When Phototherapy Might Be Necessary
When jaundice in newborn babies becomes more severe, and more intensive interventions are necessary, the most common treatment is phototherapy, where the jaundiced baby is placed under an artificial blue light. The light amplifies the effects of sunlight to help break up the bilirubin into molecules that are easily excreted from the body.
When To Call A Doctor
Most cases of jaundice are normal, but sometimes jaundice can indicate an underlying medical condition. Severe jaundice also increases the risk of bilirubin passing into the brain, which can cause permanent brain damage.
Contact your doctor if you notice the following symptoms:
- The jaundice spreads or becomes more intense.
- Your baby develops a fever over 100°F .
- Your babys yellow coloring deepens.
- Your baby feeds poorly, appears listless or lethargic, and makes high-pitched cries.
Living With Infant Jaundice
How long jaundice lasts differs from baby to baby. Often, a babys bilirubin level goes up for the first 3 to 4 days and then slowly goes back down. A baby who is breastfed may have mild jaundice for a longer time than a baby who is fed formula.
Jaundice isnt a serious problem in most healthy babies. However, very high bilirubin levels can be dangerous, and even cause brain damage. The risk of serious injury to your baby from high bilirubin levels is increased if your baby is premature. But jaundice is almost always diagnosed before the bilirubin level gets high enough to cause this kind of damage.
Recommended Reading: What To Do When Newborn Constipated
How Is Jaundice Treated
Treatment depends on the cause of the jaundice, the bilirubin levels, and a baby’s age.
Mild jaundice goes away after 1 or 2 weeks as a baby’s body gets rid of the extra bilirubin on its own. For newborns with breastfeeding jaundice, mothers should breastfeed the baby more often. If the baby is not getting enough breast milk, the doctor may suggest supplementing with formula.
For more serious cases of jaundice, treatment should start as soon as possible. Babies may get:
- fluids. A loss of fluids will cause bilirubin levels to rise.
- Babies lie under lights with little clothing so their skin is exposed. The light changes the bilirubin to a form that can easily pass out of the body. Light-therapy blankets may also be used.
- exchange blood transfusion. This emergency procedure is done if very high bilirubin levels do not come down with phototherapy. The baby’s blood is replaced with blood from a donor to quickly lower bilirubin levels.
- immunoglobulin . Babies with blood type incompatibilities get this through an IV . IVIg blocks antibodies that attack red blood cells and reduces the need for an exchange transfusion.
How Is Jaundice In Newborns Diagnosed
Your baby’s doctor will do a physical examination and ask you questions about your health and your baby’s health. For example, the doctor might ask if you and your baby have different blood types.
The doctor may place a device against your baby’s skin to check your baby’s bilirubin level. A blood test for bilirubin may be done to find out if your baby needs treatment.
More tests may be needed if the doctor thinks that a health problem is causing too much bilirubin in the blood.
Recommended Reading: How Can A Newborn Sleep At Night
Why Does My Baby Have Jaundice
Jaundice is caused by the build-up of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a yellow substance produced when red blood cells, which carry oxygen around the body, are broken down.
Jaundice is common in newborn babies because babies have a high number of red blood cells in their blood, which are broken down and replaced frequently.
Also, a newborn baby’s liver is not fully developed, so it’s less effective at removing the bilirubin from the blood.
In a small number of cases, jaundice can be the sign of an underlying health condition. This is often the case if jaundice develops shortly after birth .
How Long Does It Take For Newborn Jaundice To Go Away
Typically, jaundice goes away in a week to 10 days, though it sticks around for longer in premature babies.
If your baby is breastfed, jaundice can last a month or occasionally longer. If your baby is formula-fed, jaundice typically clears up within two weeks. If it lasts three weeks or longer, be sure to call the doctor.
Read Also: How To Treat Constipation In Newborns On Formula
How Is Jaundice Treated In A Child
Physiologic jaundice often goes away without treatment within two weeks. During this time, the babys blood may need to be tested to make sure bilirubin levels are improving.
