What Are Possible Long
The disabilities infants with HIE display as they grow vary with the severity of HIE. While infants with mild HIE exhibit little to no long-term disabilities, infant who have suffered moderate to severe HIE may die in the newborn period or have medical conditions including Cerebral Palsy, Mental Retardation, feeding difficulties, learning disabilities, visual or hearing impairment and seizures.
How Long Should Hypothermia Be Continued
Studies derived from animal models suggest that hypothermia is most effective when instituted in the latent phase, before secondary failure of oxidative mechanisms, and continued throughout the secondary phase . Most clinical trials used 72 hours of cooling in their treatment group. A recent study did not find cooling longer superior to cooling for 72 hours . Level of evidence: 1a
What Infants Qualify For Cooling
Read Also: When A Newborn Is Constipated
Hie Is Often Preventable
While there are several causes of HIE, you should know that HIE is often preventable. Oxygen deprivation and resulting HIE is often the result of a medical condition that healthcare providers mismanage or miss altogether during pregnancy, labor and delivery or shortly thereafter.
If a healthcare provider is negligent in providing care and you and/or your infant are injured as a result, you should contact a birth injury lawyer as soon as possible. You may have grounds to file a birth injury lawsuit.
At Birth Injury Guide, our legal team has handled numerous birth injury lawsuits, including many cases involving HIE. We can help you determine if your childs injury was the result of medical negligence. If so, we can help you protect your rights and seek justice for your child. Request a free consultation with one of our lawyers by calling 1-877-415-6603.
Meagan Cline is a professional legal researcher and writer. She lends her expertise to the team at Birth Injury Guide to provide up-to-date and relevant content that clients can count on.
Other National Injury Center Litigation
Study Design And Patient Population

This retrospective, multi-center case-control study was conducted in the neonatal intensive care units of St. Louis Children’s Hospital and University of Virginia Children’s Hospital from 2010 to 2018. Both centers are Level IV units serving patients from urban, suburban, and rural populations. Infants were included in the study if they underwent TH for the treatment of neonatal encephalopathy as determined by a modified Sarnat exam and had an intra-arterial catheter placed for invasive blood pressure monitoring. Treatment with dopamine was at the discretion of the medical team and given for signs or symptoms of hypotension/hypoperfusion.
Cases were determined by exposure to dopamine and were matched to controls 1:2 by gestational age and gender. Infants in the control group were otherwise identical except for exposure to dopamine. Infants were excluded if there was a known congenital or genetic anomaly at the time of birth. To prevent confounding, infants were excluded if they were exposed to other inotropes or vasopressors . Infants were also excluded if blood pressure data were not available at the time of dopamine initiation or the comparable period in control infants.
Also Check: What Should A Newborn Schedule Look Like
How Can Hie Affect A Child
In full-term infants, the effects of a hypoxic brain injury are largely determined by which part of the brain is injured, as well as the degree and duration of oxygen deprivation.
Severe cases generally involve damage to the brains deep gray matter, including the hippocampus, regions of the brain thought to control emotion, memory and the autonomic nervous system, and the basal ganglia, a complex of structures involved in motor movement, learning and habit-formation.
For most children, the brains white matter is spared from injury, even after profound oxygen deprivation. White matter is generally believed to coordinate activity between brain regions.
HIE can cause a wide range of impairments, from neuro-muscular impairments to cognitive impairment. Epilepsy and cerebral palsy are possible, along with developmental delays.
The severity of impairment, however, is unlikely to become apparent until a child reaches the age of 3 or 4.
Which Method Should Be Used To Provide Hypothermia
Two methods of cooling have been used in clinical trials selective head cooling and whole body cooling. One small single-centre trial compared both methods of cooling and found no difference in outcomes at 12 months of age in infants enrolled . Larger clinical trials found similar effects on death and disability outcomes when either method was compared with placebo .
Selective head cooling can be achieved with cooling caps fitted around an infants head, with the aim of maintaining fontanelle temperature below 30°C. A rectal temperature of 34°C ± 0.5°C is maintained using a servo-controlled radiant heater. This system is expensive and labour-intensive, and may produce scalp edema or skin breakdown. It is also more difficult to maintain rectal temperature and there is limited access for EEG leads. Whole body cooling to a rectal temperature of 33.5°C ± 0.5°C can be achieved with passive cooling, cool packs and/or commercially available cooling blankets. Servo-controlled cooling blankets produce more consistent target temperatures .
