Is Nbs The Same For All Babies In The Us
Even though every state in the U.S. requires NBS, each state manages its own NBS program. This means that NBS can be a little different in each state.
For example, some states may give parents different options during screening, have different NBS costs, or look for different conditions during screening. It is important to be familiar with how NBS works in your state.
To learn about NBS in your state, visit the State pages.
Positive Effects Of Newborn Hearing Screening
The sense of hearing is the foundation for communication and promotes social interaction. Hearing is the key to learning spoken language and is important for the cognitive development of children. Hearing loss is a barrier to education and socialization especially when it goes undetected and untreated. A baby born with hearing loss that is not detected and treated early will not achieve the typical developmental milestones expected in the first months and years of their life.
Here is a look at typical developmental milestones and by clicking on the + button, you can see how unidentified hearing loss will affect the progress toward achieving them.
With newborn hearing screening & providing intervention very early in life, children born with hearing loss can develop speech and language skills that are appropriate for their age and can start their formal education in the same classroom as their normal hearing peers.
Do you want more information? Download the whitepaper from our friends at Oticon Foundation here:
Program Evaluation And Quality Assurance
Various quality indicators and benchmarks can be used to evaluate quality assurance and performance relative to screening and diagnosis, including the following :
- The number of newborns who complete screening by 1 month of age. The benchmark is 95%.
- The number of newborns referred for diagnostic audiologic evaluation. The benchmark is 4%.
- The number of newborns who did not pass the screening and went on to have a comprehensive diagnostic audiologic evaluation by 3 months of age. The benchmark is 90%.
- The percentage of infants obtaining amplification within 1 month of hearing loss confirmation for families choosing that option. The benchmark is 95%.
Other quality assurance indicators may include
- the number of follow-up appointments scheduled and recorded
- parent/guardian satisfaction with the process
- timeliness and accuracy of screening results and
- the capacity to analyze and report data.
States can also evaluate their programs as they report the statewide findings to the CDC. CDC data collection includes the number of
- live births
- newborns passing outpatient screening and
- newborns not passing outpatient screening in one or both ears.
Don’t Miss: Why Does Newborn Cry After Feeding
What Language And Communication Approaches Might Be Available For My Child
Children who are deaf or hard-of-hearing can learn to communicate in several ways. Find out as much as you can about the communication choices and ask your health care team to refer you to experts if you want to know more. Because language development begins early, regardless of the communication mode you choose, you should engage with your child and begin intervention as soon as possible.
Common approaches used to help children with hearing loss communicate and interact with others include:
- Listening and spoken language : works to strengthen listening, talking, and reading skills through the use of natural hearing and hearing devices such as hearing aids and cochlear implants, without the use of manual communication.
- Auditory-oral: emphasizes residual natural hearing in combination with amplification devices and technology to help children develop speech and spoken-language skills. It includes the use of speech reading and natural gestures in the communication process.
- Cued speech: is a system of specific hand shapes and placements that represent groups of consonants and vowels and that are used in combination with natural lip movements.
- American Sign Language: is a visual-manual, natural language that is used in the American Deaf community.
- Combined approaches: use aspects of various communication approaches, some of which are listed above, to expose children who are deaf or hard-of-hearing to many ways to communicate with others.
When To See Your Doctor

After leaving the hospital, observe your baby for any signs of health issues. If at any point your child shows symptoms , contact your doctor or 911 right away. Babies also have physical and mental milestones as they grow. Check with your doctor to ensure your child is meeting these.
Signs of metabolic disorders include:
- Vomiting or poor appetite.
- Difficulty gaining weight or weight loss.
- Sudden lack of movement, energy, or alertness.
Signs for critical CHDs include:
- Pale or bluish skin, lips, or fingernails.
- Trouble with breathing.
- Increased or decreased heart rate.
- Swollen or puffy, especially in face, hands, legs, or feet.
- Abnormal sweating.
- Poor appetite.
- Overly tired.
Even if your baby passed the initial hearing screen, he or she still could develop hearing problems. This is known as acquired or progressive loss. Symptoms of hearing loss include:
- Doesnt respond to loud noises.
- Responds to sight but not sound.
- Hears some sound tones but not others.
- Doesnt talk or make much noise.
- Slurred or mumbled speech.
- Asks you to repeat often.
- Listens to noise at a high volume.
Also Check: What Do Seizures Look Like In Newborns
Hearing Loss In Infants Is Usually The Result Of A Temporary Treatable Condition
The tests used in newborn hearing screenings are accurate however, they cant reveal what causes the inconsistent results. In most cases, a hearing losspositive result from the tests indicates an easily treatable problem like a fluid buildup, earwax blockage or ear infection. In other cases, doctors may never identify the cause. Infants with irregular test results will be directed to an audiologist or hearing specialist for a more in-depth examination.
