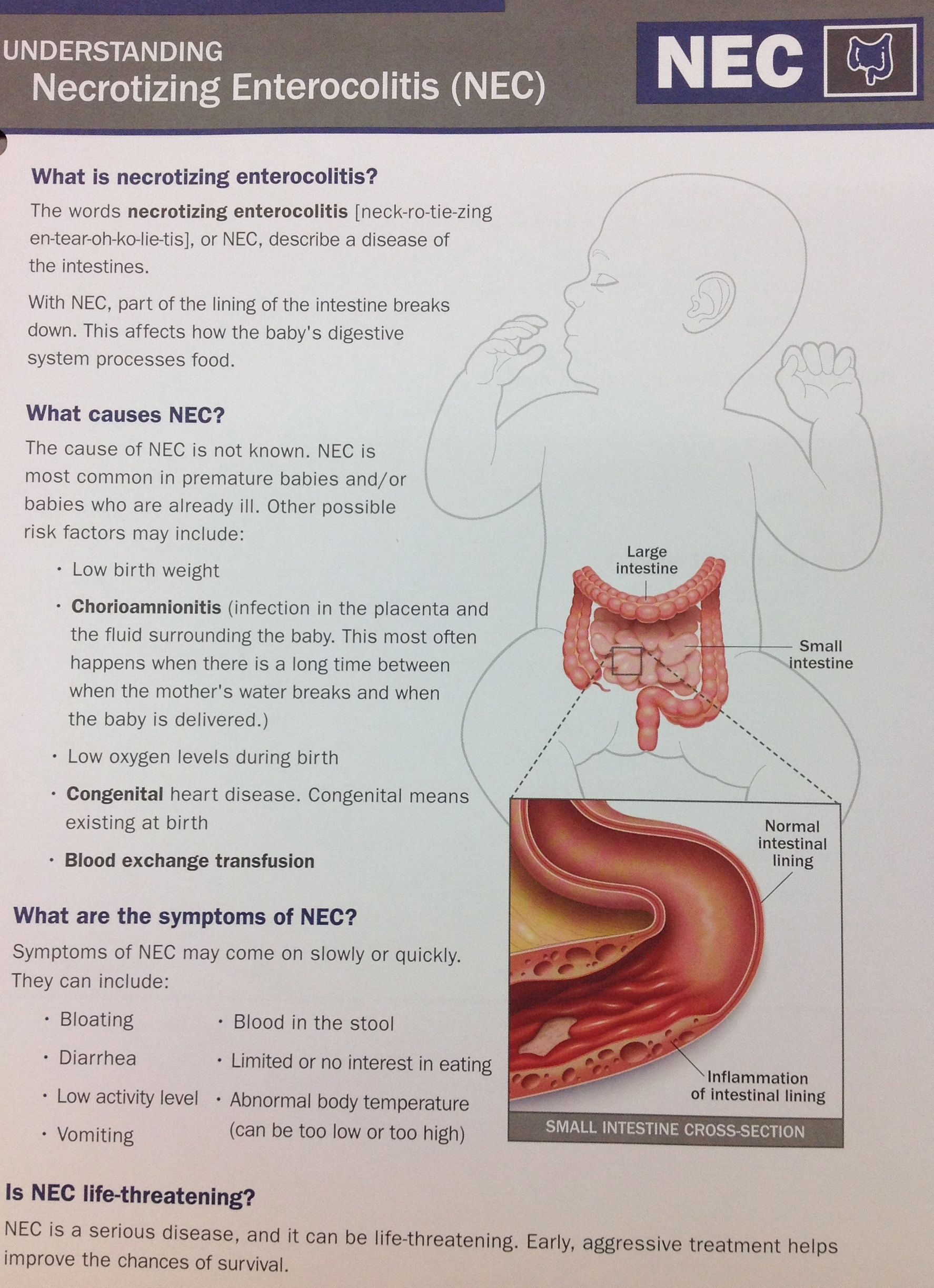
How Doctors Treat Babies With Nec
As soon as doctors confirm the babys necrotizing enterocolitis diagnosis, treatment can begin.