Whole body cooling is recommended preferentially because it is easier to set up and use, less expensive, provides better access to EEGs and is more readily available. Level of evidence: 1b
Don’t Miss: How Often Do Newborns Fail Hearing Test
Other Clinical Manifestations That Might Help With Diagnosis And Management
Continuous electroencephalographic monitoring is increasingly recognized as an important tool for the treatment and prognosis of HIE In newborns treated with hypothermia. A normal electroencephalogram is predictive of a normal or mildly abnormal MRI scan, whereas a sustained severely abnormal EEG over the course of cooling confers a poor prognosis. Amplitude-integrated electroencephalography may be an adjunctive measure of outcome in HIE studies are ongoing.
The Sarnat Clinical Stages Of Hie
In 1976, Sarnat and Sarnat were working on developing a clinical ranking system to help improve the diagnosis of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. HIE is a serious form of birth asphyxia that can cause brain damage, disability, and death. Children with HIE are at higher risk for other permanent conditions, including Cerebral Palsy.
These doctors proposed a three stage system for classifying HIE.
Stage I: describes conditions of mild HIE.
Stage II: describes conditions of moderate to severe HIE.
Stage III: describes conditions of severe HIE.
Don’t Miss: How To Take Care Of Newborn Pitbull Puppies
When Should Cooling Be Initiated
In newborn rat pups, a 12-hour delay in starting hypothermia increased brain injury after severe hypoxia-ischemia, which is of clinical concern if the same findings are applicable to human newborns . While awaiting transport to a tertiary care unit, initiation of passive cooling should be strongly considered in community hospitals, following consultation with a receiving neonatologist. Rectal temperature or, if not possible, axillary temperature should be monitored every 15 minutes to ensure the infants temperature does not decrease below 33°C.
The earlier passive cooling is initiated, the earlier target temperature will be reached . The use of ice packs or cool gels by untrained personnel, which can lead to severe hypothermia, is not recommended. Level of evidence: 2b
How Should The Infant Be Rewarmed
The speed of rewarming remains controversial. In randomized clinical trials, infants were rewarmed over 6 to 12 hours . Most centres rewarm infants by 0.5°C every 1 to 2 hours. Seizures and worsening of clinical encephalopathy upon rewarming have been reported . In such circumstances, experts suggest recooling for 24 hours and resuming rewarming . Level of evidence: 5
Read Also: How Do You Know If Your Newborn Is Constipated
If You Are Able To Confirm That The Patient Has This Disease What Treatment Should Be Initiated
Term newborns with HIE should be transferred to an intensive care nursery given their critical nature. Treatment can be separated into immediate/hospital management and long-term treatment.
Immediate/hospital management
- Arterial line/umbilical artery catheter for blood pressure and arterial blood gas monitoring
- Umbilical vein catheter for drawing blood
- Maintenance of cerebral perfusion by controlling hypotension, bradycardia, and/or apnea
- Acidosis correction as needed
- Seizure medication
- Lorazepam 0.5 mg intravenously as needed for seizure
- Phenobarbital 20 mg/kg IV for persistent seizures/status epilepticus maintenance dose usually around 5 mg/kg/d, but newborns can metabolize this quickly and the dose may need to be increasingly tritrated to effect
- Levetiracetam 20-30 mg/kg IV for persistent seizures/status epilepticus maintenance starting dose 15 mg/kg IV or orally twice daily
- Hypothermia
Poor feeding secondary to sleepiness
Hypothermia
Relatively safe in clinical trials
Cardiac arrhythmias
Coagulation disturbances
Fetus And Newborn Committee

Members: Ann L Jefferies MD Thierry Lacaze-Masmonteil MD Abraham Peliowski-Davidovich MD S Todd Sorokan MD Richard Stanwick MD Hilary EA Whyte MD
Liaisons: Michael S Dunn MD, CPS Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine Section Sandra Dunn MScN, Canadian Perinatal Programs Coalition Andrée Gagnon MD, College of Family Physicians of Canada Robert Gagnon MD, Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada Juan Andrés León MD, Public Health Agency of Canada Patricia O’Flaherty MN MEd, Canadian Association of Neonatal Nurses Lu-Ann Papile MD, American Academy of Pediatrics, Committee on Fetus and Newborn
Consultant: Robin K Whyte MD
Principal author: Abraham Peliowski-Davidovich MD
Read Also: How To Produce More Milk For Newborn
What Causes This Disease And How Frequent Is It
HIE is fairly common, and occurs in approximately 1-6/1000 live births. One fifth of children with HIE die in the newborn period. HIE is also associated with high morbidity up to one quarter of survivors go on to have recognizable motor and/or cognitive impairment. At this time, there is no known genetic predisposition to HIE.
