What Is The Chance That My Baby Will Become Hiv Positive
A baby can become infected with HIV in the womb, during delivery or while breastfeeding. If the mother does not receive treatment, 25 percent of babies born to women with HIV will be infected by the virus. With treatment that percentage can be reduced to less than 2 percent, according to the March of Dimes.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus2 Diagnosis
The possibility of human immunodeficiency virus 2 infection should be entertained in patients with the following risk factors:
-
Illness characteristic of HIV infection despite negative HIV-1 test result
-
West African origin
-
Sex partners or needle-sharing partners of a person known to be infected with HIV-2 or who is not infected but is from an HIV-2endemic area
-
Children born to women with HIV-2 or who have risk factors for HIV-2 infection
-
Persons who have participated in a HIV-vaccine trial or have receive blood products or a nonsterile injection in HIV-2endemic areas
-
People with unusual HIV-1 Western blot indeterminate patterns
Hiv Tests Used In Infants And Toddlers
The virologic assays used in infants can either be the so-called polymerase chain reaction test, which detects the presence of HIV DNA, or an HIV RNA assay, which clearly detects HIV RNA.
While the specificity of each of these tests is high at the time of birth, their sensitivity can be as low at 55% for the PCR and 25% for the HIV RNA. However, by the time the newborn reaches three months, the accuracy of the tests generally approaches 100%.
In specific circumstances, HIV antibody tests can be used in children between the ages of six and 18 months to definitively exclude HIV infection. However, they should not be used to confirm HIV infection due to concerns about residual maternal antibodies.
Confirmation of an HIV infection should be based on two positive test results taken from separate blood samples.
- Two or more negative virologic tests taken ages one month and four months, or
- Two negative antibody tests taken from separate blood samples in children over the age of six months.
In children over the age of 18 months, standard adult HIV testing guidelines apply.
Also Check: Why Does My Newborn Spit Up Breast Milk
How Can Hiv Testing Help You
About 1 in 8 people in the United States who have HIV do not know they have it.The only way to know for sure whether you have HIV is to get tested.
Knowing your HIV status gives you powerful information to help you take steps to keep you and your partner healthy:
- If you test positive, you can take medicine to treat HIV. People with HIV who take HIV medicine as prescribed can live long and healthy lives. Theres also an important prevention benefit. If you take HIV medicine as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you will not transmit HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex.
- If you test negative, you have more prevention tools available today to prevent HIV than ever before.
- If you are pregnant, you should be tested for HIV so that you can begin treatment if you’re HIV-positive. If you have HIV and take HIV medicine as prescribed throughout your pregnancy and childbirth and give HIV medicine to your baby for 4 to 6 weeks after giving birth, your risk of transmitting HIV to your baby can be less than 1%. HIV medicine will protect your own health as well.
The sooner you know your status, the better. Some people with HIV have it for years before they know it. During that time, they arent getting the treatment they need to protect their health and prevent transmission of HIV to their sexual or needle sharing partners. Thats why CDC encourages more frequent HIV testing for individuals who might have a risk for getting HIV.
How Can This Affect My Pregnancy

In most cases, HIV will not cross through the placenta from mother to baby. If the mother is healthy in other aspects, the placenta helps provide protection for the developing infant. Factors that could reduce the protective ability of the placenta include in-uterine infections, a recent HIV infection, advanced HIV infection or malnutrition.
Unless a complication should arise, there is no need to increase the number of prenatal visits. Special counseling about a healthy diet with attention given to preventing iron or vitamin deficiencies and weight loss as well as special interventions for sexually transmitted diseases or other infections should be part of the prenatal care of HIV infected women.
Health care providers should watch for symptoms of AIDS and pregnancy complications of HIV infection. In addition, providers should avoid performing any unnecessary invasive procedures such as amniocentesis in an effort to avoid transmitting HIV to the baby.
Recommended Reading: How Many Diapers Do You Need For Newborn
Can I Breastfeed If I Am Hiv Positive
About 15% of newborns born to HIV-positive women will become infected if they breastfeed for 24 months or longer.The risk of transmission is dependent upon:
- Whether the mother breastfeeds exclusively
- The duration of breastfeeding
- The mothers breast health
- The mothers nutritional and immune status
The risk is greater if the mother becomes infected with HIV while she is breastfeeding.
