How To Diagnose Low Blood Sugar In Newborns
Newborns will have blood tests to know the sugar level for a few hours. A heel stick is used for this. The healthcare professionals will keep continuing the test until the glucose level comes to normal for nearly 12 to 24 hours.
Some other tests may include screening for metabolic disorders and urine tests.
How Is Low Blood Sugar In A Newborn Managed
Neonatal hypoglycemia can usually be reversed through certain medical procedures. The treatment options available are usually based on the severity of the condition, and the feeding habits of the newborn.
Most commonly, the condition can be treated through feeding. Usually, the doctor will advise you to feed the baby frequently on breast milk. At the same time, you need to keep your baby close to you as often as you can. This will encourage the baby to feed more, and will also help to keep the baby warm and counter hypoglycemia.
In some cases, the baby may experience trouble latching onto the mother’s breasts. This should not be a cause for alarm as the baby can be fed through the mouth or nose, using a tube. The baby will be fed on a mixture containing sugar to correct the situation. Severe cases may prompt the doctors to feed the child through injections.
In cases where the mother is unable to breastfeed the baby for any reason, the baby can still use other feeds as advised by the nurses.
Sometimes, the baby may be getting enough breastmilk, but still have low blood sugar levels. In such instances, the baby may need to be fed on top up formula milk.
If this still fails to work, or the condition keeps recurring, then your baby will need to be tested for other medical conditions that may be making the blood sugar levels drop. Then the doctors will find a way to treat the root medical condition or disease.
Causes And Risk Factors
Babies get glucose from their mothers through the placenta before they are born. After birth, their sources of glucose are breast milk and formula. Glucose is also produced in the liver. Blood sugar may drop when there is too much insulin , if the baby is not producing enough or using too much or if the baby is unable to feed.
Some newborns have certain risk factors that make it easier for them to develop neonatal hypoglycemia. These may include:
- Being born too early
If your newborn is experiencing any of these symptoms, talk to the nurses and healthcare providers about blood tests. Even if the newborn does not have symptoms and you know there are risk factors, it’s still best to discuss these with your healthcare provider.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Your Newborn To Sleep In Crib
What Is The Best Thing To Eat If You Have Low Blood Sugar
Candy. When hypoglycemia occurs, patients should follow the 15-15 rule. Fresh or dried fruit. Fruits that provide the appropriate amount of carbohydrates include half a banana, 15 grapes, two tablespoons of raisins or a small apple or orange. Fruit juice. Fruit juice can also boost blood sugar levels. Fat-free milk.
How Long Will Blood Glucose Checks Or Additional Treatments Be Needed
Blood glucose levels usually get back to normal within 12 hours to 72 hours of birth, especially once your baby is feeding regularly.
Its rare for full-term babies to continue having trouble with their blood glucose levels. If this happens beyond 24 hours, your babys doctor may want to do more tests.
Also Check: Why Is My Newborn Constantly Crying
Erythroblastosis Fetalis And Beta
Although maternal diabetes is themost common cause ofhyperinsulinism in the newborn, postnatal insulinsecretion may be abnormal due toseveral other disorders. Infants whohave erythroblastosis fetalis haveincreased levels of insulin and anincrease in the number of pancreaticbeta cells. The mechanism for thisdevelopment is unclear, but onepossibility is that glutathione releasedfrom hemolyzed red cells inactivatesinsulin in the circulation, whichtriggers more insulin secretion andupregulates the beta cells. Exchangetransfusions may exacerbate theproblem because transfused bloodusually is preserved with acombination of dextrose and other agents.During the exchange, the infantreceives a significant glucose load,with subsequent exaggerated insulinresponse from the hyperplasticpancreas. At the end of the exchange,the rate of dextrose administrationreturns to baseline, but insulin levelsremain elevated, leading to furtherhypoglycemia.
Use of beta-agonist tocolyticagents such as terbutaline also isassociated with hyperinsulinemia inthe newborn, especially if the agentwas used for more than 2 weeks andwas discontinued less than 1 weekprior to delivery. Affected infantsalso appear to have reducedglycogen stores, which further aggravatesthe hyperinsulinemia and its effectson decreasing glucoseconcentrations.
