When To Delay Or Avoid Hepb Immunization
Doctors delay giving the vaccine to babies who weigh less than 4 pounds, 7 ounces at birth whose mothers do not have the virus in their blood. The baby will get the first dose at 1 month of age or when the baby is discharged from the hospital.
The vaccine is not recommended if your child:
- is currently sick, although simple colds or other minor illnesses should not prevent immunization
- had a serious allergic reaction after an earlier dose of the vaccine or is allergic to baker’s yeast
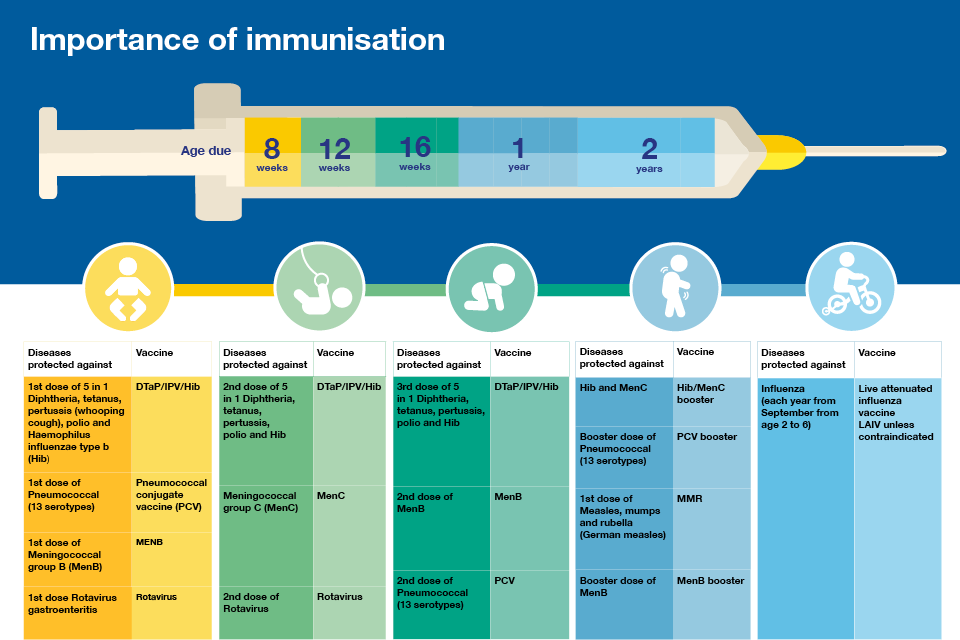
Vaccines For Your Newborn Baby
It is essential to administer the following vaccines after your baby is born. Some of them are given within the first few hours of birth, while some, in the following days, weeks, and months. These mandatory vaccinations are listed under the National Immunization Schedule . They help protect newborns against deadly diseases.
Baby Vaccination: What To Expect And How To Soothe The Pain
Make your little one’s first vaccinations as pain-free as possiblefor both of you.
No parent looks forward to Babys first vaccinations. Even though the shots are crucial to his long-term health, seeing your infant in pain will surely induce panic. But did you know that parents play a crucial role in relieving side effects of vaccines in babies, making the process more comfortable for both of you?
An study funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research focused on parental awareness and adoption of pain-relief strategies during infant immunizations. Through hospital prenatal programs at Mount Sinai Hospital in Toronto, the researchers worked with parents to create educational tools on reducing babies’ vaccination distress. The tools included a pamphlet and a video.
After parents received the tools, “we found increased use of pain interventions at future infant vaccinations, and knowledge, skills, and confidence in parents’ abilities to manage infant pain,” said Dr. Anna Taddio, professor, Leslie Dan Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Toronto, of the study.
Hopefully, evidence-based health information for soothing Baby during shots will get in the hands of new parents sooner. But if you still have questions, follow this advice to take some of the stress out of your own baby’s experience.
Don’t Miss: How To Help A Newborn With A Cold
What Vaccinations Does Your Baby Need
In the first 2 years of life, your baby gets several vaccinations to help protect her from diseases. Our vaccination schedule shows each vaccination your baby gets up to 6 years. It shows how many doses your baby gets of each vaccine and when she gets them. Its based on the schedule from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . The CDC has done lots of research to make sure vaccination schedules are safe for children.
Your provider may recommend a different vaccination schedule if your baby is at risk of getting certain diseases. For example, your baby may need a different schedule if:
- Your baby has health conditions, like HIV, sickle cell disease , heart disease and certain cancers. HIV is a virus that attacks the bodys immune system. In a healthy person, the immune system protects the body from infections, cancers and some diseases. An infection is a sickness you get from bad germs. SCD is a condition in which the red blood cells in your babys body are shaped like a sickle . This causes the blood cells to be stiff and block blood flow, which can increase your babys risk of infection.
