How Is Pulmonary Hypertension In Children Diagnosed
If your childs pediatrician or pediatric cardiologist suspects pulmonary hypertension, they may perform the following tests:
- Echocardiogram: An echocardiogram aka echo is an ultrasound of the heart. Its a noninvasive test that assesses your childs hearts function. An echo can also help the doctor estimate pulmonary pressure.
- Cardiac catheterization: If an abnormal echo indicates pulmonary hypertension, cardiac catheterization can confirm the diagnosis. A doctor called an interventional cardiologist inserts a catheter into a small incision in the groin and threads it up into the pulmonary artery on the right side of the heart. This test helps your childs doctor obtain an exact measurement of pulmonary blood pressure.
- Pulmonary vasodilator testing: During a cardiac catheterization or an echo, we may give treatments such as supplemental oxygen or other medications to relax the blood vessels in the lungs. These tests help us gauge how blood pressure in the lungs responds to certain medications.
Other Potential Target Pathways
VEGF and Impaired Vascular Growth
Vascular endothelial growth factor plays a prominent role in the normal development of the pulmonary circulation in the fetus and newborn . Impaired VEGF signaling may contribute to the pathogenesis of PPHN , since VEGF and its receptor VEGFR are markedly decreased in the lungs of PPHN lambs . VEGF levels are also decreased in blood and tracheal aspirates of infants with PPHN , further suggesting that decreased VEGF may be likewise involved in human PPHN.
Chronic in vivo inhibition of VEGFR has shown to impair vascular growth, increasing PASMC hyperplasia, and to downregulate eNOS, hence inducing PPHN in lamb fetuses . As such, VEGF contribution to PPHN is, at least in part, mediated by decreased NO-cGMP signaling , since VEGF increases NO release in vivo, leading to pulmonary vasodilation .
The mechanisms that link PPHN to decreased arterial growth and reduced alveolarization are still poorly understood, especially when associated with lung hypoplasia, as in CDH . These findings show that it may involve altered VEGFNO signaling. This is particularly relevant since severe PPHN, associated with lung hypoplasia, remains rather iNO resistant, resulting in high mortality .
Treatment with recombinant human VEGF in PPHN lamb model increases eNOS expression and activity, preserving PAECs’ function, and reverses pulmonary vascular remodeling and RV hypertrophy .
Nogo-B/NgBR Pathway
IGF-1/IGF-1R Signaling
How Is Pphn In The Newborn Treated
The goal of treatment for PPHN is to increase the oxygen to all of your babys body systems. If your babys body doesnt get enough oxygen, he or she may have long-term health problems.
Treatment will depend on your childs symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is. Treatments may include the following.
Recommended Reading: What To Get A Newborn Baby Boy
Chronic Pvd Across The Lifespan
Finally, there is a growing medical literature consistently demonstrating evidence of late echocardiographic markers of PH that persist throughout infancy, childhood, and early adulthood . There is growing evidence for PVD in older children and young adults, or PVD across the lifespan, in which there has been growing evidence for high risk of development of borderline PH and abnormal cardiac structure and function in young adults who were born preterm.
