Are There Any Reasons Not To Vaccinate My Child
Yes. There are times when some children should not get certain vaccines, or they should wait. For example, if your child has any severe, life-threatening allergies, theyve had an allergic reaction after a previous dose of vaccines, or theyre moderately or severely ill, their doctor may recommend not getting or delaying a specific vaccination.
When it comes to getting your child vaccinated against COVID-19, you dont need to delay vaccination unless you, your child or someone in your household is experiencing COVID-19 symptoms.
While staying on track with all immunizations is important, making sure your child has their annual flu shot will be especially important this year. Now that many COVID-19 health and safety guidelines have been removed, your child will likely be spending more time close to others indoors where flu viruses can thrive during cold and dry winter weather. Flu shots are typically available starting in early September.
Watch Out For Meningitis And Septicaemia
Both meningitis and septicaemia are very serious. It is important that you recognise the signs and symptoms and know what to do if you see them. Early symptoms of meningitis and septicaemia may be similar to a cold or flu .
However, people with meningitis or septicaemia can become seriously ill within hours, so it is important to act fast.
Meningitis
Meningitis is an infection of the lining of the brain. Meningitis can be caused by several types of bacteria including pneumococcus, meningococcus and Haemophilus influenzae or by viruses.
The bacteria that cause meningitis and septicaemia , can also cause pericarditis and arthritis and other serious infections.
In babies, the main symptoms of meningitis may include:
- a high-pitched, moaning cry
- being irritable when picked up
- a bulging fontanelle
- feeling drowsy and not responding to you, or being difficult to wake
- being floppy and having no energy
- stiff with jerky movements
- refusing feeds and vomiting
- having skin that is pale, blotchy or turning blue
- diarrhoea and stomach cramps
The glass test
Press the side of a clear drinking glass firmly against the rash so you can see if the rash fades and loses colour under pressure. If it doesnt change colour, contact your doctor immediately.
Further information
The following charities provide information, advice and support:
Meningitis Research Foundation
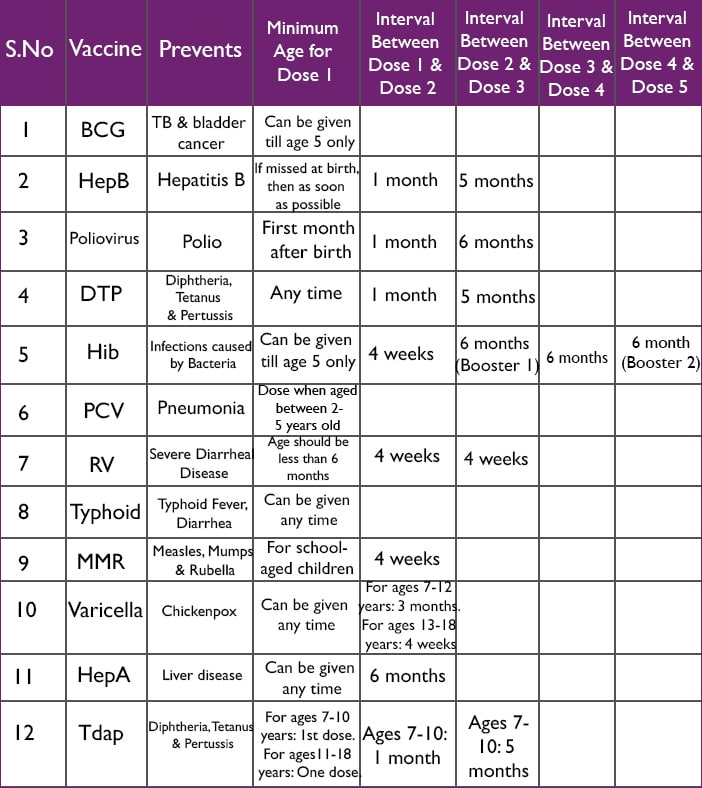
How Many Vaccines Do Children Get
By the age of 15 months, your baby may receive up to 10 different types of vaccines. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends all healthy babies receive these initial vaccines. Your child may receive additional doses and other vaccines between the ages of 15 months and 16 years old. If your child has a chronic condition or a weakened immune system, their pediatrician may recommend a different schedule.