Severe NEC cases may require immediate surgery to remove dead tissue and drain fluids from the babys abdominal cavity.
If you would like to learn more about negligence and the role it plays in your case, please contact Levin, Rojas, Camassar, and Reck, LLC today.
Early Goal Directed Therapy
is an approach to the management of severe sepsis during the initial 6 hours after diagnosis. It is a step-wise approach, with the physiologic goal of optimizing cardiac preload, afterload, and contractility. It includes giving early antibiotics. EGDT also involves monitoring of hemodynamic parameters and specific interventions to achieve key resuscitation targets which include maintaining a central venous pressure between 812 mmHg, a mean arterial pressure of between 65 and 90 mmHg, a central venous oxygen saturation greater than 70% and a urine output of greater than 0.5 ml/kg/hour. The goal is to optimize oxygen delivery to tissues and achieve a balance between systemic oxygen delivery and demand. An appropriate decrease in serum may be equivalent to ScvO2 and easier to obtain.
In the original trial, early goal-directed therapy was found to reduce mortality from 46.5% to 30.5% in those with sepsis, and the Surviving Sepsis Campaign has been recommending its use. However, three more recent large randomized control trials , did not demonstrate a 90-day mortality benefit of early goal-directed therapy when compared to standard therapy in severe sepsis. It is likely that some parts of EGDT are more important than others. Following these trials the use of EGDT is still considered reasonable.
What Are The Complications Of Necrotizing Enterocolitis
An infant with NEC is at risk for other problems, such as:
- Abdominal infection: Some infants develop a hole in the intestinal wall. This perforation allows bacteria to enter the abdominal cavity. An infection called peritonitis can result. Peritonitis increases the risk for a life-threatening blood infection called .
- Intestinal stricture: As many as 1 in 3 babies develop intestinal strictures. A stricture narrows the intestines. This condition typically occurs a few months after a baby recovers from NEC. A narrowed intestine makes it difficult for food to pass through. Some children need surgery to open up the intestine.
- Short bowel syndrome: If NEC destroys or damages part of the small intestine, a child may develop short bowel syndrome. This condition makes it hard for the body to absorb fluids and nutrients . Children with short bowel syndrome need lifelong care to get the right nutrition to grow. Some children need tube feedings.
- Growth failure and developmental delays: Important long-term complications are growth failure, poor neurodevelopmental outcomes and developmental delays, especially in infants who required surgery. These infants require close follow-up to monitor growth and development.
Also Check: How To Get Newborn To Stay Asleep
Penicillin And Other Natural Antibiotics
Observations about the growth of some microorganisms inhibiting the growth of other microorganisms have been reported since the late 19th century. These observations of antibiosis between microorganisms led to the discovery of natural antibacterials. observed, “if we could intervene in the antagonism observed between some bacteria, it would offer perhaps the greatest hopes for therapeutics”.
In 1874, physician Sir noted that cultures of the mould that is used in the making of some types of did not display bacterial contamination. In 1876, physicist also contributed to this field.
In 1895 , Italian physician, published a paper on the antibacterial power of some extracts of mold.
In 1928, Sir postulated the existence of , a molecule produced by certain moulds that kills or stops the growth of certain kinds of bacteria. Fleming was working on a culture of bacteria when he noticed the of a green mold, , in one of his . He observed that the presence of the mould killed or prevented the growth of the bacteria. Fleming postulated that the mould must secrete an antibacterial substance, which he named penicillin in 1928. Fleming believed that its antibacterial properties could be exploited for chemotherapy. He initially characterised some of its biological properties, and attempted to use a crude preparation to treat some infections, but he was unable to pursue its further development without the aid of trained chemists.