Hyperoxia And Reactive Oxygen Species
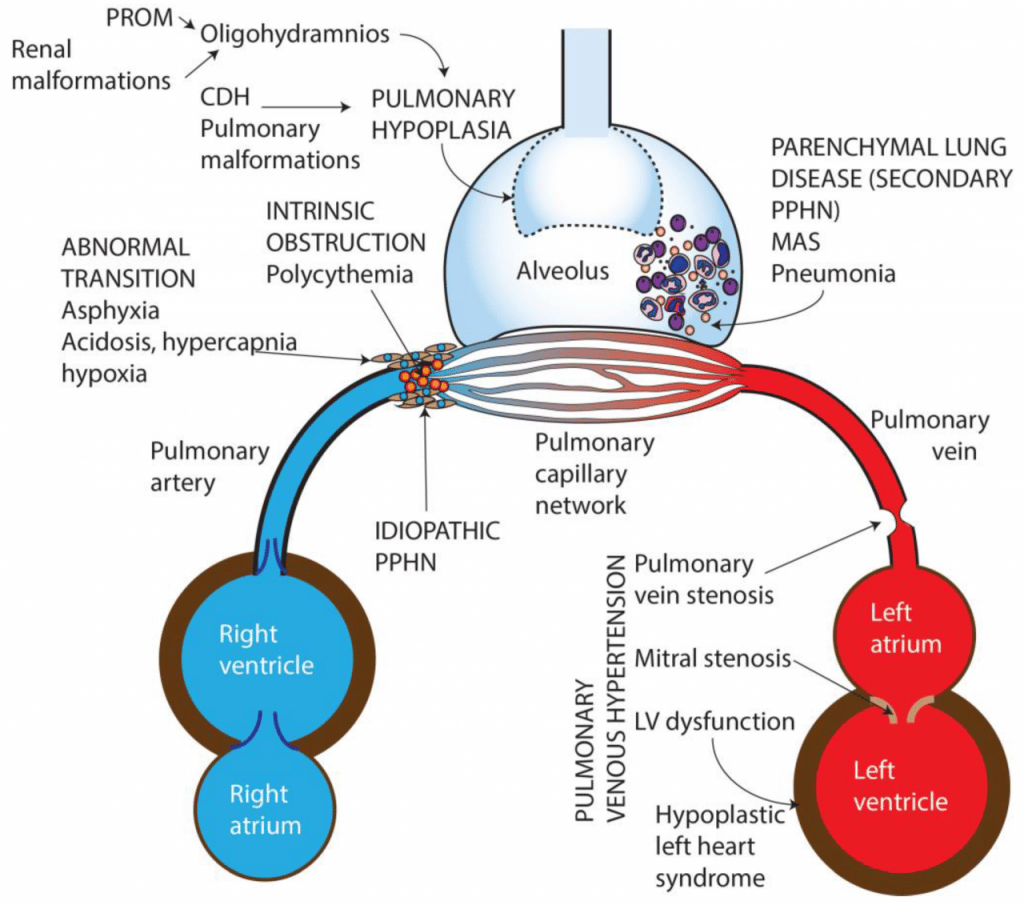
Pathway
PPHN is associated with severe hypoxemia, so ventilation with high oxygen concentrations is common in these neonates . However, hyperoxia exacerbates oxidative stress in the affected vasculature, leading to increased production of ROS. Newborns are particularly at increased risk for amplified oxidative stress, since extrauterine alveolar oxygen tension is five times higher than that in utero. As such, the fetal lung, during late gestation, goes through adaptive increases in cellular antioxidant defenses, mostly superoxide dismutase-2 .
ROS, such as superoxide, are increased in PPHN lamb and rat models , so that many signaling pathways involved in PPHN pathogenesis may act, at least in part, by increasing ROS’ levels in multiple cellular compartments of the pulmonary vasculature, ultimately leading to vasoconstriction and PASMCs proliferation .
Besides the direct effects on pulmonary vasculature, exposure to hyperoxia in premature rats results in mitochondrial dysregulation that persists into adulthood with eventual RV dysfunction, suggesting a direct deleterious effect on the RV . This effect is most likely cumulative with the direct contribution from the coexisting PPHN, since mitochondrial dysfunction and metabolic gene reprogramming in the RV have previously been identified in adults with PAH .
Potential Targeted Therapies
Tetrahydrobiopterin
Recombinant superoxide dismutase
Also Check: Do You Use Soap For Newborn Sponge Bath
Usemedications For Seizures That Might Occur With Pulmonary Hypertension
Somebabies with PH are prone to seizures, which require treatment. Some babies withPH are prone to seizures, which require treatment.
Thereare medications that can reduce the symptoms of the condition. To treatseizures, doctors may prescribe drugs that reduce or stop them.
Thesetypes of seizures can cause excessive crying and can affect a child’sdevelopment.
To findout whether a child has seizures, it is important to monitor their developmentand examine them for other problems.