Diagnosis Of Hiv In Infants And Children
HIV can be diagnosed definitively by virologic testing in most non-breastfed infants with perinatal HIV exposure by age 1 to 2 months and in almost all infants with HIV by age 4 to 6 months. Antibody tests, including the antigen/antibody combination immunoassays , do not establish the presence of HIV in infants because of transplacental transfer of maternal HIV antibodies therefore, a virologic test must be used.1,2 Positive virologic tests indicate likely HIV infection. Plasma HIV RNA or cell-associated HIV DNA NATs are generally equally recommended. However, both tests can be affected by maternal antiretroviral therapy through transplacental transfer of antiretroviral drugs from the pregnant person to fetus or by ARV drugs administered to the infant as prophylaxis or presumptive HIV therapy. In contrast, qualitative HIV proviral DNA PCR assays from whole blood detecting cell-associated virus often are less affected by ARVs.
An infant who has a positive HIV antibody test but whose mothers HIV status is unknown should be assumed to have been exposed to HIV. The infant should undergo HIV diagnostic testing, as described in Timing of Diagnostic Testing in Infants with Perinatal HIV Exposure below,15 and receive ARV prophylaxis or presumptive HIV therapy as soon as possible. For ARV management of newborns who have been exposed to HIV and newborns with HIV infection , see Antiretroviral Management of Newborns with Perinatal HIV Exposure or Perinatal HIV.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Social Security Card For Newborn
How And When Will I Know That My Baby Is Hiv Negative
The usual HIV antibody test is not used to test for HIV in babies. Babies born to HIV positive mothers will always test HIV positive using an HIV antibody test.
This is normal and does not mean your baby has HIV. Your baby shares your immune responses that the antibody test looks for. It sometimes takes up to 18 months for these responses to gradually disappear.
The baby will be tested using an HIV PCR DNA or RNA test. These tests look for virus in the babys blood.
In the UK, it is good practice to test the baby on the day she or he is born. The test is repeated after six weeks and again at three months.
If all these tests are negative, and you are not breastfeeding your baby, then your baby does not have HIV.
You will also be told that your baby no longer has your antibodies when he or she is 18 months old.
What Are The Different Types Of Hiv Screening
Human immunodeficiency virus , the virus that leads to the immune system disease called acquired immunodeficiency syndrome , is life-threatening. There are several screening methods to confirm HIV.
Rapid Antibody/Antigen HIV test:
- This type of test is useful for individuals who want same-day results from their evaluation.
- The accuracy level of this test is as high as that of a standard test. If an individual tests negative, then there is no need for additional evaluation if they have no further risk and/or the window period has passed.
Recommended Reading: How Many Ounces Of Formula Should A Newborn Eat
Screening For Hepatitis B Hiv And Syphilis
During your pregnancy, you’ll be offered a blood test for 3 infectious diseases: hepatitis B, HIV and syphilis. This is part of routine antenatal screening, which is recommended for every pregnancy.
You will usually be offered the blood test at your booking appointment with a midwife.
The blood test needs to be done as early as possible in pregnancy, ideally by 10 weeks. This is so treatment can be started early, if you need it, to reduce the risk of passing the infection on to your baby.
If you already know you have HIV or hepatitis B, you’ll need early specialist appointments to plan your care in pregnancy.
If your partner has HIV, hepatitis B or syphilis, tell your midwife as soon as possible.
Hepatitis B, HIV and syphilis can all be passed to your baby during pregnancy and birth.
Would It Be Safe For The Mother To Stop The Infants Daily Nvp At 6 Weeks
Mothers on ARV drugs for at least 12 weeks prior to onset of labour have a very low if not non-detectable viral load and NVP should be stopped at 6 weeks. Continuing with daily NVP beyond 6 weeks is only recommended for infants of breastfeeding mothers who only started on ARV treatment during the last 12 weeks of their pregnancy or with a viral load 1000 copies/ml or more.
Also Check: How Do You Give A Newborn A Bath
Do I Need To Have This Test
It’s your choice to be tested for any or all of these infections.
The tests are recommended to:
- protect your health through early treatment and care
- reduce any risk of passing an infection on to your baby, partner or other family members
If you test positive for hepatitis B, HIV or syphilis, your partner and other family members may be offered a test for the infection.