- Your baby is travelling outside the United States. Some diseases are more common in other parts of the world than in the U.S., so check with your babys provider if your baby is travelling outside this country.
- Theres a disease outbreak. An outbreak is the sudden start or increase of a disease in a certain time and place.
Do You Recommend These Same Vaccines For Grandparents And Other Family Members Who Will Be In Close Contact With The Newborn

I do. All close contacts to the newborn should be vaccinated with the annual influenza vaccine at least 2 weeks before meeting the baby.
They should also have had Tdap in the last 10 years. If they have not received that vaccine, they should get a Tdap booster at least 2 weeks before meeting the baby.
Read: How to Prepare for Flu Season: A Family Guide
Also Check: How Often Should A Newborn Drink Formula
Do Vaccinations Have Risks Or Side Effects
Like any medicine, vaccinations can cause side effects. A side effect is an effect of a drug or treatment that is not the intended result. For example, a side effect of some cold medicines is that they make you sleepy. Most of the time, side effects from vaccinations are mild, go away on their own and last only a few days. Most side effects are a good sign that your babys immune system is building up protection against the disease he was vaccinated against. Your babys immune system helps protect him from infection.
Ask your babys provider about possible side effects of vaccinations, including:
- Fussiness
- Low fever
- Redness, swelling or soreness at the spot where your baby got the shot
Severe allergic reactions to vaccines are rare. An allergic reaction is a reaction to something you touch, eat or breathe in. About 1 in 1 million doses of vaccines causes a severe allergic reaction. A severe allergic reaction happens within minutes or a few hours of the vaccination. If your baby has signs of a severe allergic reaction or a reaction that you think is an emergency, call 911. Signs of a severe allergic reaction include:
- Breathing problems
- Swelling of the throat and face
- Hives. These are red bumps on your skin that sometimes itch.
- Fever, sleepiness and not wanting to eat
- Weakness, dizziness and fast heartbeat
What Is Hib Disease
- Hib stands for Haemophilus Influenzae type b. Despite its name, it has nothing to do with the flu.
- Hib is a bacteria that starts in the nose or throat and can infect almost any other part of the body, such as the brain, lungs, heart, joints, bones and skin.
- It can cause a very serious disease called meningitis when it infects the fluid and covering of the brain and spinal cord.
- Without treatment, all children with Hib meningitis die. Even with treatment, about 1 in 20 children with Hib meningitis will die.
- About 1 in 3 children who live will have permanent brain damage.
Recommended Reading: How To Wash A Newborns Face
What Changes Were Made To The Immunization Schedule In 2021
The CDCs Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices meets three times a year to review the latest scientific research and make any necessary changes to the child vaccination schedule. The CDC officially sets the schedule based on ACIPs recommendations, and the schedule is also approved by organizations like the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Association of Family Physicians .
In 2021, no major changes were made. But the schedule was updated to include the latest guidance on catch-up vaccinations for Hib and HPV vaccines. New information about special situations was also added for several immunizations. If you have specific questions about 2021 updates and how they relate to your kids vaccine schedule, talk with your childs doctor.
Recommended Immunizations For Children Ages 11 To 12 Years Old
The immunizations that are recommended at this age are for diseases that teens and young adults are at higher risk for plus one booster dose to strengthen immunity for three diseases. Your childs annual wellness visit or back-to-school checkup is the perfect time to get these vaccines.
An overview of immunizations for kids ages 11 to 12 years old
- Tdap At this age, this immunization is whats commonly referred to as a booster shot because it boosts your childs tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis immunity. While related to the DTaP vaccine kids receive during childhood, this vaccine is formulated for adolescents and adults.
- MenACWY The first of two meningococcal vaccine doses is recommended sometime between 11 years old and 12 years old. This vaccine protects against the most common types of meningococcal bacteria that affect adolescents.
- HPV While in some cases doctors may recommend the human papillomavirus vaccine as early as age 9, this vaccine is routinely recommended to begin between 11 and 12 years old. If the initial vaccination is completed before age 14, just two doses are needed. The second dose should be completed 6 to 12 months after the first dose.
Read Also: How Do I Add My Newborn To My Medicaid
Should You Get The Covid
As more Americans receive COVID-19 vaccinations, many activities people have avoided over the last year will likely become less risky. For parents of newborns, theres the hope that they may feel safe introducing their babies to more loved ones.