Known risk factors for HIE include birth asphyxia or prolonged reduction of cerebral blood flow . However, many cases of HIE do not have a clear history of asphyxia or compromised cerebral blood flow. Because of this disconnect, some providers prefer to use the term neonatal encephalopathy or NE instead of HIE.
Are You Sure Your Patient Has Hypoxic
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy stages and symptoms are defined by the constellation of respiratory difficulties, depressed tone and reflexes, and abnormal level of consciousness in the term newborn within the first few days of life. The typical findings in the term infant include altered mental status/encephalopathy, abnormal tone and/or reflexes, and respiratory difficulties that include apnea, seizures, and feeding difficulties. Because the symptoms can overlap many neurologic and metabolic conditions in the newborn, it is imperative to rule out life-threatening or treatable causes of these symptoms .
Encephalopathy Scores
HIE is recognized as an important cause of lasting motor impairment in term newborns. More recently, HIE has been implicated in cognitive and behavioral difficulties as these children age. Variables, including Apgar scores and initial umbilical artery blood gas determinations, are of restricted value when making predictions of neurodevelopmental outcomes. Instead, the degree of encephalopathy is a valid predictor of developmental outcome. Children with mild encephalopathy tend to have no neurodevelopmental deficits, whereas those with severe encephalopathy either die early or go on to have severe disabilities.
Table I.
| Frequent or difficult to control |
Adapted from Sarnat HB, Sarnat MS. Neonatal encephalopathy following fetal distress.
A clinical and electroencephalographic study. Arch Neurol 1976 33:696-705.
HIE = hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
Read Also: What Is The Weight Of Newborn Diapers
The Expert Ren Chats Answers
mild birth hypoxia occurs almost in all, but the incidence of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy is only about 6 in 1000 full term newborns, of which only 1 in 10 to 1 in 20 show significant developmental delay. the health of the baby.the gestational age of the fetus.inconsolable shrill cry,neonatesjitteriness or seizuresEEGThe future outcomeApgar Scorenewborn brain growth restriction,Clinical featuresMRI
Common Signs Of Hypoxia In Newborns
Because hypoxia can lead to serious and permanent birth injuries, medical professionals should always be watchful for the signs of lack of adequate oxygen to the baby. This includes watching for the signs before, during, and after the child is born.
What is the first sign of hypoxia in newborns?
One of the earliest indications that a baby is having difficulty breathing is an erratic or irregular heart rate. Doctors should be closely monitoring the fetal heart rate both during and after labor to ensure that the newborn is getting ample oxygen.
Other common signs of hypoxia in the baby include:
- A lack of fetal movement
Medical professionals can observe the babys heart rate in the womb using a fetal heart monitor.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Newborn To Stay Asleep
Birth Hypoxia In Newborn Baby
Clinical Features Are Perhaps The Best Indicator of The Outcome of Birth Hypoxia
My son suffered neonatal hypoxia. He didnt cry at birth, received ventilator support and oxygen supplementation for Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy.He has been gradually weaned off oxygen. Now, at the age of 25 days, his breathing is adequate, but he is yet very drowsy and inactive. He is not even able to suck and swallow.His MRI report is normal.Doctor, will my baby be normal? When? What will be the future outcome?
