Diagnosis Of Meningitis In Babies
Tests can confirm the diagnosis of meningitis and determine what organism is causing it. Tests include:
- Blood cultures. Blood removed from your babys vein is spread on special plates that bacteria, viruses, or a fungus grows well on. If something grows, thats probably the cause of the meningitis.
- Blood tests. Some of the blood removed will be analyzed in a lab for signs of infection.
- Lumbar puncture. This test isalso called a spinal tap. Some of the fluid that surrounds your babys brain and spinal cord is removed and tested. Its also put on special plates to see if anything grows.
- CT scan. Your doctor may get a CT scan of your babys head to see if theres a pocket of infection, called an abscess.
What Is Supportive Therapy For Meningitis
While your child is recovering from meningitis, other therapies may be initiated to improve healing and comfort, and provide relief from symptoms. These may include the following:
- Bed rest.
- Medications .
- Supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation may be required if your child becomes very ill and has difficulty breathing.
How Can I Manage My Child’s Symptoms
- Help your child rest as much as possible. A dark, quiet room may help if he or she has headaches. Talk to your child’s healthcare provider about when your child can return to school or daycare.
- Give your child liquids as directed. Your child may need extra liquids to help prevent dehydration. Ask how much liquid to give your child each day and which liquids are best for him or her.
Don’t Miss: How Many Diapers Do You Need For Newborn
How Is A Meningitis Infection Transmitted
The organisms that cause meningitis are usually spread by close contact with persons who may be carrying the infection, or by touching infected objects such as doorknobs, hard surfaces, or toys and then touching the nose, mouth, or eyes. The organisms may also be transmitted through respiratory secretions from a sneeze, close conversation, or by touching infected matter. The infection usually starts in the respiratory tract and then travels into the bloodstream where it can reach the brain and spinal cord. The organism may cause a cold, sinus infection, or ear infection , and then travel through the sinuses into the brain and CSF, although this method of transmission is less common. A child may have no symptoms at all, but may carry the organism in his/her nose and throat.
Causes & Risk Factors

Meningitis is usually caused by a bacterial or viral infection that invades the cerebral spinal fluid and inflames the meninges. Cerebral spinal fluid is the fluid within the open spaces of the brain that protects and cushions the brain and spinal cord. A fungus or parasite may also cause meningitis, but this is uncommon and usually occurs in patients with unique exposures or weak immune systems. The severity of a child’s symptoms and prognosis depend on the specific organism that is causing meningitis. Meningitis can occur in infants, children, and adults. Some bacteria and viruses are more common in certain age groups than others, including the following:
Bacteria that can cause meningitis :
In newborns and young babies, the most common bacteria include the following:
- Group B Streptococcus
- Escherichia coli
- Listeria monocytogenes
- Other Gram-negative enteric bacilli
In older babies and children, the most common bacteria include the following:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
Haemophilus influenzae type b Other bacterial infections that may cause meningitis include the following:
- Treponema pallidum
Viruses that commonly cause viral meningitis include:
- Enteroviruses
- Polioviruses
- Arboviruses
Parasites are uncommon causes of meningitis. Examples include:
Meningitis caused by a virus is more common and, with the exception of herpes simplex virus infection, usually less severe. Bacterial meningitis is usually more severe and may produce long-term complications or death.
Recommended Reading: When Do You Wash A Newborn
Can You Prevent Meningitis
Several vaccines are available to prevent some of the bacterial organisms that can cause meningitis, including:
- H. influenzae type b vaccine : given as a three or four-part series during your childs routine immunizations, starting at 2 months
- pneumococcal conjugate vaccine : recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics for all children younger than age 2 and children ages 24 to 59 months of age that are at very high risk for pneumococcal infection. PCV7 can be given along with other childhood vaccines at 2 months, 4 months, 6 months, and 12 to 15 months
- meningococcal vaccine: for meningococcal meningitis, a very contagious form of bacterial meningitis. This vaccine is normally given during the routine pre-adolescent immunization visit .
How Are These Infections Treated
People who are suspected of having meningitis or encephalitis should receive immediate, aggressive medical treatment. Both diseases can progress quickly and have the potential to cause severe, irreversible neurological damage.
Meningitis
Early treatment of bacterial meningitis involves antibiotics that can cross the blood-brain barrier . Appropriate antibiotic treatment for most types of meningitis can greatly reduce the risk of dying from the disease. Anticonvulsants to prevent seizures and corticosteroids to reduce brain inflammation may be prescribed.
Infected sinuses may need to be drained. Corticosteroids such as prednisone may be ordered to relieve brain pressure and swelling and to prevent hearing loss that is common in Haemophilus influenza meningitis. Lyme disease is treated with antibiotics.
Antibiotics, developed to kill bacteria, are not effective against viruses. Fortunately, viral meningitis is rarely life threatening and no specific treatment is needed. Fungal meningitis is treated with intravenous antifungal medications.
