While Relatively Uncommon Some Babies Can Be Lactose Intolerant And The Condition Can Cause Discomfort If Left Untreated
What is lactose intolerance?
Lactose is a sugar found naturally in breast milk, cows milk and most dairy products .
Usually, lactose is broken down in the gut by an enzyme called lactase. Yet some people dont have enough of this enzyme. Without lactase to break it down, the lactose stays in the gut and bacteria eat it instead. This produces large amounts of gas, which in turn produces the symptoms of lactose intolerance.
What causes lactose intolerance?
In babies, lactose intolerance is generally caused by either:
- A congenital condition, where babies are born without lactase
- Premature birth, where the small intestine is not developed enough to produce lactase yet
- A temporary intolerance caused by a stomach bug or infection, undiagnosed coeliac disease or antibiotics
Lactose intolerance can also develop in older children whose diets are low in lactose. This is often the case in cultural groups where dairy isnt part of the everyday diet.
How do I know if my baby is lactose intolerant?
It can be tricky to diagnose lactose intolerance, as the symptoms are similar to other conditions. Things to look out for include:
- Stomach pain
- Excessive wind
These symptoms usually appear within three hours of the feed.
If your baby is showing any of these symptoms or you think he is having trouble digesting a feed, you should consult your doctor or health professional. They will be able to advise on the best way to address the condition.
Will my baby grow out of lactose intolerance?
How Is A Lactose Intolerance Diagnosed In A Baby
If your baby has signs of a lactose intolerance, dont diagnose the condition yourself. Talk to your pediatrician. Theyll have more experience distinguishing between a lactose intolerance and a milk allergy.
Since a lactose intolerance is uncommon in infants, your doctor may refer you to an allergist to rule out a dairy allergy after also ruling out other common digestive issues.
The allergist may expose your babys skin to a small amount of milk protein, and then monitor their skin for an allergic reaction.
If your baby doesnt have a milk allergy, your doctor may take a stool sample to check the acidity of their poop. Low acidity can be a sign of lactose malabsorption, and traces of glucose is evidence of undigested lactose.
Your doctor may also suggest removing lactose from their diet for 1 to 2 weeks to see if their digestive symptoms improve.
Signs Your Toddler Could Be Lactose Intolerant
Listen to this article:
Most people are familiar with lactose intolerance, likely because its said to affect two thirds of the entire adult population. As adults, lactose intolerance is a manageable, albeit annoying, condition, but as a child who can receive many of the nutrients they need to grow and develop from milk, it can be far more difficult, particularly on the parents.
The first step to learning how to treat your child with this condition is to identify the issue. Here we discuss what is lactose intolerance, the signs of lactose intolerance in toddlers, and healthy alternatives to milk that both you and your kid will love.
You May Like: Do Newborns Sleep A Lot
What Is True Lactose Intolerance
True lactose intolerance, or what is medically known or otherwise known as primary lactose intolerance, or Galactosemia is an extremely rare genetic condition, which requires medical treatment to manage.
From birth a baby with Glactosemia fails to thrive, meaning they wont put on any weight. These children require a very special diet and emergency medical treatment, with a hydrogen breath test and tests for reducing sugar in the stools undertaken for diagnosis.
Glactosemia occurs when a baby does not produce lactase, which breaks down lactose. Only a few people in the world have been diagnosed with this condition. The US National Library of Medicine states that, Classic Galactosemia occurs in 1 in 30,000 to 60,000 newborns. Galactosemia type II and type III are less common type II probably affects fewer than 1 in 100,000 newborns and type III appears to be very rare.
Dont Miss: How To Tell If My Newborn Has Colic
Treatment And Management: Lactose Intolerance In Older Children And Teenagers

If your older or teenage child is diagnosed with lactose intolerance, you can reduce the amount of lactose in her diet. But you dont need to get rid of products with lactose completely, especially if your child eats only small amounts of them with other foods during the day.
The following food and diet tips can help.
These foods are OK:
- cheeses with very low lactose content brie, camembert, cheddar, colby, edam, fetta, gouda, havarti, mozzarella, parmesan, halloumi, Swiss and Tilstat
- yoghurt the bacteria in yoghurt breaks down the lactose so its usually fine for your child to eat
- calcium-fortified soy products soy yoghurt, soy milk, soy ice-cream and soy cheese
- lactose-free cows milk
- butter and cream these contain only small amounts of lactose and are usually fine to eat
- bread, cereals, fruit, vegetables, meat and other protein foods
- full-fat milk the fat in full-fat milk gives your childs body longer to digest lactose.