Treatment For Neonatal Hypoglycaemia
Management of Hypoglycaemia in newborns is diverse and can range from the simple task of feeding to surgical intervention. Some of the treatments include:
- Adequate and timely feeding, assessing the consciousness levels and seeking early medical help is one approach to take before admitting the baby to a hospital.
- Initial stabilization and supportive care include supplemental oxygen, intravenous access and monitoring of the babys vitals.
- Intravenous 5 or 10 per cent dextrose solution may be administered to severely ill babies or in recurrent cases.
- Anti-Epileptic drugs may be necessary for recurring or refractory seizures.
- Surgical removal of a part of the pancreas may be suggested for congenital hyperinsulinism.
You May Like: How Many Ounces Of Formula For A Newborn
How Is Hypoglycemia Treated
Treatment depends on the cause of your infant’s hypoglycemia. Feed your infant often to help increase his or her glucose level. Your infant may also need to be given glucose through an IV at a hospital. An IV is a small tube placed in your infant’s vein that is used to give him or her medicine or liquids. Some infants may also need to be fed a special diet. Infants with ongoing hypoglycemia may need medicine to manage the hypoglycemia. If medicine does not work, a small or large part of the pancreas may need to be removed. The pancreas is the organ that produces insulin.
Is Low Blood Sugar In Newborns Common
Approximately about 15% of newborns are suffering from low blood sugar levels called neonatal hypoglycemia in medical terms. And this is the only condition that can be prevented to stop the brain damage in infants. Let us have a look at what causes low blood sugar levels in newborns and how low blood sugar in newborns can be addressed.
Also Check: What Time Should A Newborn Go To Bed
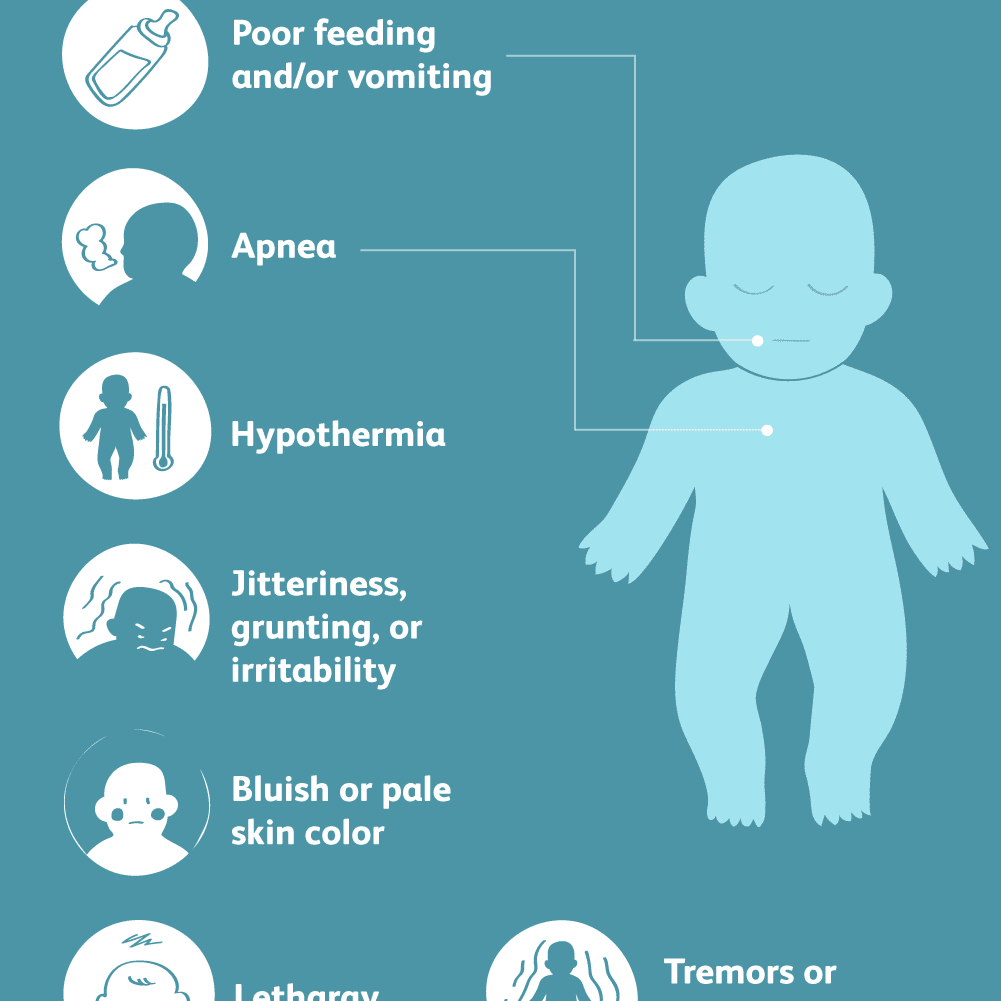
Signs Of Low Blood Sugar In Newborns
Newborns with low blood sugar will usually not show any symptoms or signs. If the baby is born with one of the above risk factors then nurses will check the babys blood glucose levels even if symptoms do not persist.