You May Like: What Does A Newborn Baby Really Need
How Does Chickenpox Spread
Chickenpox spreads easily from people with chickenpox to others who have never had the disease or never been vaccinated. Chickenpox can also spread from people with shingles.
The disease spreads mainly through close contact with someone who has chickenpox or shingles. For example, it can spread when a person touches or breathes in the virus particles that come from the blisters when they get scratched.
Chickenpox can spread 1 to 2 days before the infected person gets a rash, and then doesnt stop spreading until all the blisters have formed scabs. Vaccinated people who get chickenpox may develop lesions that do not form scabs. These people are considered contagious until no new lesions have appeared for 24 hours.
Chickenpox is very contagious. If one person has it, about 9 out of 10 people close to that person who are not protected against chickenpox will also become infected.
Importance Of Vaccines For Infant And Toddlers
For newborns, breast milk can help protect against many diseases. However, this immunity wears off after breastfeeding is over, and some children arent breastfed at all.
Whether or not children are breastfed, vaccines can help protect them from disease. Vaccines can also help prevent the spread of disease through the rest of the population through herd immunity.
Vaccines work by imitating infection of a certain disease in your childs body. This prompts your childs immune system to develop weapons called antibodies.
These antibodies fight the disease that the vaccine is meant to prevent. With their body now primed to make antibodies, your childs immune system can defeat future infection from the disease. Its an amazing feat.
Also Check: How To Let Newborn Sleep At Night
What Are Some Common Side Effects Of 4 Month Shots For Babies
Shots are not fun for babies but luckily babies wont remember getting them! You can prepare yourself by knowing that this kind of health protection might have some mild, common side effects.
Remember, side effects happen because your babys immune system is triggered to build itself by the vaccination. Shots at any age cannot cause the disease they are protecting from.
Normal side effects of 4-month shots in babies include:
- redness or swelling where the shot was given
- pain or tenderness around the shot area
- irritability or fussiness
Some kinds of medications like steroids can also temporarily weaken the immune system. Your pediatrician may delay 4-month shots if your baby is on steroids or other medications.
Reasons Why Your Baby Should Not Be Immunised
There are very few reasons why babies cannot be immunised.
Vaccines should not be given to babies who have had:
- a confirmed anaphylactic reaction to a previous dose of the vaccine
- a confirmed anaphylactic reaction to neomycin, streptomycin, or polymyxin B
In general, children who are immunosuppressed should not receive live vaccines. Children who are immunosuppressed include those:
-
whose immune system does not work properly because they are undergoing treatment for a serious condition such as a transplant or cancer
-
who have any condition which affects the immune system, such as severe primary immunodeficiency. Primary immunodeficiencies are very rare diseases that mean you are more likely to catch infections. They are usually caused by a faulty gene and are diagnosed soon after birth
If this applies to your child, you must tell your doctor, practice nurse or health visitor before the immunisation. They will need to get specialist advice on using live vaccines such as MMR, rotavirus vaccine and Bacillus CalmetteGuérin vaccine . There are no other reasons why vaccines should definitely not be given.
You May Like: How To Flea Bomb A House With A Newborn
When Should My Child Get Immunized
Your child should receive their first doses of most vaccines during their first two years of life. They may need several doses of the vaccines to reach full protection. For example, the CDC recommends children receive their first dose of the measles, mumps and rubella vaccine at 12 months of age or older. They should then receive a second dose before entering elementary school . Your baby can get their childhood vaccines at their regularly scheduled well-baby checkups.
Your Babys First Shot
Shortly after birth, your baby should receive the first dose of the vaccine to help protect against the following disease:
All babies should get the first shot of hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth.
This shot reduces the risk of your baby getting the disease from you or family members who may not know they are infected with hepatitis B.
If you have hepatitis B, your baby should get the first shot of hepatitis vaccine within 12 hours of birth. Theres additional medicine that can help protect your newborn against hepatitis B its called hepatitis B immune globin . HBIG gives your babys body extra help to fight the virus as soon as your baby is born.