Spreading Of Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Necrotizing enterocolitis seems to develop in clusters, where several babies from a same nursery are affected with this condition. Although this can be a coincidence however, there are some bacteria and viruses that are found in babies suffering from necrotizing enterocolitis. Necrotizing enterocolitis cannot spread from one infant to another however, its causative pathogen can pass from one to another.
You May Like: How To Use Gripe Water For Newborn
Does Your Child Have Nec
NEC is a serious medical condition that has a tremendous impact on your child and family. At MedMalFirm.com, our attorneys are currently investigating claims related to necrotizing enterocolitis caused by cows milk-based infant formulas. If your child was fed formula in a neonatal intensive care unit and developed NEC, contact us today to learn more about your legal rights.
Find out if you qualify for compensation related to your childs NEC by completing our online form, or by calling us at 913-0571. A case review with one of our attorneys is completely FREE.
Diagnosis Of Necrotizing Enterocolitis
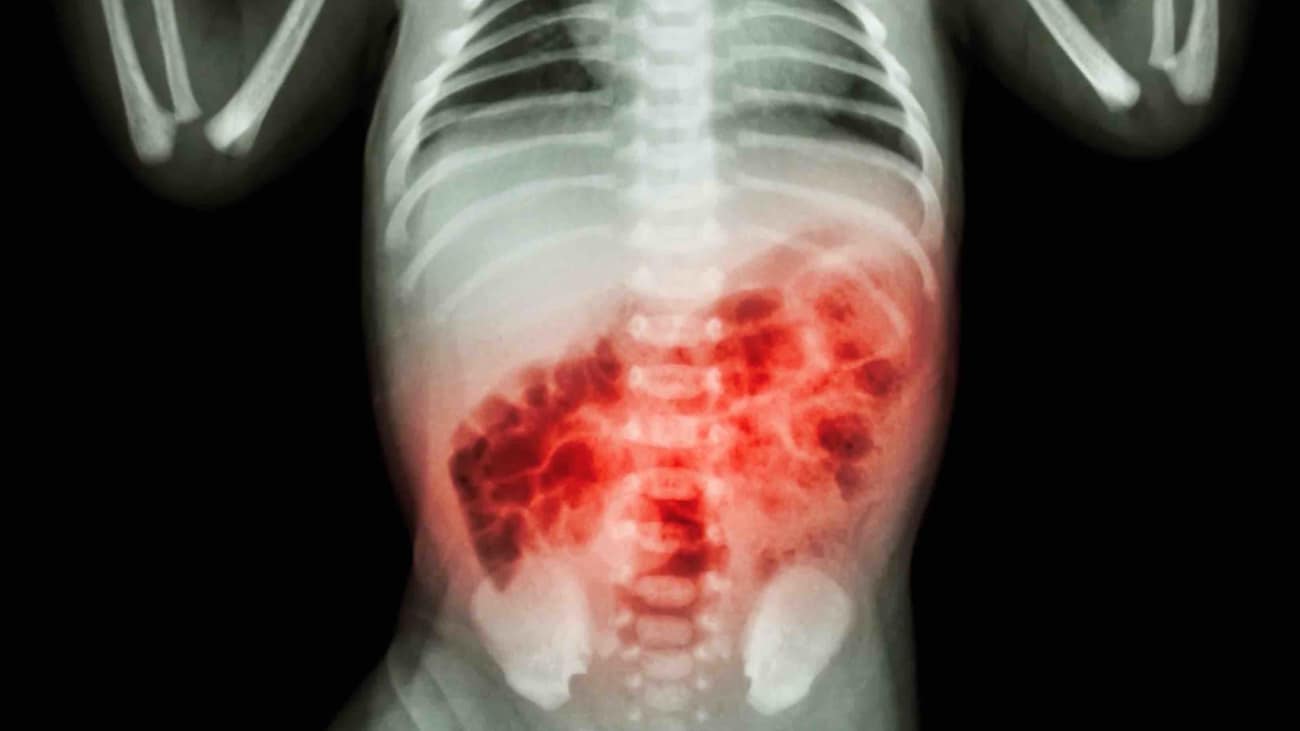
Diagnosis of necrotizing enterocolitis can be confirmed by doing an x-ray where an abnormal gas pattern can be seen, which resembles a streaky or bubbly appearance of gas in the intestinal walls.
