What Are The Possible Treatment Options
Treatment will depend on your babys symptoms and lab results. Some include:
- Intravenous fluids – These fluids help the body get rid of extra bilirubin and stay hydrated.
- Intravenous immunoglobulin – This is a fluid that contains antibodies from blood donors. It helps keep your from baby from destroying their red blood cells. As a result, it should also help lower your babys bilirubin levels.
- Blood transfusion This is when your baby receives blood from another blood donor. This is done to treat sever anemia
- Exchange transfusion – This procedure removes some of your babys blood that has a high bilirubin level and replaces it with blood that has a normal bilirubin level. This is typically only done at the Nationwide Childrens hospital NICU.
What Causes Hemolytic Disease Of The Newborn
HDN most frequently occurs when an Rh negative mother has a baby with an Rh positive father. When the baby’s Rh factor is positive, like the father’s, problems can develop if the baby’s red blood cells cross to the Rh negative mother. This usually happens at delivery when the placenta detaches. However, it may also happen anytime blood cells of the two circulations mix, such as during a miscarriage or abortion, with a fall, or during an invasive prenatal testing procedure .
The mother’s immune system sees the baby’s Rh positive red blood cells as “foreign.” Just as when bacteria invade the body, the immune system responds by developing antibodies to fight and destroy these foreign cells. The mother’s immune system then keeps the antibodies in case the foreign cells appear again, even in a future pregnancy. The mother is now “Rh sensitized.”
In a first pregnancy, Rh sensitization is not likely. Usually, it only becomes a problem in a future pregnancy with another Rh positive baby. During that pregnancy, the mother’s antibodies cross the placenta to fight the Rh positive cells in the baby’s body. As the antibodies destroy the red blood cells, the baby can become sick. This is called erythroblastosis fetalis during pregnancy. In the newborn, the condition is called hemolytic disease of the newborn.
What Causes Hdn In A Newborn
HDN happens most often when an Rh negative mother has a baby with an Rh positive father. If the baby’s Rh factor is positive, like his or her father’s, this can be an issue if the baby’s red blood cells cross to the Rh negative mother.
This often happens at birth when the placenta breaks away. But it may also happen any time the mothers and baby’s blood cells mix. This can occur during a miscarriage or fall. It may also happen during a prenatal test. These can include amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling. These tests use a needle to take a sample of tissue. They may cause bleeding.
The Rh negative mothers immune system sees the baby’s Rh positive red blood cells as foreign. Your immune system responds by making antibodies to fight and destroy these foreign cells. Your immune system stores these antibodies in case these foreign cells come back again. This can happen in a future pregnancy. You are now Rh sensitized.
Rh sensitization normally isnt a problem with a first pregnancy. Most problems occur in future pregnancies with another Rh positive baby. During that pregnancy, the mother’s antibodies cross the placenta to fight the Rh positive cells in the baby’s body. As the antibodies destroy the cells, the baby gets sick. This is called erythroblastosis fetalis during pregnancy. Once the baby is born, its called HDN.
You May Like: How To Insurance A Newborn Baby
How We Care For Hdn
Hemolytic disease of the newborn is treated through the Blood Disorders Center at Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s. Hemolytic disease of the newborn was first identified in 1932 at Boston Childrens Hospital by Dr. Louis Diamond. He went on to develop the first successful treatment, a transfusion procedure, in the 1940s.