Thefirst way to reduce the risk of seizures in infants with PH is to monitor thechild’s development.
Treatment Options For Pulmonary Hypertension In Newborns
Treatmentfor pulmonary hypertension in newborns depends on its cause.
Thereare treatments that can be given to children with pulmonary hypertension causedby abnormalities in the blood vessels of the lungs.
Treatmentfor congenital pulmonary hypertension can include the use of drugs to lowerblood pressure in the body .
Treatmentfor hereditary pulmonary hypertension involves the use of a radioactive drugcalled dexamethasone.
You canalways refer back to the risk factors, symptoms,and diagnosisof pulmonary hypertension in children before going through the treatmentoptions in this article.
Now letssee some of the available treatment methods for pulmonary hypertension innewborns as described below.
| pulmonary hypertension in newborns |
Also Check: Should Newborns Sleep Through The Night
Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension Of The Newborn: An Overview
A fetus in the womb has a unique circulatory system that allows it to get oxygen from the placenta. After birth, a baby no longer gets oxygen from the placenta. Instead, the newborn must get oxygen from the lungs. Some infants cannot make this switch: The lungs blood vessels do not open up properly, so blood cannot flow to the lungs. This restricted blood flow in infants is called persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn . Persistent means that the issue does not go away, and pulmonary hypertension refers to high blood pressure in the lungs blood vessels.
What Is The Outlook For Children With Pulmonary Hypertension
Thanks to advances in neonatology and echocardiography, its easier to diagnose and treat children with pulmonary hypertension earlier in life. Premature infants often outgrow pulmonary hypertension, once they start to feed and develop. After they leave the NICU, many babies do well with oxygen, medication and routine follow-up care.
However, if preemies grow out of it, they could still be at a higher risk for developing the condition again as adults, Nies explains. Their lung tissue wont be 100% normal, even if it does a significant amount of healing and growing.
Care for infants and young children with pulmonary hypertension usually requires the collaboration of multiple specialists, including:
- Pediatric pulmonologists
The outlook for older children and adults diagnosed with pulmonary hypertension is not as positive. Left undiagnosed and untreated, the condition can cause long-term heart damage and heart failure. Adults with pulmonary hypertension due to a congenital heart defect should seek care from an adult congenital heart specialist, such as Ari Cedars, M.D.
Recommended Reading: What Do Newborn Babies Need The Most
What Is Pulmonary Hypertension In Children
Most of us are familiar with the term hypertension, or high blood pressure. It occurs when blood puts too much force on the blood vessel walls. High blood pressure in the vessels of the lungs makes it harder for the right side of the heart to pump blood into the lungs, where it receives oxygen. Ultimately, high blood pressure in the lungs can result in poor right heart function and right heart failure, explains Melanie Nies, M.D., pediatric cardiologist at Johns Hopkins Childrens Center.
