can also be caused by complications during pregnancy. Infections such as rubella, cytomegalovirus , toxoplasmosis and herpes can cause a child to be born deaf.
There are also a range of medicines, known as ototoxic drugs, which can damage a babys hearing system before birth.
Hearing can be affected by cleft palate or cleft lip and palate, which can occur on its own or be linked to one of the syndromes listed above.
Different types of deafness can be associated with microtia and atresia, depending on which part of the ear is not formed or working as it should.
Also Check: When To Start Baby Signs
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Hearing Loss
It can be hard to tell if a child has hearing loss, especially in young children. Those with hearing loss may not respond to sounds or speech. Language development may be delayed. Talk to the doctor if your child does not reach these hearing milestones in the first year of life:
- For newborns, startling or “jumping” to sudden loud noises.
- By 3 months, recognizing a parent’s voice.
- By 6 months, turning the eyes or head toward a new sound and repeating sounds .
- By 12 months, making babbling sounds, responding to their name, imitating words, and saying a few words, such as “mama” or “bye-bye.”
As your child gets older, signs of hearing loss may include:
- limited, unclear, or no speech
- not seeming to pay attention or follow directions
- not responding to conversation-level speech or answering inappropriately
- being easily frustrated when there’s a lot of background noise
- needing a higher TV volume
- learning problems
Some hearing problems come on gradually after birth or show up later in life. If you are concerned about your childs hearing, talk to your doctor. Your child may need to see a hearing specialist called an audiologist for a complete hearing evaluation.
Risk Factors For Hearing Loss In Babies
Most hearing loss is present at birth , but some babies develop hearing loss after theyre born . The major risk factors for hearing loss in babies are:
- Premature birth
- Long-term use of ventilators in babies with respiratory problems
- Infections the mother passes to her baby in the womb
- Infections that can damage the brain after birth, such as meningitis or measles
Because of these risks, many health organizations, including the National Institutes of Health , the Joint Committee on Infant Hearing, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the American Academy of Audiology now recommend universal infant hearing screening, which we perform here at Cooper.
Recommended Reading: When Does Newborn Digestive System Mature
Genetics Of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss has many causes. 50% to 60% of hearing loss in babies is due to genetic causes. There are also a number of things in the environment that can cause hearing loss. 25% or more of hearing loss in babies is due to environmental causes such as maternal infections during pregnancy and complications after birth. Sometimes both genes and environment work together to cause hearing loss. For example, there are some medicines that can cause hearing loss, but only in people who have certain mutations in their genes.
Genes contain the instructions that tell the cells of peoples bodies how to grow and work. For example, the instructions in genes control what color a persons eyes will be. There are many genes that are involved in hearing. Sometimes, a gene does not form in the expected manner. This is called a mutation. Some mutations run in families and others do not. If more than one person in a family has hearing loss, it is said to be familial. That is, it runs in the family.
About 70% of all mutations causing hearing loss are non-syndromic. This means that the person does not have any other symptoms. About 30% of the mutations causing hearing loss are syndromic. This means that the person has other symptoms besides hearing loss. For example, some people with hearing loss are also blind.