Some babies need a treatment called phototherapy. This exposes the babys skin to a special type of bright blue light. These bili lights are very safe for most babies. The light causes a chemical reaction in the skin that lets the body remove bilirubin more easily through urine and stool. Depending on bilirubin levels, phototherapy may take anywhere from a few hours to several days.
There are two types of phototherapy for jaundice:
- Conventional phototherapy: The baby is placed on a bed under a set of bili lights. These are lamps that make a special blue light. Soft eye patches protect the babys eyes during phototherapy treatment.
- Fiberoptic phototherapy: This treatment is done with a device called a bili blanket. It is a soft pad with blue phototherapy lights inside. The baby is placed on or wrapped in the bili blanket during treatment.
If phototherapy does not bring down bilirubin levels low enough or fast enough, a baby with severe jaundice may need a blood exchange transfusion , but this is rarely needed.
For children with pathologic jaundice , the best course of treatment depends on the cause. As discussed above, pathologic jaundice can have many different causes, and various tests may be needed to find out what the problem is and how to treat it.
Red Blood Cells And Jaundice
A red blood cell has a lifespan of 120 days the cell is programmed to die at that time to keep a balance with the number of new blood cells that are being created, explains Roberta Gottlieb, M.D., of San Diego State University in Williams Hematology. Some of the contents of the dying cell are recyclable. Thus, the hemoglobin is changed to biliverdin and then bilirubin, which is attached to a protein, transported to the liver and changed once more so it can be removed in the urine or stool. A high bilirubin level in the blood causes jaundice.
You May Like: How To Create A Sleep Schedule For Newborn
What Do Parents Need To Know About Newborn Jaundice
Its important for parents to keep an eye on their babys jaundice when they go home from the hospital. Jaundice can be harder to see in dark-skinned babies. A good way to look for it is to press down for a moment on the babys skin in a spot where the bone is close . This pushes out the blood briefly and should make the skin paler for a few seconds. If it looks yellow instead of pale, there may be jaundice.
Jaundice tends to spread from the face downward as bilirubin levels go up. For that reason, doctors worry far less about a baby who is yellow just in the face and upper chest than one who is yellow below the knees.
- is looking more yellow, especially if it is spreading down below the knees
- is feeding poorly, and/or isnt wetting at least six diapers in 24 hours and having regular stools
- is very sleepy, especially if they dont wake to feed
- is very fussy and hard to console
- arches their head or back, or is otherwise acting strangely
- has a fever or is vomiting frequently.
Remember: jaundice is common, and serious problems are rare! But call your doctor if you are worried its always better to be safe than sorry.
Follow me on Twitter @drClaire
How Is Jaundice Diagnosed In A Child
Newborn babies should be tested for jaundice before going home from the hospital or birthing center. Babies at risk for jaundice, or those who are still jaundiced more than usual, might need to be checked again after a few days. Your childs health care provider can tell you if this is needed. If your baby is still jaundiced after 2 weeks of age , your provider will most likely order a blood test for total and direct bilirubin to better understand the type of jaundice and what other tests to do.
Your babys health care provider will first examine your child for signs of jaundice. Other jaundice tests may include a:
- Blood test: which measures the amount of bilirubin in the blood
- Skin test: which uses a special light to measure bilirubin in the skin
Health Tips to Your Inbox
Recommended Reading: Why Does My Newborn Cry After Feeding
What Is Newborn Jaundice
Many newborn babies develop jaundice, a condition in which the skin and whites of the eyes are yellowish in color, within a few days after birth. In fact, about half of all newborns develop mild jaundice in the first few days. In premature babies, jaundice may start early and last longer than in full-term babies.
If bilirubin levels become extremely high, complications such as brain damage , cerebral palsy, and deafness can occur.