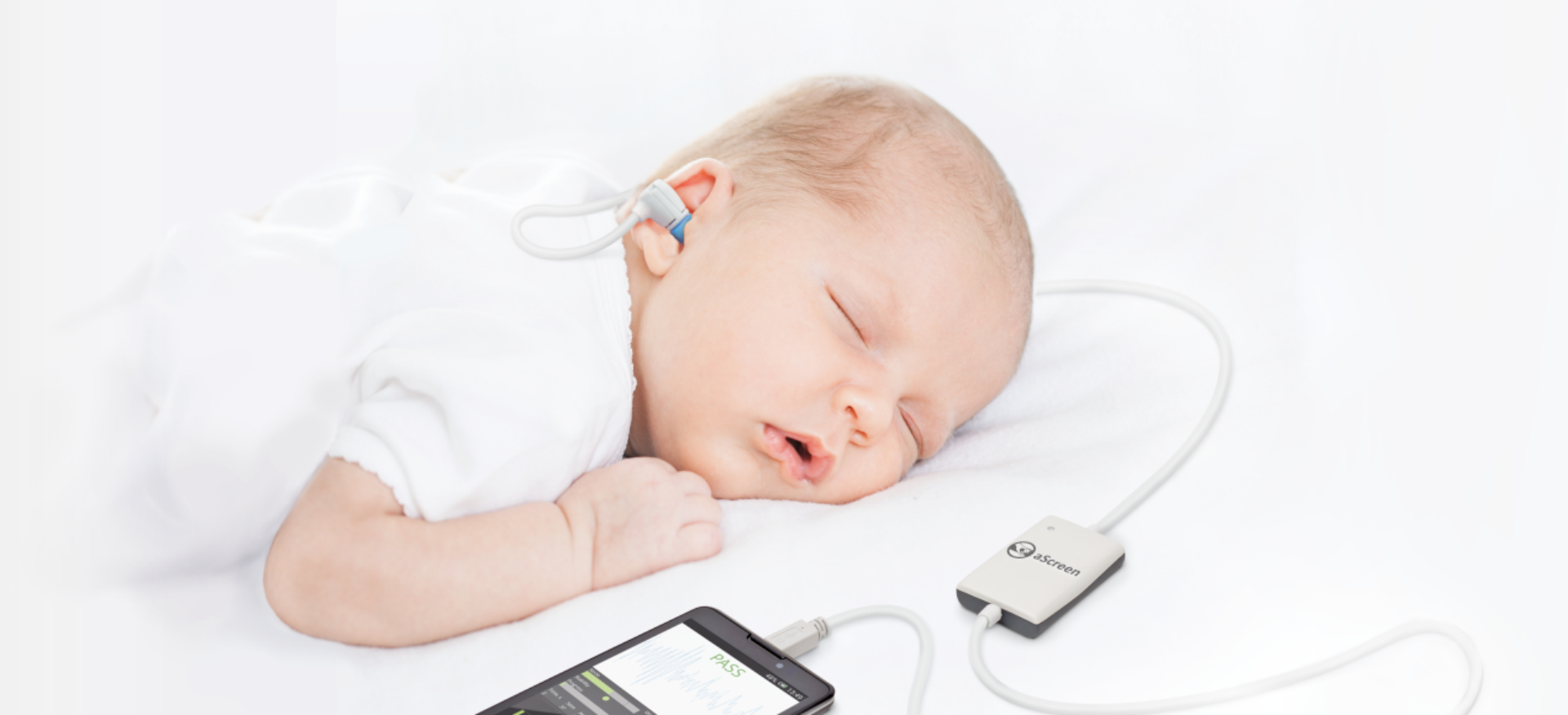
What Does The Screening Involve
A trained hearing screener carries out the hearing screening test. Two main tests are done to screen a newborn:
ABR The tester attaches leads to your baby’s forehead, back of their neck and behind their shoulder, using sticky pads. Small earphone ‘cups’ are then placed over the baby’s ears. The earphones make soft clicking sounds and the leads measure the response from your baby’s ears.
OAE A small soft-tipped earpiece is placed in the outer part of your baby’s ear, which sends clicking sounds down the ear. When an ear receives sound, the inner part, known as the cochlea, usually produces an echo. The screening equipment can pick up a response.
These tests only take a few minutes and do not hurt your baby. The hearing screening test will usually be done while your baby is asleep or settled. You can stay with your baby while the screening test is done.