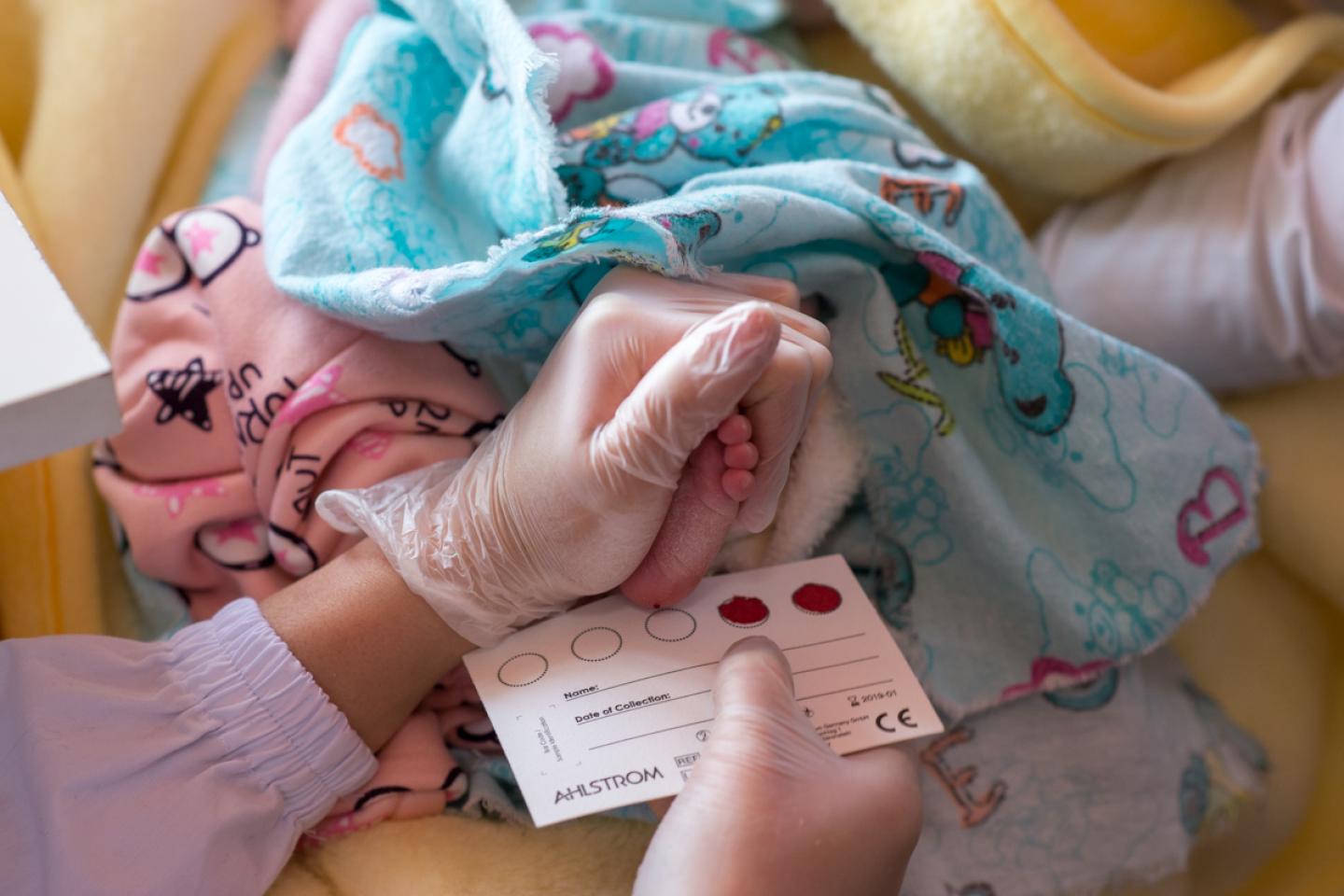
Testing Newborns For Hiv
Virtual Mentor.
Perinatal HIV refers to infection with the virus that is transmitted from an HIV-positive mother to her child during gestation, labor and delivery, or after delivery as a result of breast feeding . It would seem that a child born to an HIV-positive mother is doomed to contract the virus, but an HIV-positive mother does not automatically transfer the virus to her child . Although perinatal transmission is not perfectly understood, newborns have only about a 25 percent chance of contracting HIV during gestation . Most babies who contract the virus perinatally do so during labor and delivery .
It is possible to prevent transmission of the virus to HIV-exposed infants, but early recognition of the maternal antibodies is essential to ensuring these benefits. When treatment of newborns whose exposure to HIV was first detected after birth was begun within the first 48 hours of life, the transmission rate was approximately 9 percent when begun on day 3 of life or later, the transmission rate rises to approximately 18 percent . The survival rate for HIV-infected infants is extremely low. These infants suffer from a variety of preventable or manageable infections, including meningitis, Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia , and tuberculosis. Though there is no cure for HIV, the duration and quality of life of an infected child can be enhanced by antiretroviral drugs and other drug therapy, nutritional monitoring, and a proper immunization schedule.
Recommended Reading: How To Make Newborn Stop Crying
What Are The Early Symptoms Of Hiv Infection
Not everyone who is infected with HIV will develop early symptoms, known as acute HIV infection. Two to four weeks after exposure to HIV, some people may develop flu-like symptoms that last from a few days up to several weeks. These symptom include:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Persistent diarrhea or unusual spots on the skin or in the mouth
These symptoms are not specific to HIV – other infections may cause the same symptoms. The presence or absence of symptoms does not predict whether you have HIV or not, and only an HIV test can detect whether a person is or is not infected with HIV. If these symptoms dont go away, or get worse, you should see a doctor.