Usually below are the signs to check for
- Pale or blue-colored skin
- Breathing issues like paused breathing , grunting sound while breathing and fast breathing
- Listlessness or irritability
- Issues in keeping the warmth of the body
- Shakiness, tremors, seizures, and sweating
Regular Blood Sugar Check For Newborns
Generally, healthy full-term babies do not need to blood sugar checks. Their bodies have enough glucose stored in their liver for energy. It lasts until the newborn starts break feeding well. Some babies who need routine blood sugar checks are:
- Babies who are small or large for their gestational age
- Babies with rare medical conditions
- Premature babies born more than three weeks before their expected due date
- Babies whose mothers have either pre-existing diabetes or develop gestational diabetes
- Monitoring blood sugar levels in those levels helps in the diagnosis of hypoglycemia and immediate treatment.
Blood sugar levels of less than 30 mg/dL in the first 24-hours of birth and less than 45 mg/dL after that for the next three to four days show that your baby has hypoglycemia. Checking Plasma glucose also helps in diagnosing neonatal hypoglycemia. There is a need to do the estimation based on the underlying cause:
- Preterm and a lesser gestational age infant: 1, 6, 12, 24, 36, 48 hours and third and fourth day.
- Infant of a diabetic mother: 1, 2, 4, and 6 hours of life.
- Infants with erythroblastosis fetalis: after the exchange of transfusion with blood intermixed with citrate phosphate dextrose.
You May Like: How Often Do You Bathe A Newborn
Transient And Persistent Neonatal Hypoglycemia
There are two different types of neonatal hypoglycemia, transient and persistent . Babies who have transient NH typically have a deficiency of glycogen stores at birth. This is common in babies that are born premature, who are small for gestational age, or experienced birth asphyxia. Transient NH babies also may experience hyperinsulinism, which occurs most often in babies born to diabetic mothers .
Neonatal hypoglycemia can also occur if an IV infusion of glucose is interrupted for example, if the umbilical catheter is incorrectly positioned or the baby has sepsis. If the baby experiences NH due to an error of medication administration, this is medical malpractice.
Reasons Of Isogenic Neonatal Hypoglycemia

The most common reason of isogenic neonatal hypoglycemia are:
Recommended Reading: How Much Will A Newborn Sleep
Can Low Blood Sugar Hurt My Baby
An occasional hypoglycemic episode during pregnancy likely wont cause any harm to you or your baby. When its frequent, there can be problems. The brain needs glucose to receive messages from the body and interpret them. In severe cases in women with diabetes, hypoglycemia can lead to seizures, coma, and even death.
Latest Healthy Kids News
HealthDay Reporter
TUESDAY, Aug. 8, 2017 — Low blood sugar affects about one in six newborns, and new research suggests it could lead to brain difficulties in childhood.
Babies who experience low blood sugar at or near birth are at least two to three times more likely to face problems with planning, memory, attention, problem-solving and visual-motor coordination by the age of 4.5, New Zealand researchers said.
The low blood sugar did not affect general thinking function or IQ, but it did affect problem-solving and other skills known as “executive functioning,” and also eye-hand coordination, the findings showed. These are crucial for many tasks, said study leader Chris McKinlay. He is a neonatologist at the Liggins Institute at the University of Auckland.
“We don’t know fully what this means for learning,” McKinlay said. “We think this may have an effect on educational achievement.”