X-ray done in severe cases of necrotizing enterocolitis where there is release of the air from the intestine, shows up in the abdominal cavity or large veins of the liver. To check if there is a hole in the intestine, the doctor inserts a needle into the abdomen to withdraw fluid.
Recommended Reading: What To Buy For A Newborn Baby Boy
How Is Necrotizing Enterocolitis Managed Or Treated
Your babys intestines need time to rest and heal. The first step in treating NEC is to stop tube or oral feedings. Instead, your baby receives intravenous fluids and nutrients.
Your baby may also get these treatments:
- Nasogastric tube: Your provider inserts a long, thin tube through the nose . The tube goes into the stomach to suction out gas and fluids.
- Antibiotics:Antibiotics help fight bacterial infections.
About 1 in 4 babies need surgery to remove dead intestinal tissue and repair a hole. Your childs provider may perform an ostomy procedure. This surgery:
- Creates a small hole in the childs belly.
- Connects the large intestine to the stoma.
- Allows poop to exit the body through the stoma into a bag outside of the body.
When your baby is stronger, your provider will reattach the intestines and replace them in the abdomen.
If your child is too small or too ill for surgery, your provider may place a drain in the abdomen. The drain lessens symptoms by removing unhealthy or infected fluids and gas. If your baby still needs surgery later, the surgery will take place when your baby is bigger and healthier.
Preparing For The First Visit
Working with a medical team to find a diagnosis can be a long process that will require more than one appointment. Make better health decisions by being prepared for the first visit with each member of the medical team.
Make informed decisions about health care:
- Prepare a list of questions and concerns before the appointment
- List the most important questions first, not all questions may be answered in the first visit
- Ask questions about symptoms, possible diagnoses, tests, and treatment options
For future appointments:
- Discuss what was not addressed at the last visit
- Discuss changes in the quality of life for the patient, family, and caregivers
- Discuss health goals and other issues in the patientâs and familyâs life that may affect the health care decisions
Don’t Miss: How To Tell If Your Newborn Has Gas
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Necrotizing Enterocolitis
A baby with necrotizing enterocolitis might have these symptoms:
- a swollen, red, or tender belly
- trouble feeding
- diarrhea and/or dark or bloody stools
- being less active or lethargic
- a low or unstable body temperature
- green vomit
- bradycardia
- hypotension
Symptoms of NEC can vary from baby to baby, and be like those caused by other digestive problems.
Whats The Outlook For Nec
Most infants with this condition fully recover. In some cases, the bowel is scarred or it narrows. This may lead to a future blockage. Babies whoâve had a large piece of their intestine removed in surgery may not be able to absorb nutrients normally. In the most severe cases, they may need a bowel transplant in order to live.
Right now, thereâs no way to prevent NEC. But studies show that babies who were only fed breast milk , were less likely to develop this disease. Thatâs why doctors recommend feeding at-risk infants breast milk, starting with small amounts. Many NICU’s are now using donor breast milk when there is none available from the mother in order to reduce the incidence of NEC
Researchers are working on promising new treatments for NEC. Among them: probiotics, which are live bacteria and yeasts that are good for you, to counteract the bacteria that cause the infection, and blocking nitric oxide. Thatâs a gas which is produced as a result of NEC. It helps to destroy the wall of the intestine.
Show Sources
Don’t Miss: Do You Use Soap To Bathe A Newborn
What Are The Symptoms Of Necrotizing Enterocolitis
NEC typically occurs two to six weeks after birth, depending on the type and cause. Symptoms may come on over a few days or appear suddenly in babies who otherwise seem to be doing well.