Rhesus Hemolytic Disease Of The Newborn
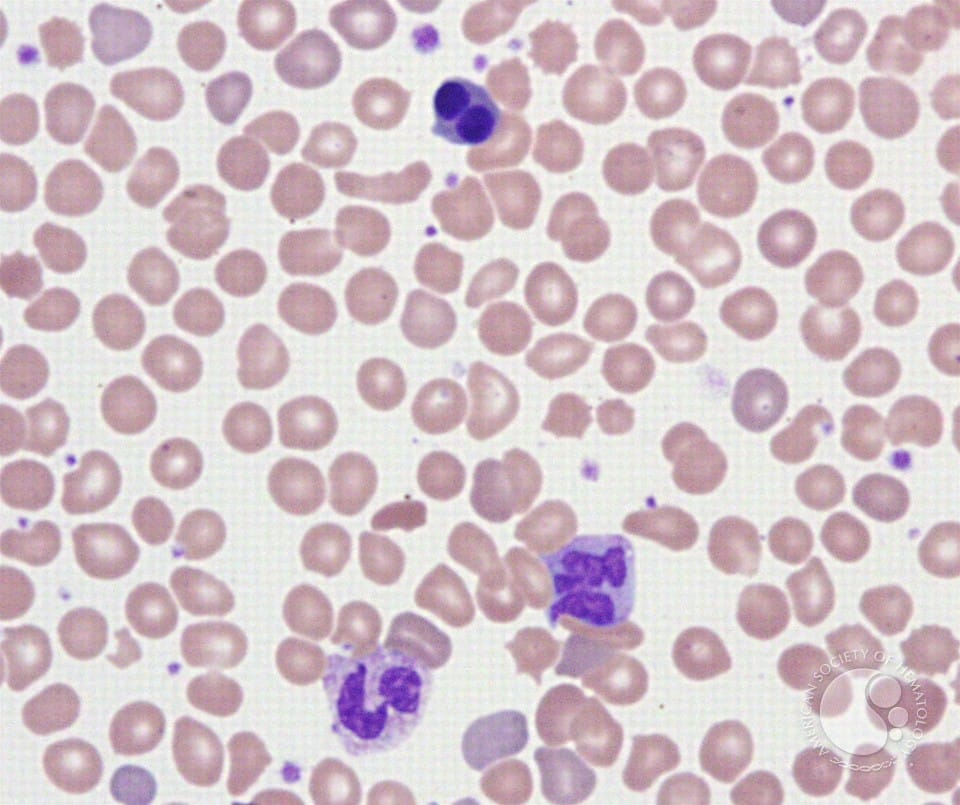
Rhesus hemolytic disease of the newborn is a serious condition of breakdown of red cells in the newborn due to an incompatibility between fetal and maternal blood. It occurs when the mother is Rh negative and the fetus Rh positive . Fetal red blood cells can mingle with the maternal blood during delivery, causing the mother to produce antibodies to the fetal blood. This may affect subsequent pregnancies, causing hemolysis of fetal blood, producing anemia, jaundice, brain damage, or death. This disease was the cause of many stillbirths and neonatal deaths until the development of exchange transfusions in newborns reduced the death rate. In the 1970s, anti-D immunoglobulin was introduced. This is given to Rh-negative women following birth of an Rh-positive baby to prevent the mother from developing antibodies that would affect the next pregnancy. Treatment with anti-D immunoglobulin should eliminate this disease, a major victory of preventive care.
Jeffrey M. Perlman, Joseph J. Volpe, in, 2018
You May Like: What Essentials Do I Need For A Newborn
How Is Hdn Diagnosed In A Newborn
- Blood test. Testing is done to look for for Rh positive antibodies in your blood.
- Ultrasound. This test can show enlarged organs or fluid buildup in your baby.
- Amniocentesis. This test is done to check the amount of bilirubin in the amniotic fluid. In this test, a needle is put into your abdominal and uterine wall. It goes through to the amniotic sac. The needle takes a sample of amniotic fluid.
- Percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling. This test is also called fetal blood sampling. In this test, a blood sample is taken from your babys umbilical cord. Your childs healthcare provider will check this blood for antibodies, bilirubin, and anemia. This is done to check if your baby needs an intrauterine blood transfusion.
The following tests are used to diagnose HDN after your baby is born:
- Testing of your baby’s umbilical cord. This can show your babys blood group, Rh factor, red blood cell count, and antibodies.
- Testing of the baby’s blood for bilirubin levels.