Watch out for these foods:
- milk ice-cream and milk desserts
- cream cheese, processed cheese and cheese spread
- muesli bars
- instant mashed potato and vegetables with added milk or white sauces.
Check the ingredients in these foods:
- biscuits, cakes and cake mixes
- soups
Also Check: How To Dream Feed Newborn
How Does A Lactose Intolerance Affect Breastfeeding And Formula Feeding
If diagnostic testing confirms a lactose intolerance, dont immediately panic and stop breastfeeding. Whether youre able to continue breastfeeding depends on the type of lactase deficiency.
For example, if your baby develops a lactose intolerance after a viral illness, the general recommendation is to continue breastfeeding. Breast milk can give their immune system a boost and help heal their gut.
If your infant has developmental lactase deficiency due to a premature birth, this condition only lasts a few weeks or months. So your baby may eventually drink milk-based formula or breast milk with no problem, although youll need to use lactose-free infant formula in the meantime.
But breastfeeding isnt an option if your baby has a congenital lactase deficiency. The lactose in your breast milk can cause severe diarrhea and lead to dehydration and electrolyte loss. Youll need to feed your baby with lactose-free infant formula.
What Is Cows’ Milk Allergy
Most infant formula milk is made from cows’ milk. The first time a baby has cows’ milk, it’s very likely to be in formula. That’s because cows’ milk itself isn’t recommended as a drink for children under the age of 1. But from around 6 months old, when a baby is being introduced to solids, they can have cowsâ milk as an ingredient in foods.
Cows’ milk allergy is one of the most common allergies for babies and young children. Experts estimate that 2% to 7.5% of U.K. babies under 12 months old have it. If it happens, your child’s immune system reacts to the proteins in milk, triggering allergy symptoms. That’s why it’s sometimes called cows’ milk protein allergy.
If your baby does get an allergy to cow’s milk, it usually starts when your baby is first exposed to cow’s milk, through formula, or later with solid foods.
Sometimes, but not very often, babies who are breastfed can have this allergy. It’s because the cows’ milk from the mum’s diet is being passed on to the baby through their breast milk.
Most children grow out of the allergy by the time they reach the age of 5.
Don’t Miss: What Temperature Water For Newborn Bath
Complications Of Lactose Intolerance
Milk and other dairy products contain calcium, protein and vitamins, such as A, B12 and D.
Lactose also helps your body absorb a number of other minerals, such as magnesium and zinc.
These vitamins and minerals are important for the development of strong, healthy bones.
If you’re lactose intolerant, getting the right amount of important vitamins and minerals can prove difficult.
This may lead to unhealthy weight loss and put you at increased risk of developing the following conditions:
- osteopenia where you have a very low bone-mineral density left untreated, it can develop into osteoporosis
- osteoporosis where your bones become thin and weak, and your risk of breaking a bone is increased
- malnutrition when the food you eat does not give you the nutrients essential for a healthy functioning body this means wounds can take longer to heal and you may start to feel tired or depressed
If you’re concerned that dietary restrictions are putting you at risk of complications, you may find it helpful to consult a dietitian.
They can advise you on your diet and whether you require food supplements.
Your GP should be able to refer you to an NHS dietitian free of charge. Or you can contact a private dietitian.
The British Dietetic Association has information on how to find a private dietitian.
Page last reviewed: 25 February 2019 Next review due: 25 February 2022
Is There A Difference Between Lactose Intolerance And Milk Allergy
Lactose intolerance is not the same as a milk protein allergy, the most common food allergy in babies. Infants who have milk protein allergy are allergic to the protein in cow’s milk. Children who are lactose intolerant cannot properly digest lactose, which is a sugar. While both groups of children may experience similar symptoms, the two conditions are very different. Learn more about symptoms of a food allergy in children.
You May Like: Why Do Newborns Have So Much Gas
How Lactose Intolerance Works
Lactoseis a sugar found in foods that many children love, including milk, ice creamand soft cheeses. Its also present in some baked goods, salad dressings,sauces, candy and other foods you might not expect. Breast milk and infantformulas contain lactose, too.
