What Is A Delayed Immunization Schedule
The immunization schedule is the same for all children. However, there may be certain adjustments needed if your child has a weakened immune system, or if sheâs taking certain medications that may weaken her immune system.Your childâs healthcare provider will take into account your little oneâs entire medical history when determining whether to give or delay a specific vaccination. In some cases a shot can be delayed, or not given at all, if the healthcare provider thinks this is the safest course of action for your little one.
Importance Of Vaccines For Infant And Toddlers
For newborns, breast milk can help protect against many diseases. However, this immunity wears off after breastfeeding is over, and some children arent breastfed at all.
Whether or not children are breastfed, vaccines can help protect them from disease. Vaccines can also help prevent the spread of disease through the rest of the population through herd immunity.
Vaccines work by imitating infection of a certain disease in your childs body. This prompts your childs immune system to develop weapons called antibodies.
These antibodies fight the disease that the vaccine is meant to prevent. With their body now primed to make antibodies, your childs immune system can defeat future infection from the disease. Its an amazing feat.
If Your Child Can’t Be Vaccinated
Some children may not be able to get some vaccines, including those with:
- specific medical conditions
- severe allergic reactions to vaccine ingredients
Examples include children who need to take high-dose steroids or who have a weakened immune system from cancer treatment . These children may need to avoid vaccines that contain a weakened live virus, such as measles, mumps, rubella and chickenpox.
These children are at risk of getting the disease that the vaccine would have prevented.
Talk to your health care provider or local public health authority if you have any concerns about your child’s health status and vaccines.
If your child can’t be vaccinated, you can help protect them by encouraging others to get vaccinated. This will help prevent the spread of disease to your child.
Read Also: How Often Should I Sponge Bathe My Newborn
Vaccines Given At Two Months
Hepatitis B Vaccine is given to your baby for the second time during the two month check-up.
DTaP Vaccine protects your baby from three life-threatening, toxin-releasing bacterial diseases: diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis . Often found in unsanitary conditions or from improper wound care, tetanus is a severe disease of the nerves that can cause the jaw to lock. Diphtheria affects breathing and the throat in small children and may cause nerve, heart, and kidney damage. Pertussis is a highly contagious disease that mostly affects babies under six months and causes coughing spells that can become severe and potentially deadly. Getting the vaccine between 27 and 36 weeks of pregnancy is also a great way to help prevent your infant from contracting pertussis.
What Vaccines Are Recommended At Two Months
If your child did not receive his second dose of Hepatitis B vaccine at their 1 month shots, he will receive this booster. Additional 2 month shots include:
IPV: Inactivated poliovirus vaccine DTaP: Diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis vaccines Hib: Haemophilus influenza type b vaccine RV: rotavirus vaccine PVC: Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine
Read Also: How Much Ml Formula For Newborn
A Newsletter You Can Relate To
Storytelling that represents you, delivered to your inbox.
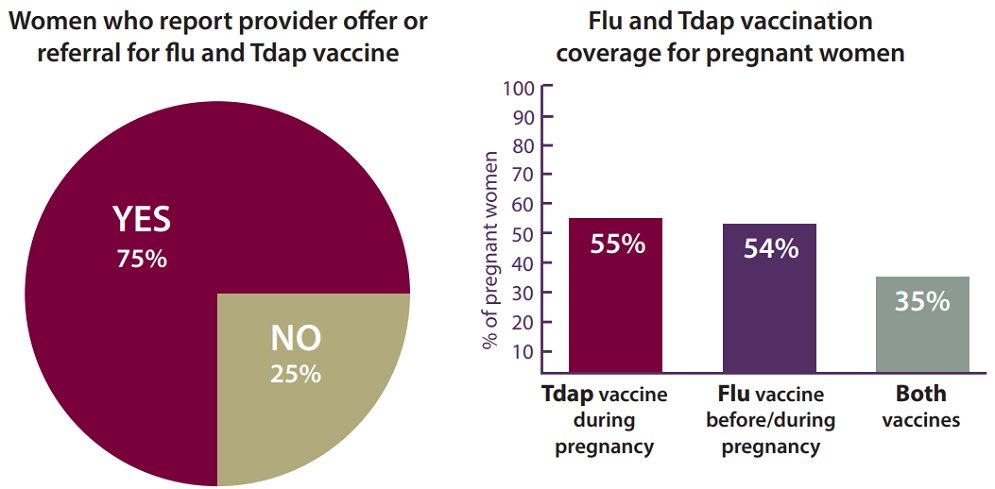
With breastfeeding, the potential for immunity is less significant as the maternal antibodies are consumed by a baby through breastmilk and then go into the gut, and not directly into the babys own bloodstream. We know that breastfed infants are less likely to have some kinds of infection when they are infants, but whether that will turn out to be true from the antibodies from the COVID vaccine remains to be seen, Gray said.