Symptoms Of Hemolytic Disease Of The Newborn
During pregnancy symptoms may include
- With amniocentesis, the amniotic fluid may have a yellow coloring and contain bilirubin
- Ultrasound of the fetus shows enlarged liver, spleen, or heart and fluid buildup in the fetusâ abdomen
After birth, symptoms may include
- A pale coloring may be evident, due to anemia
- Jaundice or yellow coloring of amniotic fluid, umbilical cord, skin, and eyes may be present. The baby may not look yellow immediately after birth, but jaundice can develop quickly, usually within 24 to 36 hours
- The newborn may have an enlarged liver and spleen
- Babies with hydrops fetalis have severe edema of the entire body and are extremely pale
- They often have difficulty breathing
- Complications of hemolytic disease of the newborn can range from mild to severe.
During pregnancy
- Mild anemia, hyper-bilirubinemia, and jaundice: The placenta helps rid some of the bilirubin, but not all.
- Severe anemia with enlargement of the liver and spleen: When these organs and the bone marrow cannot compensate for the fast destruction of red blood cells, severe anemia results and other organs are affected.
- Hydrops fetalis: This occurs as the babyâs organs are unable to handle the anemia. The heart begins to fail and large amounts of fluid buildup in the babyâs tissues and organs. A fetus with hydrops is at great risk of being stillborn .
After birth
Laboratory diagnosis of hemolytic disease of the newborn
Prenatal testing
Father testing
Molecular genotyping
Postnatal testing:
Also Check: How To Get Newborn To Sleep Alone At Night
Which Children Are At Risk For Hdn
- Youre Rh negative and have an Rh positive baby but havent received treatment.
- Youre Rh negative and have been sensitized. This can happen in a past pregnancy with an Rh positive baby. Or it can happen because of an injury or test in this pregnancy with an Rh positive baby.
HDN is about 3 times more common in Caucasian babies than in African-American babies.
What Can I Do To Prevent Hemolytic Disease Of The Newborn
If youre Rh negative and have not been sensitized, youll get a medicine called Rh immunoglobulin . This medicine can stop your antibodies from reacting to your babys Rh positive cells. Many women get RhoGAM around week 28 of pregnancy.
If your baby is Rh positive, youll get a second dose of medicine within 72 hours of giving birth. If your baby is Rh negative, you wont need a second dose
Don’t Miss: How To Help My Newborn Sleep Better
Usmle Step 1 Style Questions Usmle
A 32-year old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 39 weeks gestation comes to the emergency department with contractions. She says that she did not have any prenatal care because she does not have health insurance. Upon delivery, the infant appears and has marked hepatosplenomegaly. Serum hemoglobin is 11.6 g/dL and serum is 8 mg/dL. Direct and indirect Coombs tests are both positive. The mother has never had a . Her previous child was born healthy with no complications. Which of the following is most consistent with the presentation of this disease?
Mid To Late Pregnancy
- IUT – Intrauterine Transfusion is done either by intraperitoneal transfusion or intravenous transfusion . IVT is preferred over IPT. IUTs are only done until 35 weeks. After that, the risk of an IUT is greater than the risk from post birth transfusion.
- Steroids – Steroids are sometimes given to the mother before IUTs and early delivery to mature the fetal lungs.
- Phenobarbital – Phenobarbital is sometimes given to the mother to help mature the fetal liver and reduce hyperbilirubinemia.
- Early Delivery – Delivery can occur anytime after the age of viability. Emergency delivery due to failed IUT is possible, along with induction of labor at 3538 weeks.
Also Check: When Should You Give Your Newborn A Bath
What Are The Symptoms Of Hemolytic Disease Of The Newborn
The following are the most common symptoms of hemolytic disease of the newborn. However, each baby may experience symptoms differently. During pregnancy symptoms may include:
-
With amniocentesis, the amniotic fluid may have a yellow coloring and contain bilirubin.
-
Ultrasound of the fetus shows enlarged liver, spleen, or heart and fluid buildup in the fetus’s abdomen, around the lungs, or in the scalp.
After birth, symptoms may include:
-
A pale coloring may be evident, due to anemia.
-
Jaundice, or yellow coloring of amniotic fluid, umbilical cord, skin, and eyes may be present. The baby may not look yellow immediately after birth, but jaundice can develop quickly, usually within 24 to 36 hours.
-
The newborn may have an enlarged liver and spleen.
-
Babies with hydrops fetalis have severe edema of the entire body and are extremely pale. They often have difficulty breathing.