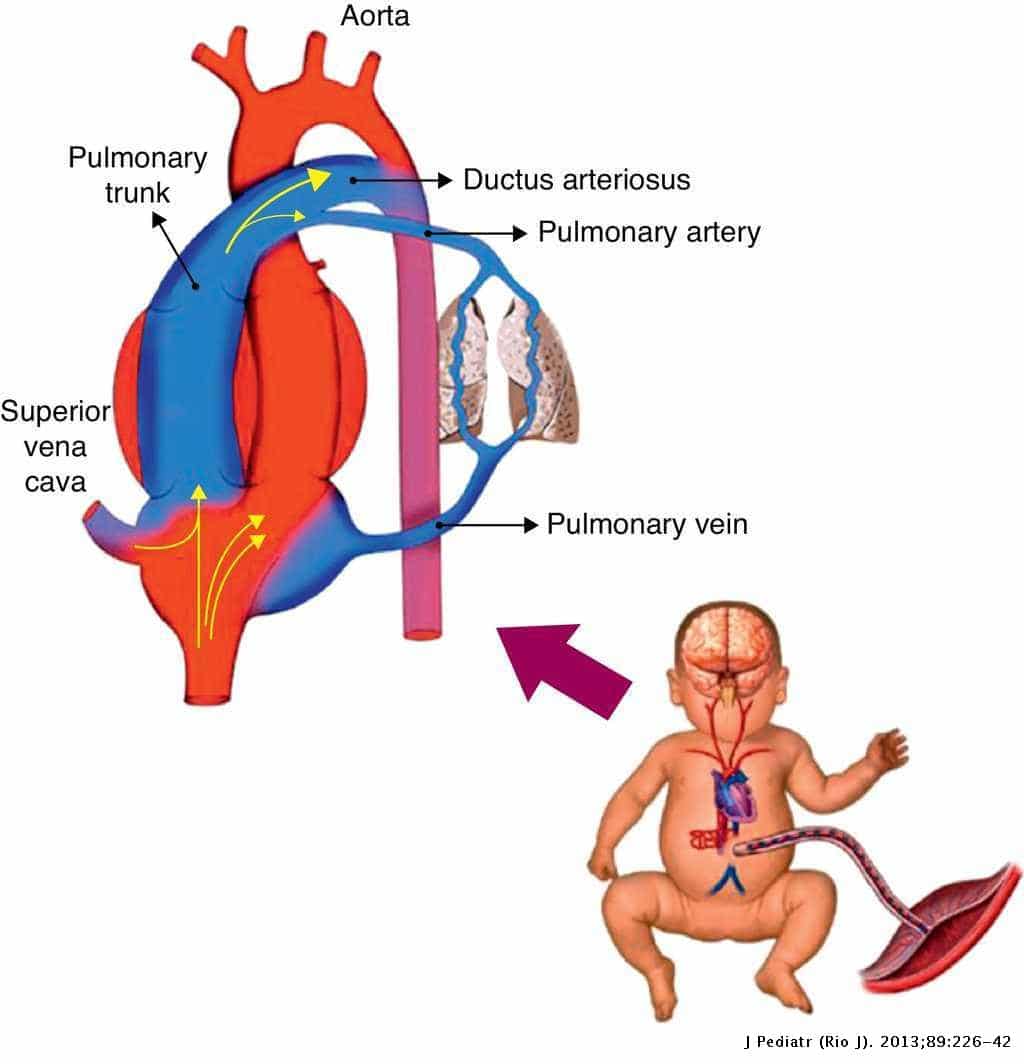
Fetal Circulation Bypasses The Lungs
While in the womb, a fetus gets oxygen differently. A fetus does not breathe instead, it gets oxygen from the placenta. The placenta is an organ that connects the mother to the fetus to exchange oxygen, nutrients, and waste. Fetal blood circulation is more complicated than normal circulation because it bypasses the lungs.
Several factors limit blood flow to the lungs blood vessels in a fetus. The low-oxygen environment of the womb and vasoconstrictors keep the blood vessels closed. The lungs themselves are also filled with fluid. This creates a situation where there is a lot of resistance to pumping blood into the lungs.
A blood vessel called the ductus arteriosus takes low-oxygen blood, bypasses the lungs, and channels it to the aorta, the bodys main artery. The blood travels through the umbilical cord to the placenta. There, the blood picks up oxygen. Oxygen-rich blood is sent back to the right side of the heart by the vena cava, the bodys main vein. This oxygen-rich blood can move directly from the right side of the heart to the left side through a hole called the foramen ovale. Oxygen-rich blood is then pumped to the brain and the body by the left side of the heart.
Increased blood pressure in the lungs blood vessels is normal in the fetus. It keeps blood out of the lungs and redirects it to the placenta.
Read Also: How To Bathe A Newborn In The Sink
Chronic Pulmonary Hypertension In Neonates
Neonates with CDH and BPD can have pulmonary hypertension lasting for weeks or months. In the hospital setting, these patients are often managed with supplemental oxygen, iNO , and oral pulmonary vasodilators, such as sildenafil or bosentan. Because of its high cost, long-term therapy with iNO is cost prohibitive, and most patients can be successfully transitioned to sildenafil after a few days.
