Is The Vaccine Safer Than Getting The Real Disease
Yes. Your child’s natural immune system has no problem handling the weak or dead germs in a vaccine. Your child may have a mild fever or a sore arm after vaccination but these side effects only last a few days and should not disrupt daily activities.
However, if an unvaccinated child catches the real disease, the result can be serious, or even fatal. This is because active germs multiply quickly, and your child’s immune system is not prepared to defend itself.
Health And Development Checks
Your baby’s health checks are very important â they are an opportunity to check that your baby is developing properly.
They are usually carried out by your health visitor either at home or in your GP surgery, baby clinic or children’s centre. These development checks are also a good opportunity for you to raise any concerns you might have.
Your baby’s very first health check takes place shortly after they are born, and they’ll continue until your child is 2 to 2 1/2 years old.
More Parents Nixing Anti
Vitamin K injections, given after birth, can prevent potentially fatal hemorrhaging in infants, but anti-vax parents are extending their fears into a general rejection of all shots
All babies lack sufficient vitamin K at birth, putting them at risk for severe bleeding in the brain or intestines until they get the vitamin by eating solid foods, typically around six months of age. The vitamin is essential for blood clotting, and a vitamin K injection after birth eliminates this bleeding risk.
A tiny percentage of parents have always declined the shot but the numbers are growing, according to a new study. The research also found that children of these parents are 15 times more likely than others, at 15 months old, to have received none of the vaccines recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and PreventionOur finding of a link between vitamin K refusal and vaccine refusal was very concerning, says senior author Shannon MacDonald, a postdoctoral fellow at the University of Calgary Faculty of Medicine. We had expected a correlation between the two but had not expected the association to be so high. Vitamin K is not a vaccine or related to the manufacturing of vaccines.
Also Check: How To Add Newborn To Medicaid Nc
Immunisation And Young Children
In the first months of life, a baby might have some protection from infectious diseases that their mother has had or been immunised against. This is known as passive immunity. It occurs when antibodies are transferred from mother to baby during pregnancy. The level of antibody protection for the baby can be low and wears off quickly. This puts them at risk of diseases that can be prevented with vaccination.Most childhood immunisations are given as an injection in the arm or leg, except rotavirus vaccine, which is given by mouth. A vaccination dose may contain a vaccine against one specific disease, or several diseases. This is known as a combination injection, and it helps to reduce the number of injections your child needs.
Your Babys First Shot

Shortly after birth, your baby should receive the first dose of the vaccine to help protect against the following disease:
All babies should get the first shot of hepatitis B vaccine within first 12 hours after birth.
This shot acts as a safety net, reducing the risk of getting the disease from you or family members who may not know they are infected with hepatitis B.
If you have hepatitis B, theres additional medicine that can help protect your newborn against hepatitis B its called hepatitis B immune globin . HBIG gives your babys body extra help to fight the virus as soon as your baby is born.
Read Also: What Size Bottle For Newborn
Why Is It Important To Keep Track Of Your Child’s Vaccination
Proof of vaccination may be requested. In some parts of Canada, children need to have all of their vaccinations up to date before starting school or daycare. This is needed to help prevent the spread of serious diseases in these settings.
Also, your child’s vaccination history is helpful if you ever need to take your child to see another healthcare provider or travel outside of Canada.
Why We Need Vaccines
Vaccines have successfully lowered the rates of disease in countries with strong vaccination programs.
Some of the diseases that vaccines prevent have no treatment or cure. These diseases can cause:
- severe illness
- disability
- death
Even with improved living conditions and modern hygiene, vaccines are still very important to prevent infections that could make your child very sick.
Some diseases are now rarely seen in Canada because of long-term high rates of vaccination in the population, including:
However, these diseases still exist in some countries, so people who live in them or travel to them may become infected. They can introduce and spread these diseases when they return to Canada. High rates of vaccination against these diseases help to prevent further spread and outbreaks.
The best way to protect your children’s health is to prevent these diseases in the first place by keeping their vaccinations up to date. Some examples include:
Measles
Measles is still a leading cause of death in children worldwide, with 89,780 cases in 2016. One person with measles can infect 12 to 18 people who haven’t had the vaccine.
Measles is a very contagious disease. You can catch it by walking into a room that an infected person sneezed in an hour before you entered.
Don’t Miss: How Many Diapers Do You Need For Newborn
What Are Some Common Side Effects Of 4 Month Shots For Babies
Shots are not fun for babies but luckily babies wont remember getting them! You can prepare yourself by knowing that this kind of health protection might have some mild, common side effects.
Remember, side effects happen because your babys immune system is triggered to build itself by the vaccination. Shots at any age cannot cause the disease they are protecting from.