NEC is a common problem among infants in NICUs. Your babys care team will be on the lookout for signs of this problem.
Symptoms of NEC include:
- Refusing to eat and lack of weight gain.
What Happens Afterwards
Your child will usually return to the intensive care unit to recover, and you will be able to visit as soon as they are settled back in the incubator. For a while after the operation, your baby will need help with breathing so will be connected to a ventilator. All babies are closely monitored after the operation, and so your child will be connected to monitors to check their breathing, heart rate and oxygen levels. They will also be given pain relief through the intravenous infusion .
While your childs bowel recovers and start to work, they will continue to be fed through a tube into their veins . This will gradually be replaced by breast or bottled milk given through the nasogastric tube, when your child is ready for this. Over time, the drips and monitors will be removed one by one.
The nurses on the ward will encourage you to look after your child as much as you feel able while they are recovering. This can be daunting, especially while they are connected to drips and monitors, but it will become easier with time. If you are worried about caring for your child, please talk to the nurses.
Your child will be transferred to another ward within the hospital or to your local hospital, once they are feeding properly and gaining weight. We will send you details of your outpatient appointment in the post, soon after you leave hospital.
Don’t Miss: How To Buy Newborn Clothes
How Is Nec Diagnosed
Your babys healthcare provider will check him or her for signs of NEC.
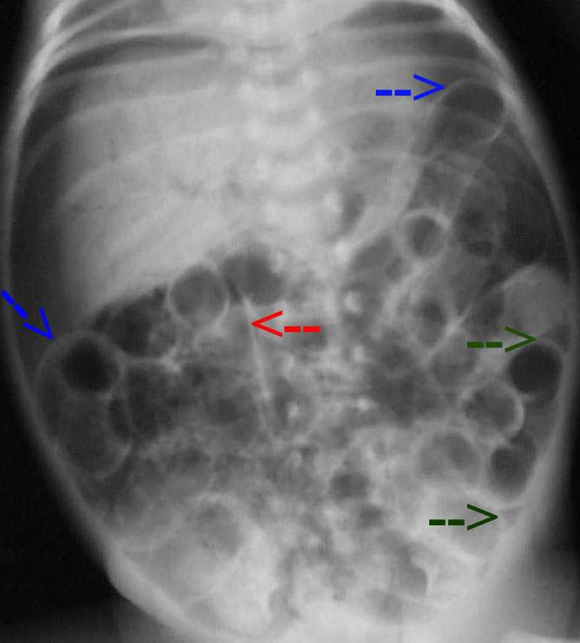
Your child may need an abdominal X-ray. An X-ray can show if your childs intestine has a bubbly appearance. It can also show signs of air or gas in the large veins of your childs liver. Air may also be on the outside of the intestines in your childs belly .
Your childs healthcare provider may also put a needle into his or her abdominal cavity. This is to look for intestinal fluid in your childs abdomen. This is a sign of a hole in the intestines.
What Causes Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Healthcare providers dont know exactly what causes NEC. We do know that premature infants have weaker immune systems. The immune system helps the body fight off infections.
An infants digestive system is also weaker. When premature babies get an intestinal infection, their immune and digestive systems have a hard time fighting it.
Oxygen-carrying blood also has a harder time reaching the intestines in premature babies. Diminished blood flow can damage intestinal tissue. This damage allows bacteria to leave the intestines and enter the abdominal cavity or bloodstream.
Don’t Miss: How Do I Know If Newborn Is Lactose Intolerant
Breast Milk Feeding And Probiotics In Protection From Nec
The microbial ligands recognized by TLR are not specific to pathogens, and signaling through TLR by commensal microbial flora in the gut may in fact enable normal assembly and function of the intestinal immune system . The intestine is devoid of bacterial flora at birth but is rapidly colonized by the recto-vaginal flora of the mother . Colonization by commensal bacteria is required for the normal development and maturation of the newborn intestine. Bacterial-host cross-talk modulates gut vascular development and promotes epithelial barrier function . For example, the intestinal flora stimulates the production of IgA in animal models . Indeed, the presence of IgA correlates with a decrease in bacterial translocation in the gut. In fact, the presence of Bacteroides fragilis in vaginally born infants, when compared with infants born by cesarean section, correlates with higher levels of IgA and IgM secreting plasma cells in peripheral blood .