What Is Neonatal Encephalopathy
Neonatal encephalopathy encompasses any form of central nervous system dysfunction caused by an injury to the brain. This term is used when discussing injury in babies born at or later than 35 weeks of gestation . Neonatal encephalopathy is estimated to occur in about two to nine of 1000 live births , and can be caused by numerous factors. These include the following :
Don’t Miss: How To Help A Newborn With A Cold
What Does A Diagnosis Of Neonatal Encephalopathy Mean
A neonatal encephalopathy diagnosis can mean many things. At its simplest, it means that the baby has some degree of brain dysfunction. Sometimes, there is swelling inside the brain due to injury. In many cases, the baby ends up with no permanent damage or long-term consequences, especially if the encephalopathy is promptly recognized and treated.
Unfortunately, there are some cases in which the effects of neonatal encephalopathy are identified later on in life when a child reaches four to five years of age and begins to miss major developmental milestones . Neonatal encephalopathy can lead to long-term conditions, such as cerebral palsy, developmental delays, or learning disabilities.
What Tests Might My Baby Have
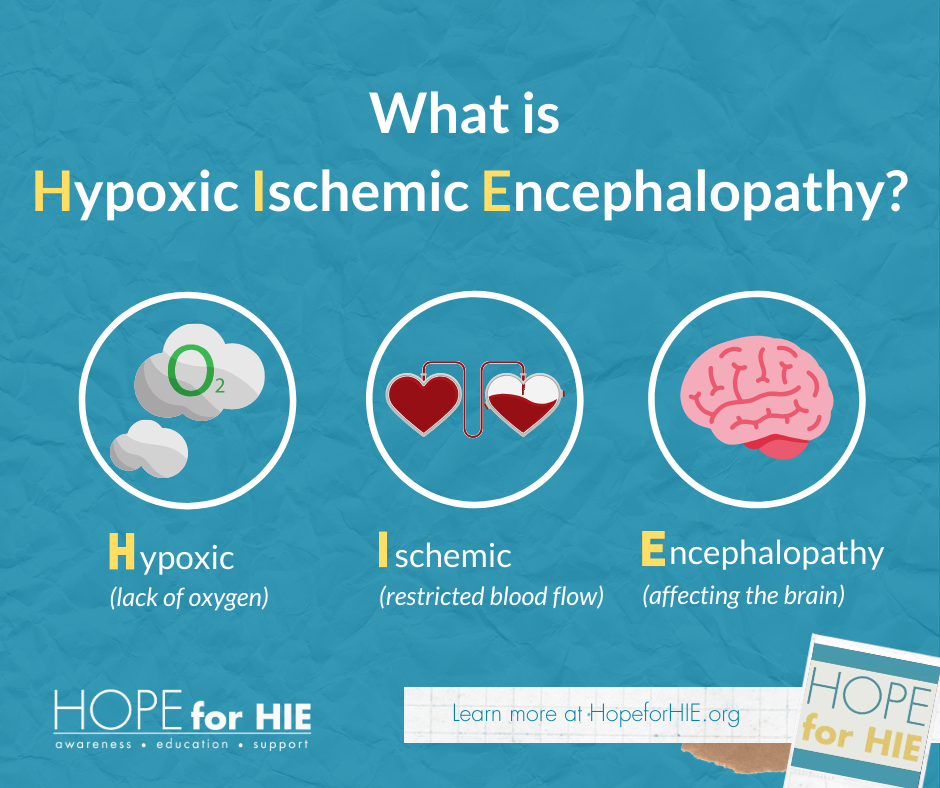
If your baby’s healthcare team are concerned about or diagnose HIE in your baby, they may arrange further tests.
These might include the following:
- Cerebral Function Monitoring CFM uses sensors to record brain activity. It is used to show the early effects of HIE on your babys brain, and can be also used to decide if your baby needs therapeutic hypothermia treatment.
- Head ultrasound scan A head ultrasound scan is used to look at images of your babys brain. It can be used to show problems such as bleeding, stroke, or swelling.
- MRI scan An MRI scan uses magnetism to build up a very detailed picture of areas of your babys brain. It is used to see if any damage has been done to your babys brain. It is usually performed after cooling treatment .
Read Also: How To Keep Newborn Baby Sleep At Night