Assessment Of Hearing Status
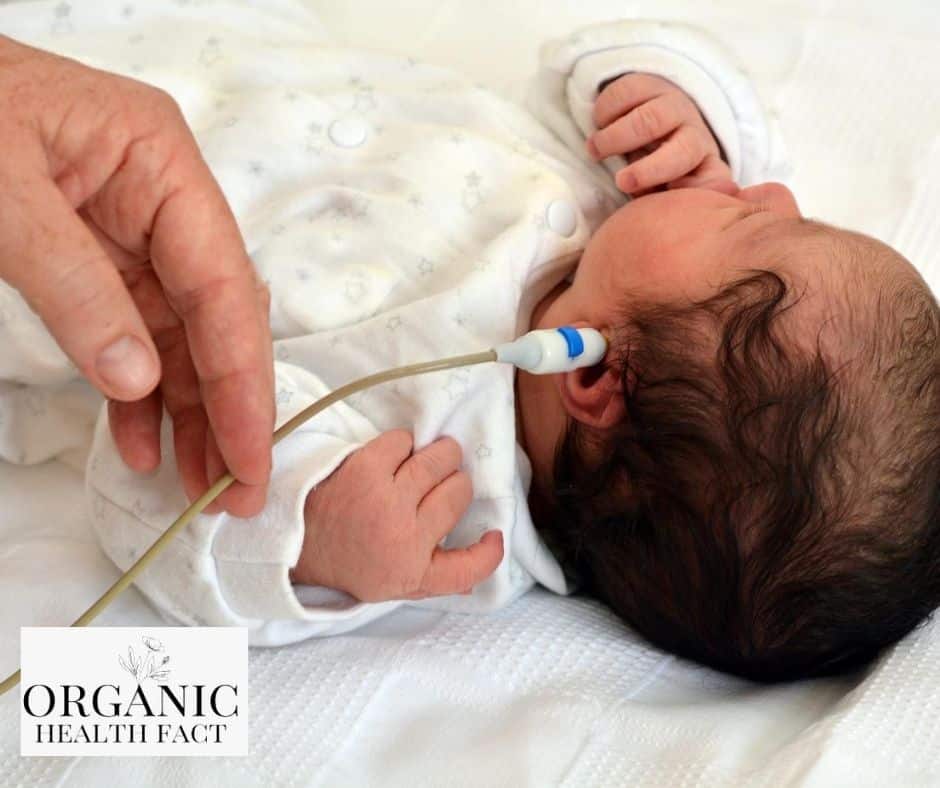
Screening usually consists of the measurement of oto-acoustic emissions repeated twice, measurement of oto-acoustic emissions and automated auditory brain stem responses , or measurement of automated auditory brain stem responses repeated twice.54 Infants who do not pass the screening require appropriate audiological and medical evaluation to confirm the presence of hearing loss, ideally before the age of 3 months. 7 However, passing the neonatal hearing test does not exclude progressive, late-onset and less-severe congenital hearing loss , which is not detected in most neonatal hearing screening programmes. Children who pass neonatal hearing screening but have risk factors for hearing loss or whose parents express concern about their childâs hearing abilities need regular follow-up, because hearing loss can develop later in life, depending upon the underlying cause.
Upon referral from neonatal hearing screening, a complete audiometric assessment is required to confirm the presence of hearing loss and to assess its severity and laterality . The severity of the hearing impairment should be applied to the better hearing ear and averaged over 500, 1,000, 2,000 and 4,000 Hz. Hearing loss is classified based on laterality and severity as mild , moderate , severe and profound . 55
Oto-acoustic emissions
Auditory brain stem responses and auditory steady state responses
Audiometry
Audiometry assessment
Don’t Miss: Can You Wash Newborn Clothes With Regular Detergent
Ototoxic Drugs Used In Medical Treatments
Ototoxic drugs used in some medical treatments can cause hearing loss, tinnitus and balance problems.
Children being treated for cancer are at particular risk of hearing loss caused by the cisplatin-based chemotherapy agents used in childhood cancer treatment. Children having chemotherapy should have their hearing levels monitored regularly to check for any deterioration early, so that oncologists can consider alternative drugs or changing treatment doses. Hearing aids can also be offered if needed.
RNID have more information about deafness caused by ototoxic drugs.
Diagnosis Of Hearing Impairment In Children
-
Electrodiagnostic testing
-
Clinical examination and tympanometry
). The initial screening test is evoked otoacoustic emissions testing Testing , using soft clicks made by a handheld device. If results are abnormal or equivocal, auditory brain stem evoked responses Testing are tested, which can be done during sleep abnormal results should be confirmed with repeat testing after 1 month. If a genetic cause is suspected, genetic testing can be done.
In children, other methods can be used. Speech and overall development are assessed clinically. The ears are examined, and tympanic membrane movement is tested in response to various frequencies to screen for middle ear effusions. In children age 6 months to 2 years, response to sounds is tested. At age > 2 years, ability to follow simple auditory commands can be assessed, as can responses to sounds using earphones. Central auditory processing evaluation Testing can be used for children > 7 years without neurocognitive deficits who seem to hear but not to comprehend.
Imaging is often indicated to identify the etiology and guide prognosis. For most cases, including when neurologic examination is abnormal, word recognition is poor, and/or hearing loss is asymmetric, gadolinium-enhanced MRI is done. If bone abnormalities are suspected, CT is done.