Figure 1
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
You may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- What caused my babys NEC?
- What type of NEC does my baby have?
- What is the best treatment for my baby?
- What are the treatment complications?
- What are the long-term effects of NEC?
- Does my baby need a special diet?
- Should I look out for signs of complications when I bring my baby home?
Recommended Reading: Is It Bad For Newborns To Sleep On Their Side
Why Is Necrotizing Enterocolitis A Concern
Damage to the intestinal tissues can lead to perforation in the intestines. This allows the bacteria normally present in the intestinal tract to leak out into the abdomen and cause infection. The damage may only exist in a small area or it may progress to large areas of the intestine. The disease can progress very quickly. Infection in the intestines can be overwhelming to a baby and, even with treatment, there may be serious complications. Problems from NEC may include the following:
- Perforation in the intestine
- Scarring or strictures of the intestine
- Problems with food absorption if large amounts of intestine must be removed
- Severe, overwhelming infection
A Note From Cleveland Clinic
It can be upsetting to see your premature baby have a setback like NEC when they seem to be doing well. Care teams in NICUs have training to spot this problem and act quickly. Some babies get better with minimal treatment. Children who need surgery often go on to lead full lives. Some children have chronic digestive problems.
You May Like: How Often To Give Newborn Formula
What Are The Symptoms Of Nec
Each child may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms usually show up in the first 2 weeks of life. They may include:
-
Bloating or swelling of the belly
-
Food doesnt move through to the intestines
-
Greenish-colored fluid in the stomach
-
Bloody bowel movements
-
Breathing that stops and starts
-
Slow heart rate
-
Sluggishness
The symptoms of NEC may be similar to symptoms of other conditions. Make sure your child sees his or her healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Congenital Anomalies Of The Bowel That Mimic Nec
Patients with Hirschsprung disease may develop inflammatory enterocolitis, an entity that leads to significant morbidity and mortality . The clinical signs of this disease include vomiting, rectal bleeding, loose stools and abdominal distention, making it sometimes difficult to differentiate from classic NEC. Intestinal obstruction due to volvulus, intussusception, and meconium ileus due to cystic fibrosis may also present with signs and symptoms of NEC including radiographic features such as pneumatosis intestinalis and should be kept in mind in the differential diagnosis of NEC.
Recommended Reading: How Does Custody Work With A Newborn
Drugwatchcom Has Been Empowering Patients For More Than A Decade
Drugwatch.com has provided reliable, trusted information about medications, medical devices and general health since 2008. Weve also connected thousands of people injured by drugs and medical devices with top-ranked national law firms to take action against negligent corporations.
Our team includes experienced medical writers, award-winning journalists, researchers and certified medical and legal experts. Drugwatch.com is HONCode certified. This means the high-quality information we provide comes from credible sources, such as peer-reviewed medical journals and expert interviews.
The information on Drugwatch.com has been medically and legally reviewed by more than 30 expert contributors, including doctors, pharmacists, lawyers, patient advocates and other health care professionals. Our writers are members of professional associations, including American Medical Writers Association, American Bar Association, The Alliance of Professional Health Advocates and International Society for Medical Publication Professionals.
Risk Factors For Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Babies that are born before 32 weeks of gestation are at higher risk for necrotizing enterocolitis. However, full-term babies suffering from health issues, such as a heart defect, can also have necrotizing enterocolitis. Babies with necrotizing enterocolitis often develop this condition in the initial 2 to 4 weeks of their life.
Read Also: What Causes Constipation In Newborns