Read Also: What Is A Heart Murmur In A Newborn
What Are The Different Types Of Vaccines
The following vaccines can help protect your child from serious infection or disease.
Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B vaccine can help protect your child against hepatitis B. The newborn vaccine schedule includes three doses of the HepB vaccine. Your newborn will generally receive their first dose within 12 hours of birth. Theyll receive their second dose at 1 to 2 months of age and their third dose between 6 and 18 months of age. Slight variations in this schedule are possible based on the birthing parents hepatitis B surface antigen status and the potential use of combination vaccines.
Rotavirus
The rotavirus vaccine can help protect your child against rotavirus. Rotavirus is a viral infection that can cause fever, vomiting and diarrhea. Your child will receive the rotavirus vaccine in two or three doses, starting at age 2 months.
Diphtheria, tetanus and acellular pertussis
The DTaP vaccine can help protect your child against diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis. Baby vaccines include five doses of the DTaP combination vaccine. Your baby will receive their first dose at 2 months of age and their second at 4 months of age. Theyll receive their third dose at 6 months, their fourth dose between 15 and 18 months of age and their fifth dose between 4 and 6 years of age.
Haemophilus influenzae type b
Pneumococcal conjugate
Inactivated poliovirus
Influenza
Measles, mumps and rubella
Varicella
Hepatitis A
Human papillomavirus
Meningococcal
Other vaccines
Texas Newborn Screening Program
Often referred to as the heelstick because blood is taken from the babys heel, these panels screen for diseases that range from common, such as sickle cell or cystic fibrosis, to much less common, such as phenylketonuria or congenital hypothyroidism. As of 2015, Texas program includes 53 diseases on its panel.
The first test is performed 24 to 48 hours after birth, and a second at one to two weeks at the pediatric care providers office. As with any screen, the goal is to find as many babies at risk as possible. When we detect these conditions early, it allows us to provide appropriate medical care such as altering the diet or providing medicine.
Its important to keep in mind that a positive screen will need to be confirmed with more specific testing.
Read Also: Why Newborn Fussy At Night
Children In Licensed Daycare Centres
If you want your child to attend daycare, and decide not to vaccinate them due to medical, religious or philosophical reasons, you will need to give your daycare a valid written exemption. If the disease appears in your childs daycare centre, your child may have to stay out of daycare until the disease is no longer present.
Why Children Are Vaccinated At Such A Young Age
Children are vaccinated at a very young age because this is when they are most vulnerable to diseases. At this point their immune system is not developed enough to be able to fight serious infections.
The vaccination schedule is based on infants’ ability to create an immune response. Vaccines are given to protect them against 14 serious diseases at a time when they are most at risk.
Medical experts do not advise delaying or spreading out the recommended vaccines. This does not provide any added benefit to your child.
Read Also: Can You Overfeed A Newborn Formula
Immunisations Your Baby Will Have At 8 12 And 16 Weeks
At 8 weeks, your baby will have immunisations against:
- Haemophilus influenzae type b
- meningococcal group B disease
These will be given as 2 injections and drops into the mouth.
At 12 weeks, your baby will have immunisations against:
These will be given as 2 injections and drops into the mouth.
At 16 weeks, your baby will have immunisations against:
These will be given as 2 injections.
If Your Child Can’t Be Vaccinated
Some children may not be able to get some vaccines, including those with:
- specific medical conditions
- severe allergic reactions to vaccine ingredients
Examples include children who need to take high-dose steroids or who have a weakened immune system from cancer treatment . These children may need to avoid vaccines that contain a weakened live virus, such as measles, mumps, rubella and chickenpox.
These children are at risk of getting the disease that the vaccine would have prevented.
Talk to your health care provider or local public health authority if you have any concerns about your child’s health status and vaccines.
If your child can’t be vaccinated, you can help protect them by encouraging others to get vaccinated. This will help prevent the spread of disease to your child.
You May Like: Why Is My Newborn Peeling
A Guide To Immunisations For Babies Born On Or After 1 January 2020
This publication is licensed under the terms of the Open Government Licence v3.0 except where otherwise stated. To view this licence, visit nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence/version/3 or write to the Information Policy Team, The National Archives, Kew, London TW9 4DU, or email: .