Low blood sugar in newborns, known as “neonatalhypoglycemia,” is the most common preventable cause of brain damage in infancy. Those at risk of low blood sugar include babies born prematurely, those small or large for their gestational age, and those born to mothers with diabetes.
For these high-risk infants, it is common to do a blood glucose test, using a heel prick. If the level is too low, the child can be treated with a form of sugar to return it to normal levels.
The study was published online Aug. 7 in JAMA Pediatrics.
Don’t Miss: When Do Newborns Start Sleeping Better
What Increases My Infant’s Risk For Short
- Your infant was born earlier than expected .
- Your infant was born at a low birth weight and length.
- Your infant’s body makes too much insulin. Insulin is a hormone that moves glucose out of the blood stream and into the cells to be used for energy. This condition is called hyperinsulinism.
- You have diabetes or had toxemia while you were pregnant.
Do All Newborn Babies Need Blood Glucose Checks
Healthy full-term babies do not need blood glucose checks. They have enough stored energy to last them until breastfeeding is going well. Babies who are not well will need blood glucose checks and other tests.
Some babies are more at risk for low blood glucose. Babies who need routine glucose checks include:
- Preterm babies born more than 3 weeks before they are due .
- Babies who are small for their gestational age , particularly if their growth was poor in the last few weeks of pregnancy.
- Babies whose mothers had diabetes during or before pregnancy.
- Babies who are large for their gestational age.
- Babies with rare medical conditions that cause low blood glucose.
Also Check: How To Boost A Newborn’s Immune System
These Babies 2 To 3 Times More Apt To Struggle With Planning Memory Attention At Age 4 Study Finds
TUESDAY, Aug. 8, 2017 — Low blood sugar affects about one in six newborns, and new research suggests it could lead to brain difficulties in childhood.
Babies who experience low blood sugar at or near birth are at least two to three times more likely to face problems with planning, memory, attention, problem-solving and visual-motor coordination by the age of 4.5, New Zealand researchers said.
The low blood sugar did not affect general thinking function or IQ, but it did affect problem-solving and other skills known as “executive functioning,” and also eye-hand coordination, the findings showed. These are crucial for many tasks, said study leader Chris McKinlay. He is a neonatologist at the Liggins Institute at the University of Auckland.
“We don’t know fully what this means for learning,” McKinlay said. “We think this may have an effect on educational achievement.”
Low blood sugar in newborns, known as “neonatal hypoglycemia,” is the most common preventable cause of brain damage in infancy. Those at risk of low blood sugar include babies born prematurely, those small or large for their gestational age, and those born to mothers with diabetes.
For these high-risk infants, it is common to do a blood glucose test, using a heel prick. If the level is too low, the child can be treated with a form of sugar to return it to normal levels.
The study was published online Aug. 7 in JAMA Pediatrics.
More information
JAMA Pediatrics
Causes Of Hypoglycaemia In Newborn Babies
Various conditions that might be the causes of low blood sugar in new-born babies include:
- Infants of diabetic mother : Uncontrolled diabetes in the mother results in excessive insulin production. Although insulin does not cross the placenta, glucose and other nutrients do. So extra blood glucose goes through the placenta, giving the baby high blood glucose levels. This causes the babys pancreas to make extra insulin to get rid of the blood glucose.
- Premature births: Babies who are born before term are prone to hypoglycaemia.
- Birth weight: Less than 2 kg babies.
- Mothers on certain medications: Like Terbutaline, Propanolol, Labetalol, oral hypoglycaemic agents, etc.
- Advanced RH Haemolytic diseases : Rh Blood group mismatch between mother and child can cause hypoglycaemia.
- Congenital defects and metabolic diseases since birth: Genetic and metabolic disorders since birth may cause lower blood sugars in the new-born.
- Birth Asphyxia: Babies that have suffered low oxygen levels during birth and in the first few hours after birth are prone to hypoglycaemia.
- Cold stress : Hypothermia or abnormally low body temperatures may be a cause of hypoglycaemia.
- Liver diseases
- Infections: New-borns with maternal or congenital infections may suffer low blood sugars.
Recommended Reading: How Do I Add My Newborn To My Medicaid