Bosentan is an endothelin 1 receptor blocker that may be beneficial in the management of PPHN. However, the results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled exploratory trial of bosentan did not have any additive effect on the top of iNO in term neonates with PPHN.
ECMO is a modified cardiopulmonary bypass used for a prolonged period to support heart and lung function. The use of neonatal ECMO has decreased from a peak of more than 1,500 cases per year in the early 1990s to approximately 750 cases per year. This decline is likely due to improvements in both perinatal care and availability of advanced therapies for neonatal hypoxemic respiratory failure, including high-frequency ventilators, surfactant, and iNO. Generally accepted criteria to start ECMO are persistent hypoxemia and the presence of hemodynamic instability .
What Is The Outlook For Babies Who Have Had Pphn
PPHN is a serious condition, and if a child has been moved to the intensive care units at GOSH, that is because the baby is very poorly. The mortality is thought to be under 10 per cent .
There are undoubtedly some after-effects from the lack of oxygen to the brain during the illness, and up to a quarter of babies affected will have some impairment because of their illness as they grow older. This includes difficulties such as learning problems and deafness.
Also Check: How Do You Help Newborn With Constipation
Treatments For Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension Of The Newborn
Treatment starts with keeping the baby warm. Doctors can give them oxygen through a mask, incubator, hood or tubes inserted in the baby’s mouth or nostrils. Babies with PPHN can also benefit from a machine that gives them oxygen and breathe for them.
Other treatments for PPHN may include:
- Medications that increase blood pressure in the baby’s body
- Nitric oxide gas therapy along with oxygen to open the blood vessels in the lungs
- A process that bypasses the lungs and directly delivers oxygen to the brain and through the baby’s body
Once the baby can breathe on their own, it’s extremely important that doctors and nurses continue to monitor the infant. There’s a high rate of death with this very serious condition. It can sometimes take weeks or even months for the baby’s lungs to recover all the way.
Current Therapy For Pphn
Treatment of PPHN depends on the underlying disorder, aiming to decrease PVR and reduce the magnitude of the right-to-left shunt, mainly by administering pulmonary vasodilators . Depending on the severity, some infants may also require aggressive support of cardiac function, systemic blood pressure, and perfusion. Ventilation is crucial for improving ventilation/perfusion matching, and oxygen, although a recognized pulmonary vasodilator, hence many times used in high concentrations in these infants, may also be deleterious . If such treatment fails, with persisting severe respiratory failure, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation is required as a bridge therapy in the management of newborns with PPHN .
Inhaled nitric oxide is the only approved pulmonary vasodilator specifically for the treatment of PPHN, although it does not improve survival and ~40% of neonates fail to respond to it . Therefore, knowledge on different pathophysiological pathways, which might serve as potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of iNO-resistant PPHN , might be the key for ameliorating outcomes and improving survival of these infants.
Don’t Miss: How Much Formula Should A Newborn Baby Drink
Pulmonary Hypertension Linked With Lung Disease Or Lack Of Oxygen
Pulmonary hypertension is also sometimes linked with lung diseases or lack of oxygen , including:
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease a number of lung conditions that affect breathing
- interstitial lung disease a group of lung disorders that cause scarring of the lung tissue, which makes it difficult to get enough oxygen into your body
- conditions that affect breathing while youre in a deep sleep such as obstructive sleep apnoea
Low levels of oxygen in the blood make the pulmonary arteries narrow. This squeezes the blood into a smaller space, which increases blood pressure, causing pulmonary hypertension.
Pulmonary Hypertension In Premature Infants
Although PPHN is traditionally considered a disease of term and late preterm infants, it is increasingly being diagnosed in extremely preterm infants. Some preterm infants with RDS present with PPHN in the first few days after birth, whereas preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia may be diagnosed as having pulmonary hypertension later in the hospital course or after discharge from the NICU. Pulmonary artery hypertension complicating BPD is a process somewhat distinct from PPHN and tends to run a much more protracted course. It appears to be a consequence of the reduced pulmonary capillary bed secondary to the simplified lung of new BPD and pulmonary vascular remodeling. Pulmonary vascular disease is challenging to treat and significantly increases morbidity and mortality in BPD.