Can Hemolytic Disease Of The Newborn Be Prevented
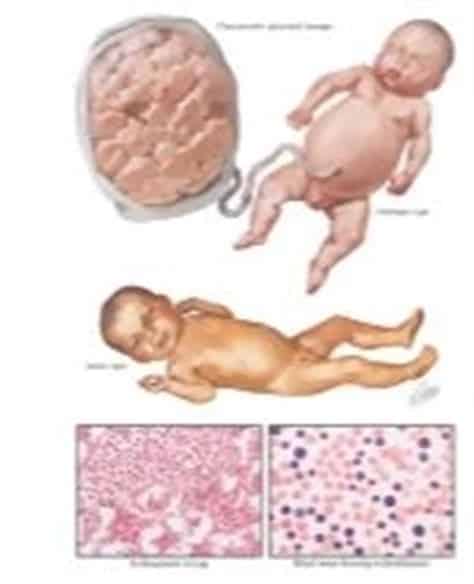
Hemolytic disease of the newborn is preventable. During your prenatal care visits, your doctor will most likely perform a blood test to learn your blood type. If necessary, your doctor can give you a medication called Rh immunoglobulin at around 28 weeks to stop your bodyâs antibodies from attacking your babyâs cells.
Show Sources
Recommended Reading: How Much Formula Does A Newborn Drink
Hemolytic Disease Of The Fetus And Newborn
Drs Ross and de Alarcón have disclosed no financial relationships relevant to this article. This commentary does not contain a discussion of an unapproved/investigative use of a commercial product/device.
Neoreviews
Mary Beth Ross, Pedro de Alarcón Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn. Neoreviews February 2013 14 : e83e88.
Hemolytic Disease Of The Newborn
| Hemolytic disease of the newborn |
|---|
| Other names |
| heart failure, splenomegaly |
Hemolytic disease of the newborn, also known as hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, HDN, HDFN, or erythroblastosis foetalis, is an alloimmune condition that develops in a fetus at or around birth, when the IgG molecules produced by the mother pass through the placenta. Among these antibodies are some which attack antigens on the red blood cells in the fetal circulation, breaking down and destroying the cells. The fetus can develop reticulocytosis and anemia. The intensity of this fetal disease ranges from mild to very severe, and fetal death from heart failure can occur. When the disease is moderate or severe, many erythroblasts are present in the fetal blood, earning these forms of the disease the name erythroblastosis fetalis .
HDFN represents a breach of immune privilege for the fetus or some other form of impairment of the immune tolerance in pregnancy. Various types of HDFN are classified by which alloantigen provokes the response. The types include ABO, anti-RhD, anti-RhE, anti-Rhc, anti-Rhe, anti-RhC, multiantigen combinations, and anti-Kell. Although global prevalence studies of the differential contribution of those types are lacking, regional population studies have shown the anti-RhD type to be the most common cause of HDFN, followed by anti-RhE, anti-RhC, and anti-Rhc.
Recommended Reading: When Can You Take A Newborn Out For A Walk
Who Is At Risk Of Getting Hemolytic Disease In The Newborn
Who is at risk of developing the hemolytic disease in the newborn? Babies in Neonatal intensive care units are at major risk of developing hemolytic diseases. These babies are usually premature, have heart or respiratory disorders, or have blood-clotting disorders. The hemolytic disease can also be caused by an incompatibility in blood types between mother and baby. The two main hemolytic diseases that cause this are ABO incompatibility and Rh incompatibility.
What To Expect At Birth
Fetuses that require transfusions within the uterus usually deliver between 34 and 37 weeks gestational age. About half of these newborns will require a transfusion after birth, and almost all will require treatment for jaundice , usually with phototherapy . The newborn will often need to be in the hospital longer than the mother. Some babies may be 4-6 months old before they completely recover the ability to make their own red blood cells, so they must be closely followed by an experienced pediatrician.