You May Like: When Do Newborns Stop Crying So Much
Determining The Apgar Score
The first test your newborn will receive is the Apgar test. The doctor or nurse will complete this in the delivery room at the hospital. They usually test within 1 minute of birth, and again at 5 minutes. Based on those scores, they might test a third time at 10 minutes.
The Apgar test is named after Virgina Apgar, who created it in the 1950s. It also is an acronym for the tests measures. Your doctor or nurse will check 5 areas of your newborn babys health. He or she will score each area based on a scale of 0 to 2. A score of 2 is the highest and a score of 0 is the lowest. The 5 areas and ranges are:
- A Your babys skin color can range from pink to bluish-gray.
- P Your babys heart rate can be above 100 beats per minute , below 100 beats per minute , or absent.
- G This checks your babys facial and physical reflexes.
- A This checks your babys muscle tone.
- R This checks your babys breathing. The rate and effort can range from normal to slow to absent.
The total possible Apgar score is 10. Its very uncommon to get 10, at least on the first try. It takes most babies several minutes to warm up, regulate their breathing, and adjust to their new settings. A score of 7 or more is good. A score less than 7 means your baby might require additional care. He or she might need simple oxygen or heat. Most babies are healthy after Apgar testing.
What Is An Oae Evaluation
An otoacoustic emission test measures an acoustic response that is produced by the inner ear , which in essence bounces back out of the ear in response to a sound stimulus.
- The test is performed by placing a small probe that contains a microphone and speaker into the infant’s ear.
- As the infant rests quietly, sounds are generated in the probe.
- Once the cochlea processes the sound, an electrical stimulus is sent to the brainstem.
- In addition, there is a second and separate sound that does not travel up the nerve but comes back out into the infant’s ear canal. This “byproduct” is the otoacoustic emission.
- The emission is then recorded with the microphone probe and represented pictorially on a computer screen.
- The audiologist can determine which sounds yielded a response/emission and the strength of those responses.
- If there is an emission present for those sounds that are critical to speech comprehension, then the infant has “passed” the hearing screen.
- Testing generally takes about five to eight minutes.
You May Like: What Can I Give My Newborn Baby For Constipation
There Are Two Common Hearing Tests Used For Newborns
The first is called an Auditory Brainstem Response test, which measures a babys hearing nerve response using electrodes. The second is the Otoacoustic Emissions test, which uses a microphone and earphone to calculate an infants hearing abilities by measuring the reflection of a sounds echo as it passes through the ear canal.
Why Is Early Detection So Important
Nearly three of every 1,000 babies are born with some form of hearing loss. However, in most cases, hearing issues arent discovered in children until they are at least 2 years old. The first two years of a childs life are critical in physical development and forming emotional, learning and communication skills. Because of this, babies with moderate to severe hearing loss often experience major developmental setbacks.
Despite many years of developing and refining these hearing tests for babies just a few months old, studying infant hearing loss still presents many challenges. If youre a new parent preparing for a newborn hearing screening, there are several important factors and facts you need to know before your appointment.
Also Check: How Much Similac Can A Newborn Have
There Are Two Common Hearing Evaluations Used For Newborns
The first is called an Auditory Brainstem Response test, which measures the response of a babys hearing nerve using electrodes. The second is the Otoacoustic Emissions test, which uses a microphone and earphone to calculate an infants hearing abilities by measuring the reflection of a sounds echo as it passes through the ear canal.
Both tests are non-invasive and can be done while the baby sleeps naturally.