Read Also: How To Prevent Diaper Rash In Newborns
How Is Sensorineural Hearing Loss Treated
Sensorineural hearing loss is usually permanent. Because hearing is central to a childs ability to develop language skills, it is important to seek treatment as soon as possible.
Early intervention helps children with hearing loss develop language skills using a combination of reading, speaking, lip reading, sign language, and other tools. It can also teach parents skills to help them communicate with their child effectively.
Early intervention is most effective when started early. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that babies with hearing loss start receiving intervention services as soon as possible, no later than 6 months of age. The earlier a child with hearing loss starts learning speech, language and social skills, the better.
Hearing aids are electronic or battery-operated devices that amplify sound. For many children with mild or moderate hearing loss, a hearing aid can produce almost normal clarity of speech in a quiet room. Children with severe or profound hearing loss will be able to pick up some sounds through a hearing aid but typically need to combine lip-reading or sign language to understand speech and participate in conversations fully.
What Causes Hearing Loss In Babies And Children
The most common reason for hearing loss in children is middle ear inflammation or blocked ear canals. This loss of hearing:
- results from interference in sound being conducted to the inner ear
- may or may not be due to infection
- is called glue ear if there is a long-term build-up of thick or sticky fluid behind the eardrum
- may be accompanied by visible secretions leaking from the ear.
A smaller number of babies are born with permanent congenital hearing loss.
You May Like: Why Does My Newborn Cry All The Time
What Is Hearing Loss In Babies
Hearing loss is one of the most common birth defects. Although most babies are born with perfect hearing, between 1 and 3 in every 1,000 healthy babies in the United States are born with hearing loss.
Hearing loss in babies can range from mild where a baby can hear some sounds but not soft sounds of speech to inability to hear any sounds. Babies who need to enter the neonatal intensive care unit have a higher risk of hearing loss.
There are two types of hearing loss:
- Congenital hearing loss, meaning the baby was born with it, and
- Acquired hearing loss, meaning the baby lost hearing sometime after birth.
Most babies have their hearing screened just after birth. Because they rely on their hearing to learn from the beginning, it’s crucial to identify any hearing loss early so your child can get fit with hearing devices or receive other interventions that allow them to develop spoken communication. If your child has hearing loss, you’ll want to act quickly so they can learn to listen, talk, and read.
The best time for children with hearing loss to receive help is before they’re 6 months old. The sooner a child with a hearing problem is diagnosed and treated, the more likely they are to meet developmental milestones for spoken communication.
What Are The Types And Causes Of Hearing Loss
Having a hearing loss means that a child has lost some hearing in one or both ears.
There are many types and degrees of hearing loss, and they are described according to how much hearing has been lost and which part of the ear is affected. Loss is also described as mild, moderate, moderate to severe, severe or profound.
Loss is also explained as mild, moderate, moderate to severe, severe or profound. There are 2 main types of hearing impairment: ‘conductive’ and ‘sensorineural’. Having both types is called a ‘mixed loss’.
Conductive hearing loss occurs when something interferes with sound waves travelling through the outer and middle parts of the ear to the inner ear.
It can be caused by a wax blockage, middle ear infection , a fluid build-up in the middle ear, or damage to the tiny bones in the middle ear. Conductive hearing loss may be either temporary or permanent.
Sensorineural hearing loss is caused by a problem in the innermost part of the ear or in the nerve that carries hearing, the auditory nerve. It can be caused by abnormal inner ear development, a physical injury to the inner ear, damage to the ear from diseases such as meningitis and rubella, or a tumour.
Sensorineural hearing losses are usually permanent. Sometimes the problem with the inner ear also causes problems with balance. Children with both hearing and balance problems may have delayed development of their motor skills.
Don’t Miss: Which Wipes Are Best For Newborns
General Categories Of Causes:
Genetics
Genetic hearing loss can be present at birth or can develop later in life. An infant can inherit hearing loss from one or both parents, as the gene can be carried even if both parents hear at average levels. The hearing loss may be part of another genetic syndrome, such as Down syndrome, Usher syndrome, or Treacher Collins syndrome. Gene mutations can also cause one of two different kinds of hearing loss syndromic where the hearing loss happens along with other health problems, or non-syndromic where the hearing loss is the only condition the baby has and is more common. Congenital hearing loss is when a baby is born with hearing loss, but genetics can also cause hearing loss as infants get older as well.