I recognize it is very hard to parent without your village. This past year has been very difficult for parents of newborns, said Jaime Friedman, a San Diego-based pediatrician and director of marketing at Childrens Primary Care Medical Group.
Luckily we now have vaccines that are very effective so that more and more family and friends can begin to visit or help out, she added. As our vaccine access and eligibility improves, it will be easier for families to surround themselves with other vaccinated adults.
Recent promising data has suggested that vaccinated people may not transmit the virus and that vaccinated mothers likely can pass COVID-19 antibodies to their babies through the placenta and breast milk, which may provide protection to newborns.
Still, as we remain cautiously optimistic, its important to make wise choices when it comes to newborn babies. Below, pediatricians share what you need to know about interactions with newborns in the age of COVID-19 vaccinations.
How Does Immunisation Work
Immunisation is a simple, safe and effective way to protect children against certain diseases. The serious health risks of these diseases are far greater than the very small risks of immunisation.
Immunisation protects children against harmful infections before they come into contact with them in the community.
It uses the bodys natural defence mechanism the immune system to build resistance to specific infections. Generally it takes about 2 weeks after vaccination for the immune system to respond fully.
Vaccination is the term used for getting a vaccine that is, getting the injection or taking an oral vaccine dose. Immunisation refers to the process of both getting the vaccine and becoming immune to the disease after vaccination.
Learn more about the difference between vaccination and immunisation.
Vaccines for babies and young children are funded under the Department of Health’s National Immunisation Program.
In Australia, babies and children are immunised against the following diseases:
The hepatitis A vaccine is free for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander children living in high-risk areas .
Children aged 6 months to under 5 years can have the flu vaccine for free each year. It is available in autumn. Children aged 12 to 13 should be vaccinated against human papillomavirus through their schools.
Most vaccines recommended in the program are given by injection. Some combine several vaccines in the one injection.
Don’t Miss: How To Apply For Medicaid For Newborn
Are There Any Reasons Not To Vaccinate My Child Especially During The Covid
Yes. There are times when some children should not get certain vaccines or they should wait. For example, if your child has any severe, life-threatening allergies, theyve had an allergic reaction after a previous dose of vaccines, or theyre moderately or severely ill, their doctor may recommend not getting or delaying a specific vaccination.
When it comes to the COVID-19 pandemic, you dont need to delay the immunizations or care your child needs unless of course you, your child or someone in your household is experiencing COVID-19 symptoms.
While staying on track with all immunizations is important, making sure your child has their annual flu shot will be especially important this year. As the pandemic continues, so too will the high amounts of time we spend at home and indoors where flu viruses can thrive during cold and dry winter weather. Flu shots are typically available starting in late August, and this year HealthPartners and Park Nicollet is offering both shot and FluMist options.
Why We Need Vaccines
Vaccines have successfully lowered the rates of disease in countries with strong vaccination programs.
Some of the diseases that vaccines prevent have no treatment or cure. These diseases can cause:
- severe illness
- disability
- death
Even with improved living conditions and modern hygiene, vaccines are still very important to prevent infections that could make your child very sick.
Some diseases are now rarely seen in Canada because of long-term high rates of vaccination in the population, including:
However, these diseases still exist in some countries, so people who live in them or travel to them may become infected. They can introduce and spread these diseases when they return to Canada. High rates of vaccination against these diseases help to prevent further spread and outbreaks.
The best way to protect your children’s health is to prevent these diseases in the first place by keeping their vaccinations up to date. Some examples include:
Measles
Measles is still a leading cause of death in children worldwide, with 89,780 cases in 2016. One person with measles can infect 12 to 18 people who haven’t had the vaccine.
Measles is a very contagious disease. You can catch it by walking into a room that an infected person sneezed in an hour before you entered.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Good Gift For A Newborn Baby Boy
There Are Risks To Falling Behind On The Schedule
The CDCs vaccine schedule is recommended for a reason: It works. For some shots, more than one dose is required to build up full immunity for others, immunity wanes with time. Skipping or delaying shots puts your baby at risk of getting sick from the illnesses they protect against starting early in your child’s life. So be sure to stick to the schedule and attend all of your babys postnatal follow-up appointments.
Signs Of A Serious Reaction To Vaccinations
As mentioned earlier, severe reactions after vaccination are pretty rare however, you should immediately consult a paediatrician in case the baby shows the following symptoms:
- Visible rash on any part of the body
- Swollen face or eyelids
If your baby has no allergic reaction but shows the signs that are deemed normal for babies to show after vaccination, you can soothe his discomfort/pain with some remedies. Read on to know how you can soothe your baby after vaccination.
Read Also: How Should You Lay A Newborn Baby Down To Sleep