Lactoseis made up of two simple sugar molecules glucose and galactose. In order forit to be absorbed by the body, lactose has to be split into its two componentsby an enzyme called lactase, which is found in the lining of thesmall intestine.
But for those who are lactose intolerant, the activity of lactase is ineffective, and its unable to digest and absorb lactose in the small intestine. The lactose then passes into the large intestine, where it is fermented by gut bacteria. This process produces carbon dioxide and hydrogen, as well as certain byproducts that have a laxative effect.
What Foods Are Most Likely To Be A Problem
Some of the most likely suspects are cows milk products, soy, wheat, corn, eggs, and peanuts.
Other suspect foods:
- Any food that a family member is allergic to
- A food that mom recently ate a large amount of
- A new food
- A food that mom doesnt like, but is eating while breastfeeding for the benefit of her baby
- A food that mom craves, or feels she has to have after a bad day
Conscious likes and dislikes of foods are signals that your body may be reacting to them in an abnormal way.
Keeping a food journal with a record of foods eaten and babys behavior/symptoms, with time of day for each, may be helpful when trying to pinpoint a problem food.
Read Also: How To Bathe A Newborn Baby With Umbilical Cord
Can Lactose Intolerance Cause Immediate Diarrhea
Lactose intolerance typically produces gastrointestinal symptoms such as gas, bloating, and diarrhea 30 minutes to two hours after consuming milk or other lactose-containing dairy products. Lactose intolerance is also called “lactose malabsorption.” Symptoms of lactose intolerance may be mild or severe depending on how much lactose is consumed. If you are able to consume small amounts of milk without experiencing problems, then your body is likely tolerant of the protein casein as well as the sugar lactose. However, if you have large doses of either protein or sugar, your body will respond by producing acids that cause pain throughout your digestive system.
Diarrhea is the passage of many watery stools in a short period of time. It is usually caused by a specific problem with one of the organs involved in digestion – the intestines, pancreas, or colon. Diarrhea can be categorized as having liquid or solid content. Liquid diarrhea contains many watery bowel movements daily. Solid diarrhea consists of very soft or slightly hard stools.
If you are drinking liquids to stay hydrated but are still passing out diarrhea, you may want to consider additional electrolytes. These can come in the form of supplements or additives found in some foods and beverages.
How Can I Tell If My Baby Is Lactose Intolerant
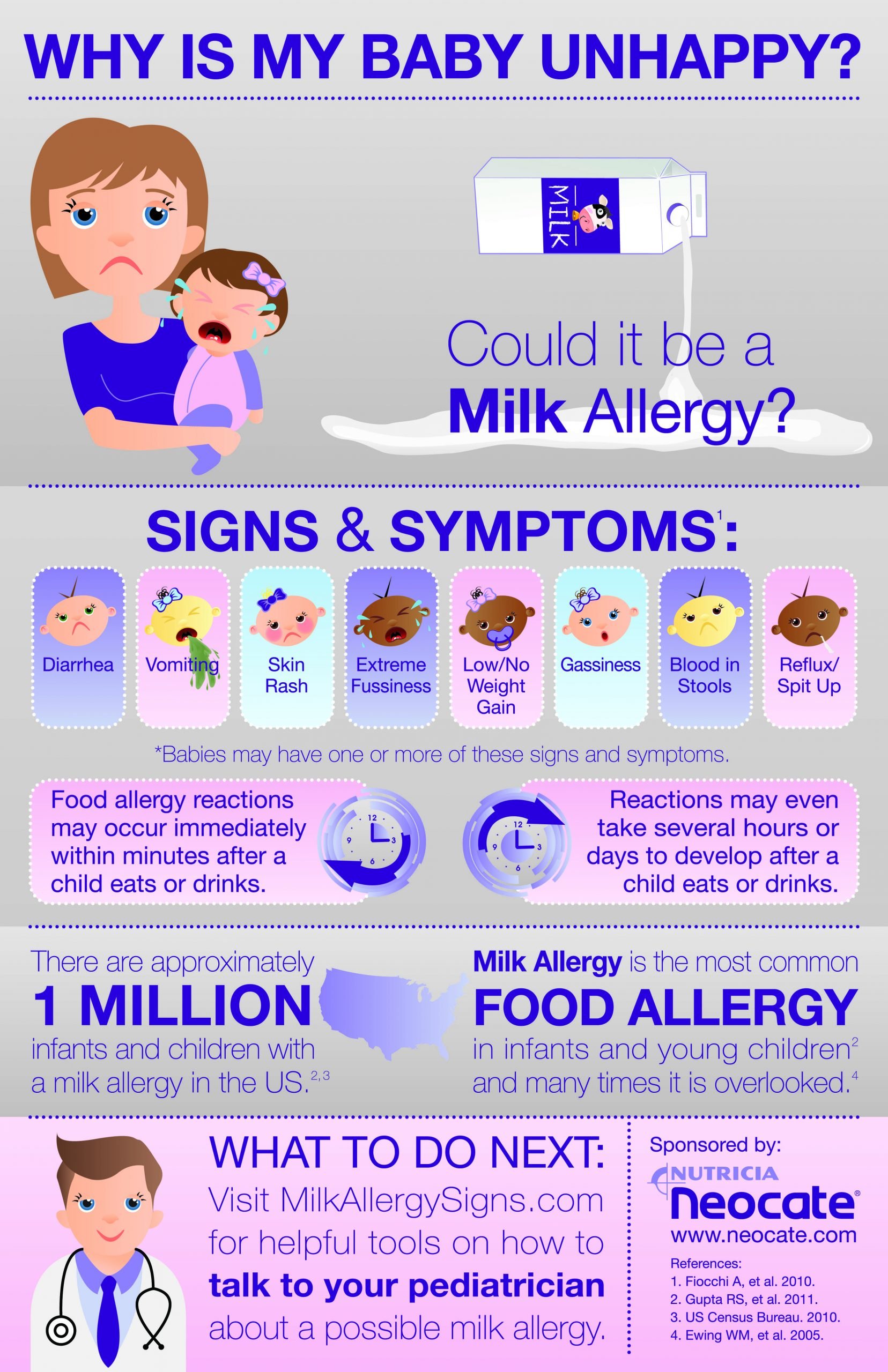