Jaundice And Sunlight By Marc Sorenson Edd
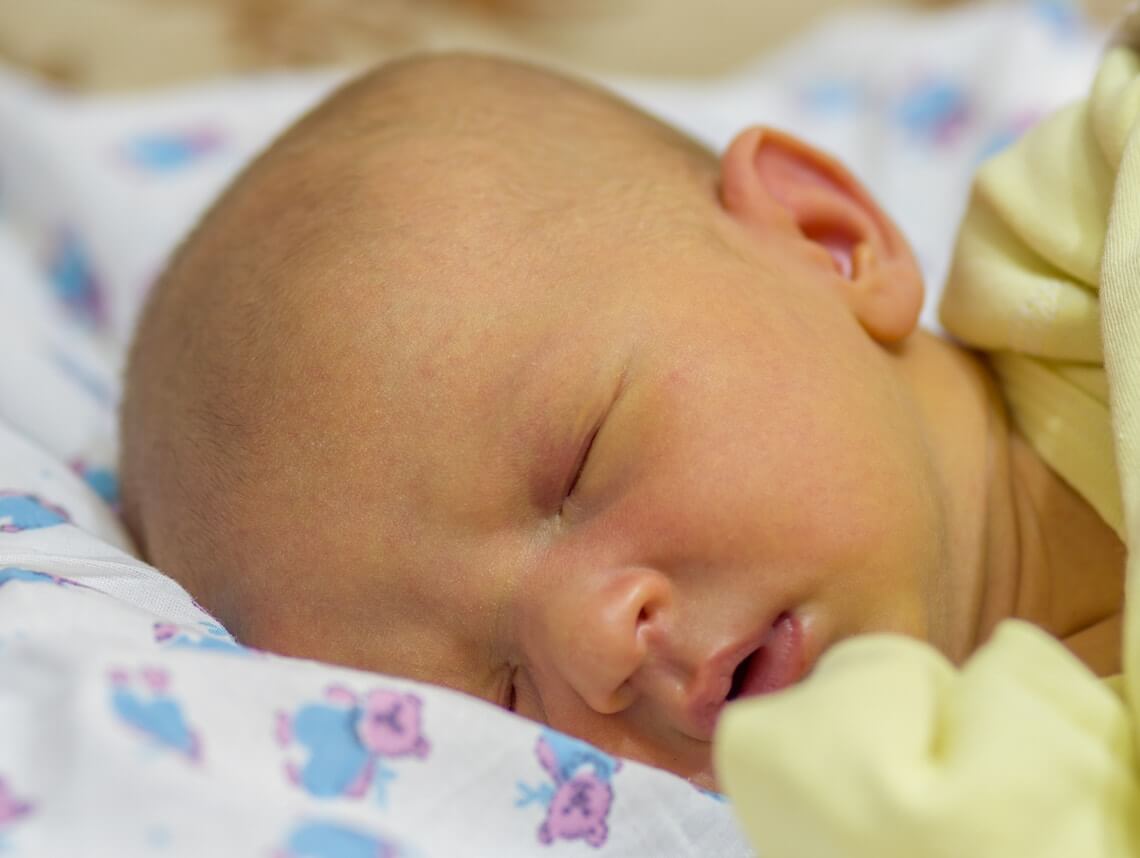

Jaundice is a disorder, usually temporary, that occurs in newborn babies and occasionally adults. It usually is innocuous, but sometimes may be dangerous. At least nine of 19 babies are born with the disease, and it is dangerous only occasionally. It is common in premature newborns, and those babies often manifest the disorder by a yellow skin. Furthermore, the children may manifest yellowing of the whites of the eyes. Most noteworthy, babies at birth have a higher number of red blood cells at birth. Thus, as the excess blood cells break down after birth, they produce a waste product called bilirubin. Due to the yellowish color of Bilirubin, skin and whites of the eyes may change. So, when bilirubin levels become excessive , jaundice usually manifests itself.
Don’t Miss: How To Sponge Bathe A Newborn With Umbilical Cord
How Can You Help Your Baby
If your baby has jaundice, you have an important role to play.
- Look closely at your baby’s skin 2 times a day to make sure that the colour is returning to normal. If your baby has dark skin, look at the white part of the eyes.