Where we have identified any third party copyright information you will need to obtain permission from the copyright holders concerned.
This publication is available at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/a-guide-to-immunisations-for-babies-up-to-13-months-of-age/a-guide-to-immunisations-for-babies-born-on-or-after-1-january-2020
Is Your Baby Protected From Vaccine
Your baby will be given a handful of vaccines and supplements in the first months of life. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends the carefully-planned childhood vaccine schedule. Following the schedule in the coming months and years will put your infant on track for life-long immunity to dangerous diseases.
The vaccines recommended for your young baby are closely monitored by the CDC and the Food and Drug Administration for safety and effectiveness. Here are the vaccines that your baby will receive from birth through two months.
Don’t Miss: How Much Enfamil Should A Newborn Drink
Are Some Babies Allergic To Vaccines
Very rarely, children can have an allergic reaction soon after immunisation. This reaction may be a rash or itching affecting part or all of the body. The doctor or nurse giving the vaccine will know how to treat this. It does not mean that your child should stop having immunisations.
Even more rarely, children can have a severe reaction, within a few minutes of the immunisation, which causes breathing difficulties and can cause the child to collapse. This is called an anaphylactic reaction. A recent study has shown that there is only 1 anaphylactic reaction in about a million immunisations.
An anaphylactic reaction is a severe and immediate allergic reaction that needs urgent medical attention.
The people who give immunisations are trained to deal with anaphylactic reactions and children recover completely with treatment.
Baby Vaccine Schedule: Recommended Immunizations For Children Ages 0 To 18 Months
When do babies get their first shots? Staying on track with childhood immunizations starts early, with immunizations beginning at birth and coinciding with baby and child wellness schedules.
Remember, baby and child vaccination schedules are made with young immune systems in mind. If you have specific questions about when or why specific childhood vaccines are recommended for your newborn baby, infant or toddler, talk with your childs doctor.
An overview of immunizations for newborns to 18-month-olds
Don’t Miss: Do Newborns Sleep A Lot
How Many Times Do Newborns Nurse A Day