Events during pregnancy
Viruses and infections can be passed to babies while in the womb. Some of the viruses and infections that can cause hearing loss include cytomegalovirus, herpes, measles, rubella, syphilis, and toxoplasmosis. Symptoms like body aches, headache, fatigue, fever, coughs, and rashes can be associated with these, so pregnant women should always reach out to their doctor with any health concerns during pregnancy.
Hearing problems can also be caused by the way the ears, head, or face develop in the womb. If the shape or structure of the babys ears is different, it can affect their hearing. Regular checkups and ultrasounds during pregnancy can monitor the babys development to track possible changes in development.
Events after birth
How We Care For Hearing Loss

Our clinicians in the Department of Otolaryngology and Communication Enhancement at Boston Childrens Hospital have extensive expertise evaluating and treating hearing loss. Our Hearing Disorders Clinic and Audiology Program offer comprehensive, multi-disciplinary evaluation and management of various degrees of hearing loss in infants, children and adolescents. We work closely with specialists in Boston Childrens Deaf and Hard of Hearing Program, one of the largest, most comprehensive hearing-loss programs in the country, to provide comprehensive evaluation and consultative services for children who are deaf or hard of hearing.
Also Check: How Many Oz Should A Newborn Eat Of Formula
What Causes Babies To Fail Their Hearing Screening
Deafness and hearing loss can be caused by genetic abnormalities, birth defects, or maternal infections during pregnancy. In some cases, the baby will immediately show signs of hearing loss, such as not responding to sounds or failing their hearing screening.
Rarely, a baby who can hear and process sound might nonetheless fail their newborn hearing screening. Some of these include babies who:
If your baby experienced these issues and passed their newborn hearing screening, they still will likely need follow-up screenings throughout childhood. Hearing loss can develop over time, and your baby may need close monitoring and screening for hearing loss through young adulthood.
If the baby did not pass the newborn hearing screening, its important that the baby receive an advanced follow-up screening within 10-12 days for the best chance at receiving early intervention and unlocking their early language development.
How Do You Stimulate A Newborns Hearing
While preparing dinner, keep your baby close to you and place him or her in a baby seat in front of a noisy older sibling who is laughing and playing. A baby rattle or a musical mobile are also excellent ways to promote your babys hearing.
Because of its ability to hear, babies can perceive the sounds around them. This is the most developed of the five senses in newborns. When babies are young, they are expected to learn the fundamentals of life, such as how to interact with others. To accomplish this, parents must keep in touch with their children on a regular basis. When the baby is talking to you or making funny faces, it is easier for him to connect the meaning to the word. Playing with these multi-sensory activities will help the child develop his other senses at the same time.
You May Like: Why Preserve Newborn Stem Cells
What Is Deafness And Hearing Loss
Deafness or hearing loss can be present at birth or develop as your baby grows. Hearing loss is a group of conditions that make it more difficult for your baby to hear and understand sounds.
Hearing loss can be caused by a change in the ear or a change in the part of the brain that processes sounds. Your baby could have one of these changes or a mix of the two.
Hearing loss can be mild, moderate, severe, or profound. Your baby may be deaf or hard of hearing in one ear or both ears . Their hearing may get better or worse over time or stay the same over time . The changes to their ears or brain lead to the signs and symptoms of this condition.
Any hearing loss that makes it difficult for babies to hear speech can affect language development and communication skills. It is important to find out if your baby is deaf or hard of hearing as early as possible.
While the term hearing loss is most commonly used by the health care system, it is important to understand that using the words deaf or hard of hearing is socially acceptable and often preferred. Often when children with hearing loss grow older, or as adults, they will identify themselves as D/deaf or hard of hearing. The Deaf community views the term Deaf as a positive word and includes any person who experiences life with a hearing loss.
Joy Victory Managing Editor Healthy Hearing
Joy Victory has extensive experience editing consumer health information. Her training in particular has focused on how to best communicate evidence-based medical guidelines and clinical trial results to the public. She strives to make health content accurate, accessible and engaging to the public.Read more about Joy.
You May Like: What Is Hemolytic Disease Of The Newborn