Read Also: What Shots Do Newborn Puppies Need
How Is Hemolytic Disease Of The Newborn Diagnosed
Because anemia, hyperbilirubinemia, and hydrops fetalis can occur with other diseases and conditions, the accurate diagnosis of HDN depends on determining if there is a blood group or blood type incompatibility. Sometimes, the diagnosis can be made during pregnancy based on information from the following tests:
-
Testing for the presence of Rh positive antibodies in the mother’s blood
-
Ultrasound – to detect organ enlargement or fluid buildup in the fetus. Ultrasound is a diagnostic imaging technique which uses high-frequency sound waves and a computer to create images of blood vessels, tissues, and organs. Ultrasound is used to view internal organs as they function, and to assess blood flow through various vessels.
-
Amniocentesis – to measure the amount of bilirubin in the amniotic fluid. Amniocentesis is a test performed to determine chromosomal and genetic disorders and certain birth defects. The test involves inserting a needle through the abdominal and uterine wall into the amniotic sac to retrieve a sample of amniotic fluid.
-
Sampling of some of the blood from the fetal umbilical cord during pregnancy to check for antibodies, bilirubin, and anemia in the fetus.
Once a baby is born, diagnostic tests for HDN may include the following:
-
Testing of the baby’s umbilical cord blood for blood group, Rh factor, red blood cell count, and antibodies
-
Testing of the baby’s blood for bilirubin levels
Physiologic Basis Of Biophysical Monitoring:
Application of the biophysical profile:
Postnatal , treatment may include
- Blood transfusions
- Intravenous fluids
- Help for respiratory distress using oxygen or a mechanical breathing machine
- Exchange transfusion to replace the babyâs damaged blood with fresh blood: The exchange transfusion helps increase the red blood cell count and lower the levels of bilirubin. An exchange transfusion is done by alternating giving and withdrawing blood in small amounts through a vein or artery
- Human Serum Albumin: Human serum albumin can also be transfused, either separately or as part of an exchange transfusion in place of Fresh Frozen Plasma . Albumin binds unconjugated bilirubin, thus preventing its deposition in the fat-rich brain cells. Albumin must be used judiciously, because it can aggravate congestive heart failure
Intrauterine transfusion
Immunomodulators
Management of Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn
- Severe anaemia: Hb
- Severe hyperbilirubinaemia in the first 48 h of life or rapidly increasing hyperbilirubinaemia
Management of the sensitized neonate
Prevention of hemolytic disease of the newborn
Read Also: What Is The Best Gas Drops For Newborns
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Enhancing interprofessional team outcomes for patients with hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn requires close collaboration between both OB/GYN and pediatric providers, nurses, pharmacists, and blood bank personnel. With HDFN, there are two patients to consider at all times – the mother and the fetus/newborn. When HDFN is identified in utero, the delivery team should be well versed and prepared ahead of time to identify signs and symptoms of HDFN as these infants may need timely transfusions at birth. Pharmacists and providers must identify if and when Rh-D immunoprophylaxis is indicated to prevent future HDFN cases throughout the pregnancy. Through the development of Rh-D immunoprophylaxis and newborn work-up protocols, the incidence of HDFN has dramatically dropped in the past 50 years. Still, it will take continued interprofessional collaboration to ensure the incidence of HDFN remains low.
How The Infant Is Affected
As discussed above, in he first pregnancy with an Rh-positive baby, there are no problems. If this mismatch is unknown in the first pregnancy or if proper preventative measures are not taken, future pregnancies can be affected. After the first affected pregnancy, the severity of hemolytic disease of the newborn worsens with each pregnancy.
Symptoms are determined by the severity of the red blood cell breakdown . If the infant is only mildly affected, there may be minimal problems such as mild anemia and/or jaundice that do not require treatment. If the amount of hemolysis is severe, he/she will have significant jaundice shortly after birth.
Unfortunately, the hemolysis doesn’t stop when the baby is born as the maternal antibodies linger for several weeks. These excessive levels of bilirubin can cause damage to the brain. In some cases, the anemia is so severe in utero that the liver and spleen enlarge to increase red blood cell production leading to liver failure. The hemolytic disease may also lead to hydrops fetalis with generalized edema , fluid around organs, and even death.
Also Check: How To Treat Severe Diaper Rash On A Newborn