- Take your baby for any follow-up testing your doctor recommends.
The best thing you can do to reduce jaundice is to make sure that your baby gets enough to eat. That will help your baby’s body get rid of the extra bilirubin.
- If you are breastfeeding, feed your baby about 8 to 12 times every 24 hours.
- If you are feeding your baby from a bottle, stay on your schedule .
If you aren’t sure that your baby is getting enough milk, ask your doctor, a nurse, or a lactation consultant for help.
Who Is At Risk For Breast Milk Jaundice
Breast milk jaundice can occur in any breast-fed newborn. Since doctors dont know the exact cause of the condition yet, there are few risk factors associated with it. However, breast milk jaundice may be genetic, so a family history of jaundice in breast-fed infants might increase your babys risk.
Don’t Miss: Is Infant Formula Safe For Newborns
When To See Your Doctor
Jaundice is usually harmless, but a nurse or doctor should check and monitor all cases of jaundice in newborn babies. Some babies have severe jaundice, which very occasionally can lead to deafness and even brain damage if not treated promptly.
You should take your baby to the doctor if:
- your baby is unwell, feeding poorly and not gaining enough weight
- your baby’s poo becomes pale or their wee becomes dark
- your baby develops jaundice in the first 48 hours after birth
- the jaundice becomes more noticeable after a week
- the jaundice hasn’t gone away after 2 weeks
Why Is The Coombs Test Done
The Coombs test checks the blood to see if it contains certain antibodies. Antibodies are proteins that your immune system makes when it detects that something may be harmful to your health.
These antibodies will destroy the harmful invader. If the immune systems detection is wrong, it can sometimes make antibodies toward your own cells. This can cause many kinds of health problems.
The Coombs test will help your doctor determine if you have antibodies in your bloodstream that are causing your immune system to attack and destroy your own red blood cells. If your red blood cells are being destroyed, this can result in a condition called hemolytic anemia.
There are two types of Coombs tests: the direct Coombs test and the indirect Coombs test. The direct test is more common and checks for antibodies that are attached to the surface of your red blood cells.
The indirect test checks for unattached antibodies that are floating in the bloodstream. Its also administered to determine if there was a potential bad reaction to a blood transfusion.
Also Check: When Should You Bathe Newborn
What Are The Current Recommendations On Screening For Hyperbilirubinemia
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends universal screening with TSB or transcutaneous bilirubin levels, or targeted screening based on risk factors.5 Universal TSB/TcB screening can accurately identify infants whose TSB level is likely to exceed the 95th percentile for age.6,7 Some studies have found that the use of risk scores is as accurate as universal screening for predicting hyperbilirubinemia.8,9 A combination of universal screening and risk factor scoring seems to be the most effective method for identifying infants at risk of hyperbilirubinemia.1,7 A sample risk score is listed in Table 1.9
Risk Score for Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia
| Variable | |
|---|---|
|
2,000 to 2,500 g |
|
|
2,501 to 3,000 g |
|
|
3,001 to 3,500 g |
|
|
3,501 to 4,000 g |
|
|
4,001 to 4,500 g |
|
|
4,501 to 5,000 g |
|
|
Oxytocin used during delivery |
|
|
Gestational age < 38 weeks |
note: A total score of 8 or more suggests an increased risk of hyperbilirubinemia total serum bilirubin or transcutaneous bilirubin level should be obtained.
Adapted with permission from Keren R, Bhutani VK, Luan X, Nihtianova S, Cnaan A, Schwartz JS. Identifying newborns at risk of significant hyperbilirubinaemia: a comparison of two recommended approaches. Arch Dis Child. 2005 90:417.
Risk Score for Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia
| Variable | |
|---|---|
|
2,000 to 2,500 g |
|
|
2,501 to 3,000 g |
|
|
3,001 to 3,500 g |
|
|
3,501 to 4,000 g |
|
|
4,001 to 4,500 g |
|
|
4,501 to 5,000 g |
|
|
Oxytocin used during delivery |
|
|
Gestational age < 38 weeks |