Lactose intolerance symptoms can appear minutes to hours after drinking milk or eating dairy products and range from mild to severe depending on the quantity ingested and tolerated. Here are some indications to look out for: nausea. Pain, cramping, and bloating in the abdomen. Constipation or diarrhea. Fatigue. Headaches. Difficulty concentrating.
If you think that your baby may be lactose intolerant, take his or her weight and multiply by 0.8 to find his or her body mass index . Then, divide that number by 15 to get estimated fat percentage. Finally, subtract this number from 20 to determine whether your baby is at risk for developing lactose intolerance.
Here are some questions to ask yourself or your doctor before you start including dairy products in your baby’s diet: Do I have any allergies? If so, which ones? Is there anything unusual about my baby’s stools? How long after I give my baby milk will he or she begin to show signs of intolerance?
Your doctor may also want to conduct various tests, such as a stool sample analysis performed by a laboratory technician who is trained in gastrointestinal health. This test measures levels of lactose in your baby’s blood or urine to see if he or she has an intolerance to this nutrient.
Read Also: What All Do You Need For A Newborn Baby
What If A Specific Food Appears To Be A Problem
If you think your baby is reacting to a particular food, then eliminate that food from your diet for 2-3 weeks to see if babys symptoms improve. If babys symptoms do improve, then this food may be a problem for your baby. Eliminating a food for less than 2-3 weeks may not be effectivecows milk protein, for example, can persist in moms body for 1½ 2 weeks, and it may be another 1½ 2 weeks before the protein is out of babys system.
Babys symptoms will usually begin to improve within 5-7 days of eliminating a problem food. Your baby may not improve immediately, however, especially if the reaction is to a food that has been a regular part of moms diet. Some babies seem to feel worse for about a week before symptoms begin to improve. Sometimes it takes several weeks to see an improvement.
One way to confirm that a particular food is a problem for your baby is to eat that food again to see whether baby has the same reaction. The more severe your babys original symptoms, the longer you may wish to wait before reintroducing it into your dietfor a very severe reaction you may not reintroduce the food at all. If you reintroduce a food and your baby does not have the same reaction as before, then baby is probably not sensitive to that food. If he does react in the same way, you will want to limit or avoid this food for a time until baby is older or in some cases until baby has weaned.