Encephalitis
Antiviral drugs used to treat viral encephalitis include acyclovir and ganciclovir. For most encephalitis-causing viruses, no specific treatment is available.
Autoimmune causes of encephalitis are treated with additional immunosuppressant drugs and screening for underlying tumors when appropriate. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, a non-infectious inflammatory brain disease mostly seen in children, is treated with steroids.
Read Also: How High Should Crib Mattress Be For Newborn
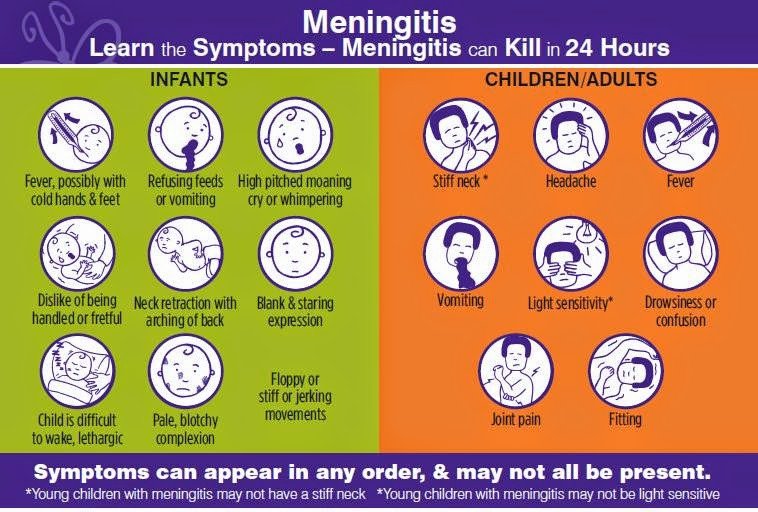
Symptoms Of Meningitis In Babies
Symptoms of meningitis often appear rapidly. At first, most parents only notice tiredness or irritability. But then the symptoms appear quickly and it is important to get your child medical attention right away. If your infant suddenly begins experiencing symptoms, it may be difficult to comfort them. They may be experiencing a variety of symptoms that they cant tell you about, so it is important to recognize the symptoms and when to get help.
Symptoms of meningitis in babies often include:
- Bulging in the babys soft spot, or fontanel
- Fever
- Infants who have a high fever may also experience seizures if they have meningitis
- Dark or red rash marks across the body
- Cold hands and feet but torso is warm
- Neck stiffness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Extreme sleepiness or difficulty waking
- Not being as active as usual
- Being more irritable than usual
- Poor feeding habits
With newborns, many symptoms are difficult to identify, such as headaches or nausea. However, many of the symptoms above can be readily identified by attentive parents or caregivers. It is important that any signs of infection are taken seriously and the baby is assessed by a doctor as soon as possible.
Can Meningitis And Encephalitis Be Prevented
People should avoid sharing food, utensils, glasses, and other objects with someone who may be exposed to or have the infection. People should wash their hands often with soap and rinse under running water.
Effective vaccines are available to prevent Haemophilus influenza, pneumococcal and meningococcal meningitis.
People who live, work, or go to school with someone who has been diagnosed with bacterial meningitis may be asked to take antibiotics for a few days as a preventive measure.
To lessen the risk of being bitten by an infected mosquito or other arthropod, people should limit outdoor activities at night, wear long-sleeved clothing when outdoors, use insect repellents that are most effective for that particular region of the country, and rid lawn and outdoor areas of free-standing pools of water, in which mosquitoes breed. Repellants should not be over-applied, particularly on young children and especially infants, as chemicals such as DEET may be absorbed through the skin.
Read Also: How Long Should A Newborn Baby Sleep
Etiology Of Neonatal Bacterial Meningitis
The predominant pathogens are
, and Streptococcus pneumoniae Streptococcal Infections Streptococci are gram-positive aerobic organisms that cause many disorders, including pharyngitis, pneumonia, wound and skin infections, sepsis, and endocarditis. Symptoms vary with the organ… read more .
Neonatal bacterial meningitis most frequently results from the bacteremia that occurs with neonatal sepsis Neonatal Sepsis Neonatal sepsis is invasive infection, usually bacterial, occurring during the neonatal period. Signs are multiple, nonspecific, and include diminished spontaneous activity, less vigorous sucking… read more the higher the colony count in the blood culture, the higher the risk of meningitis. Neonatal bacterial meningitis may also result from scalp lesions, particularly when developmental defects lead to communication between the skin surface and the subarachnoid space, which predisposes to thrombophlebitis of the diploic veins. Rarely, there is direct extension to the central nervous system from a contiguous otic focus .
What Problems Can Happen
Complications of bacterial meningitis might need extra treatment. Someone with shock or low blood pressure might get more IV fluids and medicines to increase blood pressure. Some kids may need extra oxygen or mechanical ventilation if they have trouble breathing.