Newborn babies should breastfeed 812 times per day for about the first month. Breast milk is easily digested, so newborns are hungry often. Frequent feedings helps stimulate your milk production during the first few weeks. By the time your baby is 12 months old, he or she probably will nurse 79 times a day.
When Do Babies Lose Their Body Hair
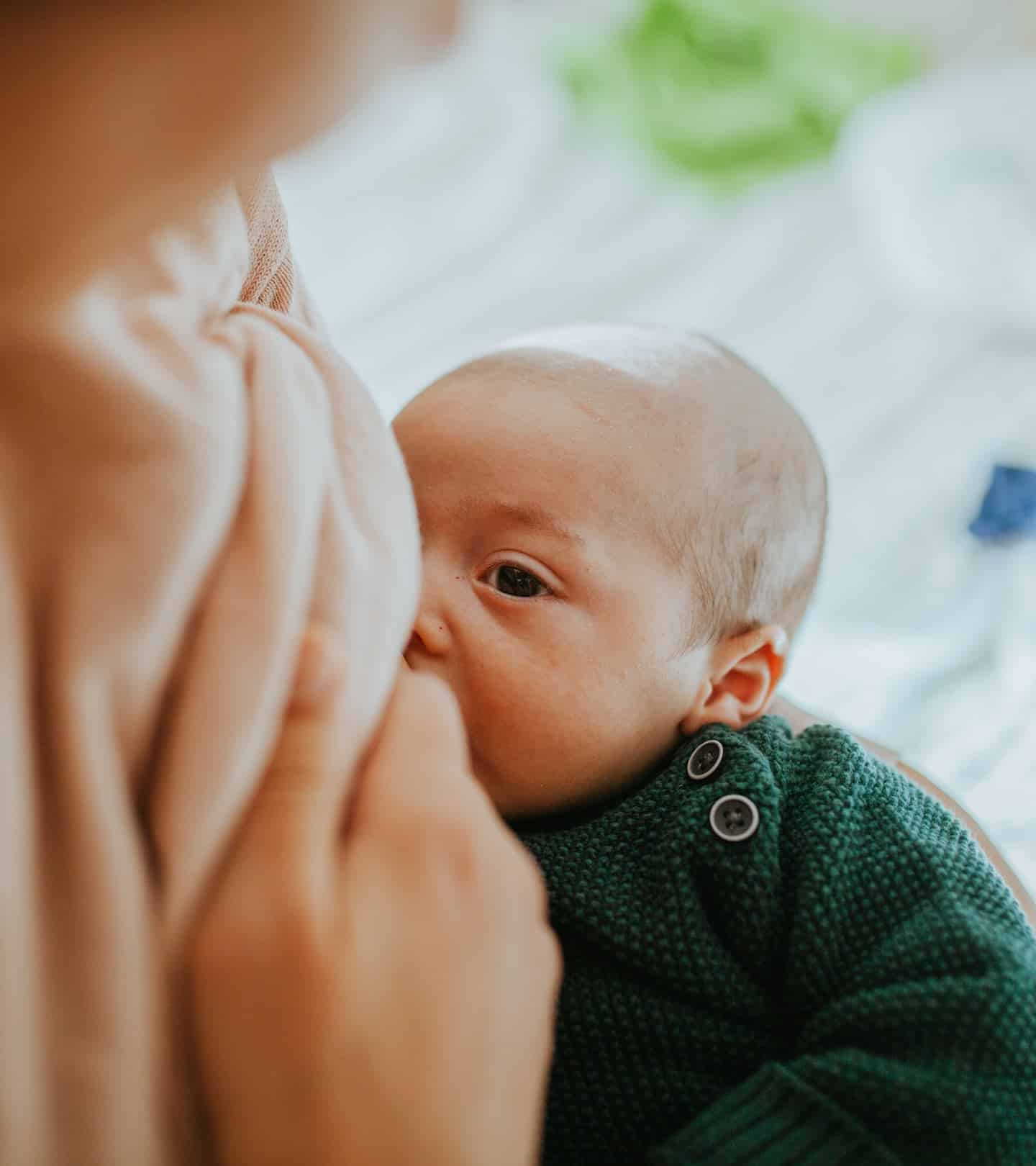

This thin, soft hair, called lanugo, is common: All fetuses grow it in the womb. It usually disappears by 36 to 40 weeks gestation, which explains why babies born early are especially likely to have it. Rest assured that the hair will fall out on its own by the time your baby is 4 months old.
Read Also: How Do I Get My Newborns Ssn
Why Should Parents Feel Confident About Vaccinating Their Babies
I understand that parents hear lots of scary things about vaccines. I know they see things on the internet, they hear scary stories from friends. I just want to reassure them that the evidence that we have overwhelmingly shows that vaccines are safe and effective, and they are by far the best way to protect children from disease. And so parents can be reassured that their healthcare provider is really doing whats best for their children when they vaccinate them.
What Is The Childhood Immunization Schedule
The childhood immunization schedule, or childhood vaccine schedule, is the list of common vaccines the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends most children should receive. Immunization is a way to protect your child from getting many different infections and diseases. Many of these illnesses spread easily from child to child and can cause serious health problems. They can even cause death.
Read Also: How To Take Newborn Pictures
Health And Development Checks
Your baby’s health checks are very important â they are an opportunity to check that your baby is developing properly.
They are usually carried out by your health visitor either at home or in your GP surgery, baby clinic or children’s centre. These development checks are also a good opportunity for you to raise any concerns you might have.
Your baby’s very first health check takes place shortly after they are born, and they’ll continue until your child is 2 to 2 1/2 years old.
Vaccinations And Newborn Screening Tests
One of the best ways to protect your baby against diseases like measles, rubella, tetanus and meningitis is through immunisation. Your baby needs their first injections at eight weeks, then 12 weeks, 16 weeks and one year.
Vaccinations are offered free of charge in the UK â just book your appointments with your GP. Remember, as well as protecting your own baby, you’re also protecting other babies and children by preventing the spread of disease.
Don’t Miss: What Can You Feed Newborn Puppies