What Important Information Should Be Provided To The Mother
The advantages of breastfeeding should be explained to the mother. The overall HIV free survival in HIV-exposed infants from poor communities is significantly better when women breastfeed compared to women who formula feed. The risk of death due to gastroenteritis, pneumonia and undernutrition is significantly increased especially in poor communities.
Recommended Reading: What Can I Give My Newborn For Constipation
Hiv Testing Among Pregnant Women
Since 1994, the availability of increasingly effective antiretroviral drugs for both the prevention of perinatal human immunodeficiency virus transmission and maternal treatment has resulted in a greater emphasis on prenatal HIV testing and substantial increases in prenatal testing rates. In 2000, preliminary data indicated that 766 of 824 HIV-infected women in 25 states knew their HIV status before delivery . However, an estimated 280–370 perinatal HIV transmissions continue to occur in the United States each year . The primary strategy to prevent perinatal HIV transmission is to maximize prenatal HIV testing of pregnant women. States and Canadian provinces have implemented three different prenatal HIV-testing approaches. To assess their effectiveness, CDC reviewed prenatal HIV-antibody testing rates associated with these approaches. Medical record data suggest that the “opt-in” voluntary testing approach is associated with lower testing rates than either the “opt-out” voluntary testing approach or the mandatory newborn HIV testing approach.
Is Hiv Testing Recommended For Pregnant Women
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that all women get tested for HIV before they become pregnant or as early as possible during each pregnancy. The earlier HIV is detected, the sooner HIV medicines can be started.
All women who are pregnant or trying to get pregnant should encourage their partners also to get tested for HIV and, if possible, screened for other sexually transmitted diseases . STDs can increase viral loads in people with HIV. If any partner has HIV, that partner should take HIV medicine as prescribed to stay healthy and prevent transmission.
You May Like: What Helps A Gassy Newborn
Will My Baby Need To Be Treated
After your baby’s born, they’ll be given HIV medication, usually for about 4 weeks, to stop them developing HIV.
Your baby will be tested for HIV within 48 hours of birth. They’ll usually be tested again at 6 and 12 weeks. A final test is also needed when your baby is 18 months old. If you choose to breastfeed, your baby will be tested more often.
Read the answers to more questions about sexual health and questions about pregnancy.
Get Tested For Hiv As Soon As Possible To Know Your Status
- If you are pregnant or planning to get pregnant, get tested for HIV as early as possible during each pregnancy. Knowing your HIV status gives you powerful information.
- If you learn you have HIV, the sooner you start treatment the betterfor your health and your babys health and to prevent transmitting HIV to your partner.
- If you learn you dont have HIV, but you are at increased risk of acquiring it, get tested again in your third trimester.
- You should also encourage your partner to get tested for HIV.
Read Also: How Much Formula To Give Newborn
What Is Perinatal Transmission Of Hiv
Perinatal transmission of HIV is when HIV is passed from a woman with HIV to her child during pregnancy, childbirth , or breastfeeding . Perinatal transmission of HIV is also called mother-to-child transmission of HIV.
The use of HIV medicines and other strategies have helped to lower the rate of perinatal transmission of HIV to 1% or less in the United States and Europe.
Health Care Setting Or Lab

If you get an HIV test in a health care setting or lab, the health care provider will take a sample of blood or oral fluid.
- With a rapid test , you may be able to wait for the results.
- With a lab test, it may take several days for your results to be available.
Your health care provider may talk with you about your risk factors, answer any questions you might have, and discuss next steps.
You May Like: Where To Buy Newborn Baby Stuff
Oral Fluid And Urine Hiv Testing
An FDA-approved EIA known as OraQuick Advanced is available for the testing of human immunodeficiency virus -1 and HIV-2 in oral fluid and blood in non-clinical settings . In addition, there are the Avioq HIV-1 Microelisa System as well as the DPP HIV-1/2 Assay . While the DPP HIV-1/2 Assay can also be used to test whole blood, the Avioq HIV-1 Microelisa System can only be used with oral fluid and dried blood spots.
The main concern with the oral fluid test has been clusters of high rates of false-positive results in several US cities, mainly New York City and San Francisco. When whole-blood specimens were used for testing, there was no observed increase in false-positive rates. The CDC and the Food and Drug Administration are aware of these reports and have recommended continued use of rapid HIV testing on oral fluid as long as test subjects are informed of the need for additional testing in case of a positive result.
The urine test Calypte HIV-1 is an EIA test that requires administration by a physician. Positive results should be followed by confirmation with a serologic test.