Preterm infants with fetal growth restriction and those who are born after prolonged rupture of membranes with varying degrees of pulmonary hypoplasia are at higher risk of developing pulmonary hypertension.
You May Like: How Much Is Insurance For A Newborn
How Is Pphn Treated
Initial treatment of PPHN will consist of simple measures such as keeping the baby warm and giving oxygen, usually through small prongs in the nostrils, or in an incubator. Doctors will usually insert a cannula or drip into the babys hand or foot, and use this to give some antibiotics.
As a baby is not likely to feed well while they have PPHN, they will receive fluids containing sugar for energy through a drip. If these simple measures do not bring the oxygen levels up easily, the baby is likely to need to be moved to a neonatal intensive care unit or NICU.
What Causes Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension In The Neonate
The cause of PPHN is not known.
In PPHN, failure of lung vessels to open enough can cause back-pressure and force the heart to keep using fetal circulation pathways. These shortcuts the ductus arteriosus and the foramen ovale allow low-oxygen blood to mix in with blood pumped to the rest of the babys body.
Read Also: What To Pack For Your Newborn At The Hospital
Closed Blood Vessels In The Lungs Cause Pphn
In rare cases, a newborns circulatory system might not properly switch to the lungs for oxygen. The blood vessels to the lungs stay closed, and blood still passes through the ductus arteriosus and foramen ovale. This allows low-oxygen blood to pump to the rest of the body and leads to a condition called hypoxemia .
This condition is called persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. It is fatal if left untreated. Fortunately, there are several effective treatments for newborns with PPHN.
Inhaled Nitric Oxide For Pphn
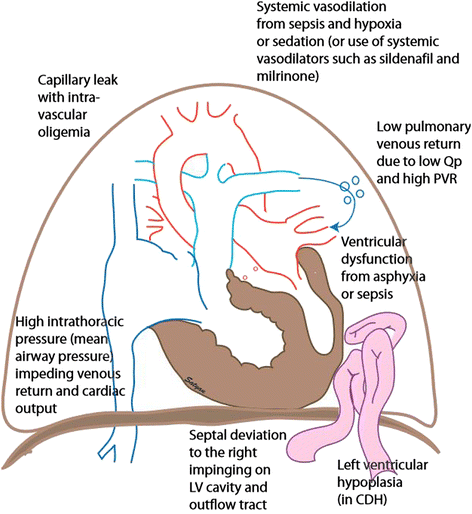
The primary goal of PPHN therapy is selective pulmonary vasodilation. Intravenous dilators such as prostacyclin and tolazoline may produce non-selective effects on the systemic circulation, leading to hypotension. In contrast, inhaled NO is well suited for the treatment of PPHN : it is a rapid and potent vasodilator, and because NO is a small gas molecule, it can be delivered as inhalation therapy to airspaces approximating the pulmonary vascular bed. Large placebo-controlled trials provide clear evidence that iNO significantly decreases the need for extracorporeal life support in newborns with PPHN . While these trials led to the FDA approval of iNO as therapy for PPHN, it is important to note that iNO did not reduce mortality, length of hospitalization, or reduce the risk of neurodevelopmental impairment. Further, beginning iNO at a milder or earlier point in the disease course , did not decrease the incidence of ECMO and/or death, or improve other patient outcomes, including the incidence of neurodevelopmental impairment .
Don’t Miss: What Is The Average Length Of A Newborn Baby
What Are Possible Complications Of Pphn In The Newborn
When blood is directed away from your baby’s lungs, its hard for their lungs to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. Babies with PPHN have low blood oxygen levels even when they breathe air thats 100% oxygen. This can cause serious problems. All of your babys organs need a regular supply of oxygen-rich blood. Your babys organs can become damaged if they dont get enough oxygen.