But what about parents who were infected with COVID-19 during pregnancy? Wouldnt they pass on antibodies as well?
The research on that was less clear.
Dr. Carolynn Dude, an assistant professor of maternal fetal medicine at Emory University, helped lead a study on that subject. The results, which appear in the most recent issue of the journal Obstetrics and Gynecology, show that while parents were found to have mounted a robust immunological response after contracting COVID, with a significant of neutralizing antibodies present in their blood samples at the time of delivery, these same protective antibodies were found in only 25 percent of infants born to these same patients.
This, Dude said, suggested that the vaccines might offer more protection to babies than a parents bout with the disease.
- More from The 19th
- Exclusive: Study finds pregnancy-related health care coverage varies widely from state to state
Rotavirus Vaccine Given At 2 And 4 Months
What is rotavirus?
Rotavirus is a common infection that causes vomiting and diarrhea in infants and children. Rotavirus is very contagious, spreading easily from children who are already infected to other infants, children and sometimes adults. Most children are infected with rotavirus at least once by five years of age. Serious but rare symptoms commonly seen in children less than two years of age include severe diarrhea, leading to hospitalization.
Rotavirus infection is a major cause of visits to health care providers and hospital stays for infants and children under five years of age in Ontario. Deaths in Ontario due to rotavirus are rare.
Some immunizations are required for children to attend school in Ontario. Please see the school immunization checklist for more information.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Signs Of Colic In Newborns
Measles Mumps Rubella And Varicella Vaccine
The Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care recently introduced a new measles, mumps, rubella and varicella vaccine to the Publicly Funded Immunization Schedules for Ontario.
Immunization against measles, mumps and rubella is required by law for all children attending school in Ontario, unless exempted. Immunization against varicella is also required for children born in 2010 or later.
What is measles?
Measles can be a serious infection. It causes high fever, cough, rash, runny nose and watery eyes. Measles lasts for one to two weeks. Ear infections or pneumonia can happen in one out of every 10 children with measles. Measles can also be complicated by encephalitis, an infection of the brain, in about one out of every 1,000 children with measles. This may cause brain damage and developmental delays. Measles can also make a pregnant woman have a miscarriage or give birth prematurely.
Measles spreads from person to person very easily and quickly. People can get measles from an infected person coughing or sneezing around them or simply talking to them.
What is mumps?
Mumps can cause very painful, swollen testicles in about one out of four teenage boys or adult men, and painful infection of the ovaries in one out of 20 women. Mumps infection during the first three months of pregnancy may increase the risk of miscarriage. Mumps can cause deafness in some people.
What is rubella ?
What is varicella ?
How The Body Reacts To Vaccines All At Once
Approximately 90%-95% of recipients of a single dose of certain live vaccines administered by injection at the recommended age develop protective antibodies, generally within 14 days of the dose. For varicella and mumps vaccines, 80%-85% of vaccines are protected after a single dose. However, because a limited proportion of measles, mumps, and rubella or varicella vaccinees fail to respond to 1 dose, a second dose is recommended to provide another opportunity to develop immunity . Of those who do not respond to the first dose of the measles component of MMR or varicella vaccine, 97%-99% respond to a second dose.
Scientific data show that getting several vaccines at the same time does not cause any chronic health problems. A number of studies have been done to look at the effects of giving various combinations of vaccines, and when every new vaccine is licensed, it has been tested along with the vaccines already recommended for a particular aged child.
The recommended vaccines have been shown to be as effective in combination as they are individually. Sometimes, certain combinations of vaccines given together can cause fever, and occasionally febrile seizures these are temporary and do not cause any lasting damage. Based on this information, both the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend getting all routine childhood vaccines on time.
You May Also Like
You May Like: What If My Newborn Is Constipated
How To Prepare Your Child For A Vaccination
If your little one is old enough to understand whatâs going on, try describing the immunization appointment and whatâs about to happen. Offer assurance that even though the shot may hurt a little, the pain wonât last. Also, consider bringing along your childâs favorite toy or even a security blanket. This may help comfort her.During the appointment, you may be able to hold your child in your lap, which can offer additional comfort. Also, consider trying to distract him with a toy, a story, or pointing out things in the room. For a very young child, you might consider breastfeeding or bottle-feeding afterward. Even swaddling may help comfort her especially if sheâs crying after the shot.You may consider asking the doctor or the nurse who administers the shot if there are any steps you could take to help your child feel more comfortable. You may be told to have your child move his arm around after the vaccination, which can help reduce any pain or swelling.