Normal side effects of 4-month shots in babies include:
- redness or swelling where the shot was given
- pain or tenderness around the shot area
- irritability or fussiness
- severe asthma
Some kinds of medications like steroids can also temporarily weaken the immune system. Your pediatrician may delay 4-month shots if your baby is on steroids or other medications.
How Do I Keep Track Of My Child’s Vaccination
You will be given a vaccination record with your child’s recommended schedule at your first clinic visit. If your healthcare provider forgets, be sure to ask for one. It is important to bring this record with you every time you visit a healthcare provider. This is to make sure that it can be updated each time your child receives a vaccine.
You might find it helpful to use the checklist at the back of this guide, or download the CANImmunize mobile app to help you keep track of your family’s vaccinations.
Don’t Miss: What Size Diapers Should I Buy For A Newborn
What Is The Immune System
The immune system is a special network in the body that protects you from germs, like bacteria and viruses that cause diseases. Through a series of steps called the immune response, the immune system learns how to recognize germs in order to fight them if your child is exposed to them in the future.
Your child is exposed to thousands of germs daily at home, at daycare or in the grocery store. Even a sweet kiss from a brother or sister can be full of germs. Most of these germs are harmless and are easily handled by your child’s immune system. But some germs can make your child very sick.
Thanks to vaccination, your child’s immune system learns how to recognize harmful germs. Vaccines help your child to develop the necessary defences to fight disease, and to stay healthy!
Order a print copy in:
Type: Guide
Immunisation Schedule For Victorian Babies And Young Children
The Victorian immunisation schedule outlines the vaccines that are routinely provided free of charge to all Victorian children under the National Immunisation Program and the Victorian funded program. It also outlines the age at which each vaccination should be given. New vaccines against serious infections continue to be developed and the schedule might be updated in the future.
|
Influenza vaccine |
Fever, feeling unwell, muscle aches, injection site pain, redness and swelling |
Additional vaccines are given to children with certain medical risk conditions that put them at increased risk of complications from vaccine preventable diseases, such as:
- babies that are born prematurely or low birth weight
- children with chronic medical risk conditions. Talk with your doctor to see if your child should get extra vaccines.
Don’t Miss: What Can I Put On My Newborns Dry Scalp
When To Call Your Healthcare Provider
Serious reactions to vaccines are very rare. Call your healthcare provider or public health office if your child has unusual symptoms after vaccination.
Unusual symptoms may include:
- a fever above 40°C
- crying or fussing for more than 24 hours
- worsening swelling where the needle went in and/or
- unusual sleepiness.
You know your child best. If you notice anything that is not normal after a vaccination, check with your healthcare provider.
Which Vaccines Do You Recommend For Patients Planning On Starting A Family
First, aspiring parents should be up-to-date on all their childhood vaccines.
Rubella is one of the most important for a mother who wishes to become pregnant, because congenital rubella infection can cause many problems with a growing baby. This vaccine should be given before getting pregnant, as it is a live-virus vaccine and shouldnt be given to pregnant women.
“The antibodies generated by the flu shot will also circulate to the baby during pregnancy and protect the baby in early life.”
Read Also: What Is Considered A Fever For A Newborn
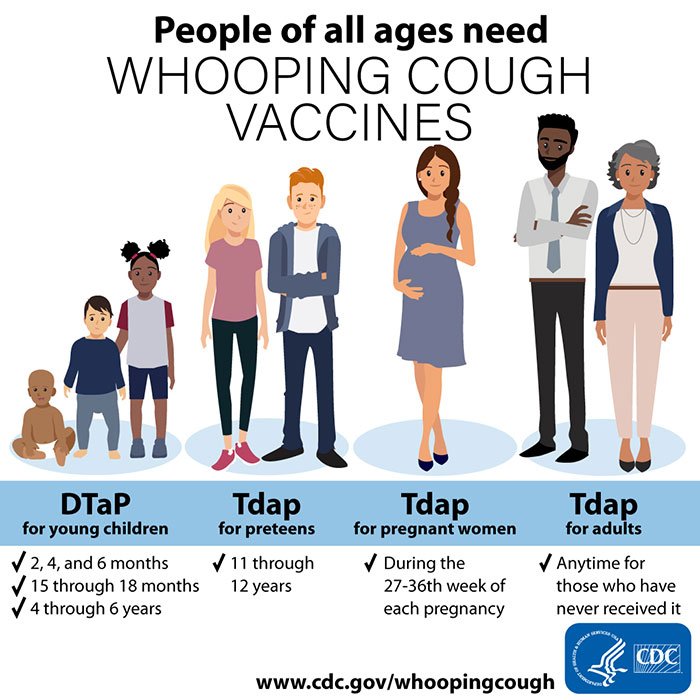
Diphtheria Tetanus And Pertussis
These vaccines have been given in combination since the late 1940s. The version used for babies is referred to as DTaP. It made sense to put these vaccines together, reducing three shots to one, because they are made in the same way, and they protect against these diseases in a similar way.
Diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis are each caused by bacteria that make people sick by producing harmful proteins, called toxins. These toxins act like poisons, causing illness. By using inactivated toxins, called toxoids, as the vaccine, people develop antibodies that protect them if they are infected.
Of these three diseases, a baby is most likely to be exposed to pertussis, and pertussis is also the most dangerous because it causes a narrowing of the windpipes that makes it difficult for babies to get enough oxygen when they experience repeated bouts of coughing. Pertussis tends to be under-diagnosed in older children and adults, who frequently transmit it to babies. Unfortunately, of these three vaccines, pertussis is also the one that is least effective. Nonetheless, those immunized with pertussis vaccine are seven times less likely to be infected during an outbreak than those who arent immunized.
Why Weren’t Children Included In The First Covid
Childrens immune systems are very different from those of adults, and their immune responses can vary according to their age, explains Dr. OLeary.
While a teenager may respond to a vaccine similarly as an adult, an elementary school-age child, a toddler or an infant could have a very different reaction. Thats why its so important to always hold clinical trials in kids separately.
The upcoming trials in children will go through two stages. The first stage will look at different dose levels specifically doses that are one-quarter, one-half or equal to the doses given to adults, explains Dr. Fernando. As a next step, those doses will then be tested against placebo injections.
About 24 percent of the U.S. population around 74 million people is under 18, and experts say getting kids vaccinated is key to ending the pandemic.
Its crucial to get these vaccine studies done in children, explains Dr. Fernando. In order to reach herd immunity the point where enough people have achieved immunity to the COVID-19 vaccine to stop its spread at least 70 to 80 percent of the entire population needs to be vaccinated. That means we absolutely have to include children.
Also Check: How Much Is Child Care For A Newborn
Community Immunity And Disease Prevention
The more people who are vaccinated in the community, the lower the risk of infection for those who:
- aren’t vaccinated
- developed only partial immunity from the vaccine
This means that when your child is vaccinated, you protect them as well as those around them.
Community immunity helps protect those at high risk of developing disease and severe complications or death, such as:
- adults 65 years of age and older
- infants and children too young to be fully vaccinated
- people with health conditions that affect their immune system, such as those undergoing chemotherapy to treat cancer
How Vaccines Are Given
Most vaccines are given by needle in the upper arm or thigh. Some vaccines, like the rotavirus vaccine, are given by mouth. There’s also a flu vaccine for children that’s sprayed into the nose.
Some vaccines are given separately. Others, like the MMR vaccine, protect against 3 diseases in one vaccine.
Your child’s immune system can learn from more than 1 vaccine at a time. For instance, babies can respond to 10,000 different antigens at any one time.
Recommended Reading: How Many Newborn Pajamas Do I Need
What Do You Suggest Expecting Parents Do If Family Members Are Hesitantor Outright Refuseto Get Vaccinated
I personally take a strong stanceif a family member is not willing to get vaccinated, I dont let them near my children until my kids have been adequately vaccinated and are a bit older .
The issue of vaccines should be brought up the same way that an expecting parent speaks to family members about other illnesses.
Just as you would ask them to wash their hands, check themselves for signs/symptoms of illness , anyone wanting to be close to a newborn should be willing to vaccinate themselves against infections that could seriously harm the baby.
Live Weakened Viral Vaccines: Mmr And Varicella
Four of the five vaccines given at this age are live, weakened viral vaccines, including measles, mumps and rubella in the MMR vaccine, and varicella, more commonly known as chickenpox. This means that immunity is the result of the vaccine virus replicating after the vaccine is given. Because the vaccine virus has been grown in the laboratory, it does not replicate as efficiently. The result is development of a robust immune response without actually being ill.
Because these vaccines rely on viral replication, the timing for their receipt has been carefully determined. Like threading a needle, public health officials have to, on one hand, protect babies before they are likely to be exposed, while on the other hand, delay vaccination until maternal antibodies are less likely to interfere with the development of immunity. This balance is one of the reasons healthcare providers were so scared during the recent measles outbreaks. They understand just how vulnerable their patients less than 1 year old are. Measles is one of if not the most contagious of infectious diseases, making it very adept at finding the non-immune among us.
Experience has also shown that people who received the chickenpox vaccine are less likely to develop shingles as adults. And if they do, their cases are less severe because the virus that is reactivating is the vaccine strain, which is less damaging.
Also Check: How To Help A Newborn With A Cold