Auditory Brainstem Response Test
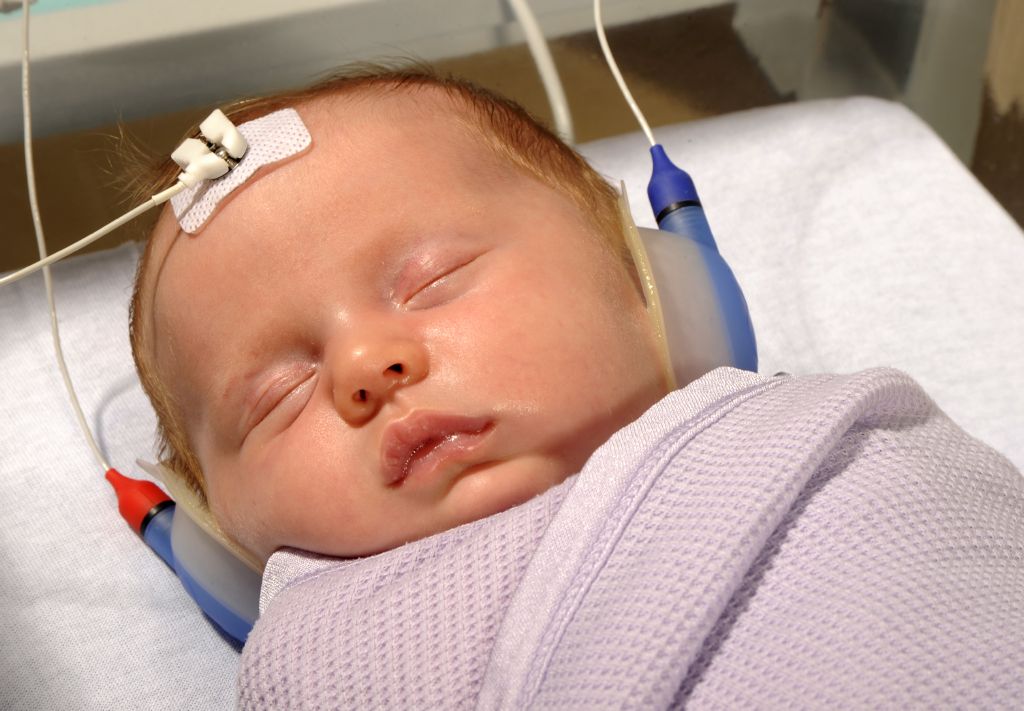
The auditory brainstem response test provides information about the inner ear and brain pathways for hearing. When conducting ABR tests, hearing specialists play sounds into the babys ears. Bandage-like electrodes are placed on the babys head to detect brain wave activity. This test measures how the hearing nerve responds to sounds and can identify babies who have a hearing loss.
During ABR tests, the infant being tested rests quietly or sleeps while the test is performed. In newborn screenings only one intensity or loudness level is checked, and the baby either passes or fails the screen.
Recommended Reading: How To Make Newborn Stop Crying
Why Is It Important To Screen For Hearing Loss In All Newborn Infants
Significant hearing loss is the most common disorder at birth. Approximately 1%-2% of newborns are affected.
Several national committees, including the National Institutes of Health, the American Academy of Otolaryngology/Head and Neck Surgery, and the American Academy of Pediatrics, have recommended that hearing loss in infants be identified, and when possible treated, prior to 6 months of age.
This recommendation is based on studies that have shown that children identified with hearing loss prior to 6 months of age have a better chance of developing skills equivalent to their peers by the time they enter kindergarten.
Children not identified until later may ultimately suffer from irreversible and permanent impairments in speech, language, and cognitive abilities when compared to their peers.
Prior to the implementation of hearing screen programs, it was customary to only test those newborns who had known significant risk factors for hearing loss. This group included infants whose mothers suffered from illness during pregnancy, those who had a family history of hearing loss, or those who were exposed to drugs known to affect hearing. In addition, infants with the following conditions were included for hearing screening:
However, despite the testing of all infants who fell into this “high-risk registry,” over half of all newborns with hearing loss were missed!
How Is The Newborn Hearing Test Done
The newborn hearing test is called the automated otoacoustic emission test. It takes just a few minutes.
A small soft-tipped earpiece is placed in your baby’s ear and gentle clicking sounds are played.
It’s not always possible to get clear responses from the 1st test. This happens with lots of babies, and does not always mean your baby has permanent hearing loss.
It could mean:
- your baby was unsettled when the test was done
- there was background noise
- your baby has fluid or a temporary blockage in their ear
In these cases, your baby will be offered a 2nd test. This may be the same as the 1st test, or another type called the automated auditory brainstem response test.
The AABR test involves placing 3 small sensors on your baby’s head and neck. Soft headphones are placed over your baby’s ears and gentle clicking sounds are played. This test takes between 5 and 15 minutes.
These tests will not harm your baby in any way.
You May Like: What Temperature Should A Newborn Bath Be
Older Babies And Children
- If you think a child might have hearing loss, ask the doctor for a hearing test as soon as possible.
- Children who are at risk for acquired, progressive, or delayed-onset hearing loss should have at least one hearing test by 2 to 2 1/2 years of age. Hearing loss that gets worse over time is known as acquired or progressive hearing loss. Hearing loss that develops after the baby is born is called delayed-onset hearing loss. Find out if a child may be at risk for hearing loss.
- If a child does not pass a hearing screening, its very important to get a full hearing test as soon as possible.
How Can I Help My Child With Hearing Loss Develop Language Skills
When interventions begin early, children with hearing loss can develop language skills that help them communicate freely and learn actively. The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act ensures that all children with disabilities have access to the services they need to get a good education. Your community may also offer additional services to help support your child.
Your babys health care team will help you find services and methods to overcome communication barriers. You may also be referred to a speech-language pathologist or a teacher who is experienced in working with children with hearing loss. Talk to and communicate with your child often and stay up-to-date with all health care appointments.
Also Check: How Does Custody Work With A Newborn