What Is Herd Immunity
If enough people in your community are immunized against a certain disease, you can reach something called herd immunity. When this happens, diseases cant spread easily from person to person because most people are immune. This provides a layer of protection against the disease even for those who cannot be vaccinated, such as infants.
Herd immunity also prevents outbreaks by making it difficult for the disease to spread. The disease will become more and more rare, sometimes even disappearing entirely from the community.
Don’t Miss: How Often To Bathe A Newborn Baby
A Guide To Immunisations For Babies Born On Or After 1 January 2020
This publication is licensed under the terms of the Open Government Licence v3.0 except where otherwise stated. To view this licence, visit nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence/version/3 or write to the Information Policy Team, The National Archives, Kew, London TW9 4DU, or email: .
Where we have identified any third party copyright information you will need to obtain permission from the copyright holders concerned.
This publication is available at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/a-guide-to-immunisations-for-babies-up-to-13-months-of-age/a-guide-to-immunisations-for-babies-born-on-or-after-1-january-2020
Do Vaccination Needles Hurt

Although generally quick, getting vaccinations can be painful for your child. The best way you can make it as painless as possible is to hold your child, and soothe and comfort them. Breastfeeding can also help reduce pain. You can use a number of other techniques to reduce the pain your child might experience.
Don’t Miss: What Can I Do If My Newborn Baby Is Constipated
Your Vaccine History Since Birth
The majority of children are given shots at a young age because this is when they are at highest risk of getting sick or dying if they get these diseases. In fact, many school systems wont allow children in school unless they have vaccines for diseases that used to be deadly . Newborn babies are immune to some diseases because they have antibodies they get from their mothers, usually before they are born. However, this immunity lasts a few months. Most babies do not get protective antibodies against diphtheria, whooping cough, polio, tetanus, hepatitis B, or Hib from their mothers. Thats why the CDC says its important for the child to get the vaccine first before the child is exposed to the disease.
Vaccines contain weakened or killed versions of the germs that cause the disease. These elements of vaccines, and other molecules and micro-organisms that stimulate the immune system, are called antigens. Babies are exposed to thousands of germs and other antigens in the environment from the time they are born. When a baby is born, his or her immune system is ready to respond to the many antigens in the environment and the selected antigens in vaccines.
You May Also Like
Preparing For Your Child’s Immunisation
When you take your child for each vaccination, it important to take your child’s My Health and Development Record or your child’s health record booklet, so that the doctor, nurse or health worker can record your child’s visit. These records are an important reminder of when your child’s next immunisations are due and which children in the family are immunised.
There is also the option of setting up an eHealth record for your child and downloading the My Child’s eHealth Record app.
Before the immunisation, you need to tell the doctor or nurse if your child:
Read Also: How Many Hours Should A Newborn Sleep At Night
How Do Vaccines Work
Vaccines are shots that contain harmless versions of the same germs that cause a specific disease. These germs are either dead or weakened to the point that they donât do any harm. The vaccine, once itâs injected, stimulates the bodyâs immune system to produce antibodies.A person who is vaccinated will then develop immunity to that specific disease without ever having contracted it. Unlike medications that cure diseases, vaccines help prevent them in the first place.When it comes to your baby or toddler, through routine immunizations, your little one is protected from serious diseases like polio, whooping cough, and all the others listed here. Young infants are at the greatest risk, so itâs important that babies and toddlers get all the recommended immunizations before their second birthday.Some vaccines require more than one dose. Here are some situations in which additional doses may be needed, depending on the type of vaccine:
For inactivated vaccines, one dose doesnât provide enough immunity, so follow-up doses are required. The Hib vaccine is a good example of this type.
Immunity may wear off after time for certain vaccines. In this case a booster shot is needed to raise immunity levels again. The DTaP vaccine is a good example of this. The booster shot needed for older children and adults is the Tdap vaccine.
Concerns About Side Effects Of Immunisation
If a side effect following immunisation is unexpected, persistent or severe or if you are worried about yourself or your child’s condition after a vaccination, see your doctor or immunisation nurse as soon as possible or go directly to a hospital. Immunisation side effects may be reported to SAEFVIC, the Victorian vaccine safety service .
You can discuss with your immunisation provider how to report adverse events in other states or territories.
It is important to seek medical advice if you are unwell, as this may be due to other illness rather than because of the vaccination.
Don’t Miss: What Kind Of Toys Do Newborns Need