Bacterial meningitis complications can be severe and include neurological problems, such as hearing loss, vision problems, seizures, and learning disabilities. Because impaired hearing is a common complication, those who’ve had bacterial meningitis should have a hearing test after they recover.
The heart, kidneys, and also might be affected, depending on the cause of the infection. Although some kids develop long-lasting neurological problems, most who get a quick diagnosis and treatment recover fully.
Read Also: How To Give Bath To A Newborn
How Contagious Is Meningitis
Several types of meningitis are not contagious. Fungal, parasitic and non-infectious meningitis are not contagious.
Viral meningitis is contagious. Its spread through direct contact with body fluids, including mucus, feces, and saliva. Droplets of infected fluid can be spread and shared with sneezing and coughing. You do not have to come into direct contact with an infected person to pick up this infection.
Bacterial meningitis, the most serious form of meningitis, can also be contagious, especially if its meningococcal meningitis. Its spread through extended contact with an infected person. Schools, daycare centers, military barracks, hospitals, and college dormitories are prime locations for sharing this infection. Some types of meningitis are spread through person-to-person contact but not all. Learn more about the types that are contagious and how you can avoid them.
Babies who develop meningitis may show different signs and symptoms of an infection than adults. These symptoms can include:
- fever
- irritable and grumpy
- doesnt feel well and has a weak suck during breastfeeding
Viral meningitis is common in infants. It develops as a result of colds, cold sores, flu, and diarrhea. The viruses that cause these common conditions also cause viral meningitis.
Meningitis becomes more common in children as they grow older and reach high school and college ages. Symptoms of viral and bacterial meningitis in children are very similar to symptoms in adults. These include:
Who Should Be Vaccinated Against Meningococcal Meningitis
These five groups are considered at risk and should get a meningitis vaccine:
- college freshmen who live in dorms and havent been vaccinated
- adolescents who are 11 to 12 years old
- people traveling to countries where meningococcal disease is common
- children ages 2 or older who dont have a spleen or who have a compromised immune system
Read Also: How Many Bottles Do You Need For Newborn
Sepsis Or Septic Shock
If meningitis is a result of an infection, it can cause sepsis. This is also known as blood poisoning which is also the body’s often deadly response to an infection or injury. Medical attention should be sought immediately when symptoms are noticed in order to improve the outcome for an infant with an infection like meningitis that can lead to sepsis.
They will also watch other end-organ function. An antimicrobial agent is often administered as treatment. In some cases, surgical intervention is also necessary.
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Meningitis
Meningitis symptoms vary, depending on the person’s age and the cause of the infection. The first symptoms can come on quickly or start several days after someone has had a cold, diarrhea, vomiting, or other signs of an infection.
Common symptoms include:
- skin rash
Meningitis in Infants
Infants with meningitis might have different symptoms. Babies might be cranky, feed poorly, and be sleepy or hard to wake up. It may be hard to comfort them, even when they’re picked up and rocked. They also may have a fever or bulging fontanelle .
Other symptoms of meningitis in babies can include:
- jaundice
- stiffness of the body and neck
- a lower-than-normal temperature
- a high-pitched cry
Read Also: What Things Needed For Newborn Baby
Symptoms Of Group B Strep Among Mothers
Most mothers do not know that they have Group B Strep. In fact, doctors say that around 40% of women carry Group B Strep in the lower intestines, rectum and vagina without even knowing it. There are no symptoms that indicate that the mother has the bacteria in her system these women are called asymptomatic carriers. Women who do have symptoms may experience more frequent urinary tract infections , blood infections or pneumonia.
Vaccines To Prevent Meningitis
Vaccines that help protect against meningitis include those that protect against:
- Measles
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Hib
Avoiding exposure to infections is also crucial. Donât let anyone who has an infection touch your baby or get near your baby. Maintain hygiene, such as hand washing before you touch your baby and before you touch their food. Be sure that fresh food is washed thoroughly before your baby eats it.
Also Check: How To Add Newborn To Bcbs Insurance
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
The diagnosis of neonatal meningitis can be a devastating one. However, today mortality is lower, due to aggressive treatment with antibiotics, antiviral, and advanced neonatal medicine. An interprofessional team approach including physicians, nurses, pharmacists, and caseworkers can help not only treat the patient but the parents as well. Neurologic sequelae that can result will require, in many cases, lifelong care. Over his or her lifetime, they will need physical therapy, cognitive therapy, medication, and social support. This will center on the childs primary pediatrician, who can coordinate therapies and specialist consultations, including neurology, and if the sequelae are severe enough, home health care.
There are clinical decision rules to help determine which children should be admitted and who can be safely discharged. The Bacterial Meningitis Score, which can identify very low risk patients, has been tested and reaffirmed in several studies and shows it can help decrease costs and increase patient safety by decreasing unnecessary, and possibly harmful, treatments and testing. However, it cannot be used in the less than 60-day-old age group, as there has been uncertainty regarding its validity in this population.
