When Is It Ordered
Screening
Because many infected people do not have any noticeable symptoms, a number of health organizations recommend regular chlamydia screening for certain people:
Women
All sexually active women younger than age 25 and sexually active women age 25 and older who are at increased risk should get yearly screening for chlamydia, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists . The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force and the American Academy of Pediatrics also recommend routine screening for these women .
Examples of risk factors for chlamydia infection include:
For pregnant women, the CDC recommends screening for chlamydia during the first trimester or first prenatal visit. For women younger than age 25 or at increased risk of infection, testing is repeated in the third trimester. Pregnant women diagnosed with chlamydia should be retested about 3 months after completing treatment.
Diagnosis
Chlamydia testing may also be done when your sex partner has been diagnosed with chlamydia or when you have signs and symptoms of chlamydia.
For women, if symptoms occur, they may include:
For men, symptoms may include:
What Are The Different Types Of Stis
There are many different types of STIs. The most common STIs in Australia are:
- sore, swollen lymph nodes, especially in the groin
- pain in the lower abdomen
- rash on the body, hands or feet
If you have one or more of these symptoms it doesnt necessarily mean you have an STI, but it would be wise to see your doctor for a check-up.
Keep Your Baby Safe From Infection
Even if you have an STD, you can prevent your baby from becoming infected. Here are the most common steps doctors recommend to reduce the chance of passing an STD to your baby:
Cesarean section delivery. A C-section is often recommended for women who have an STD that can be passed to baby in the birth canal.
Medicines and vaccines. In many cases, anti-viral medicines and vaccines are also given to newborn babies to reduce the chance that they will become infected with an STD.
Do not breastfeed. If you have HIV, you should not breastfeed your baby. Breast milk contains the HIV virus and can increase the risk of HIV transmission to your baby.
Many moms who follow these precautions can deliver healthy, infection-free babies. In fact, ACOG says studies show that 99 percent of HIV-infected mothers who take anti-viral medicines during pregnancy and labor, deliver their babies by C-section and do not breastfeed will not pass the HIV infection to their newborns.
Recommended Reading: How To Do Tummy Time Newborn
Testing In Rural And Remote Areas
It is acknowledged that in Australia, access to tests may vary , storing tests and samples appropriately may be challenging and there may be difficulties in recalling women to receive test results. In these situations, resources should be focused on responding to local needs .
- 23Tests are offered in the context of engagement and consultation with women. Health professionals must use standard precautions for infection prevention and control. Tests evolve with advances in technology and health professionals must keep up-to-date with the latest developments and evidence.
Can Chlamydia Be Cured

Yes, chlamydia can be cured with the right treatment. It is important that you take all of the medication your doctor prescribes to cure your infection. When taken properly it will stop the infection and could decrease your chances of having complications later on. You should not share medication for chlamydia with anyone.
Repeat infection with chlamydia is common. You should be tested again about three months after you are treated, even if your sex partner was treated.
Also Check: How To Know If Newborn Has Milk Allergy
How To Prevent An Std During Pregnancy
There are a few different ways you can prevent yourself from STDs during pregnancy, including:
- Abstaining from sex
- Staying with a long-term, monogamous, uninfected partner
- Wait to have sex until you and your partner have tested negative for STDs
- Use latex condoms and dental dams correctly and consistently
Can I Breastfeed If I Have An Sti
Maybe. Some STIs affect breastfeeding, and some don’t. The following are some general guidelines, but talk to your doctor, nurse, or a lactation consultant about the risk of passing the STI to your baby while breastfeeding:
- If you have HIV, do not breastfeed. You can pass the virus to your baby. In countries like the United States where clean water is available, using a breastmilk substitute like formula is recommended.
- If you have chlamydia, gonorrhea, or HPV, you can breastfeed your baby.
- If you have trichomoniasis, you can take the antibiotic metronidazole if you are breastfeeding. You may need to wait 12 to 24 hours after taking the medicine to breastfeed.
- If you have syphilis or herpes, you can breastfeed as long as your baby or pumping equipment does not touch a sore. It is possible to spread syphilis or herpes to any part of your breast, including your nipple and areola. If you have sores on your breast, pump or hand-express your milk until the sores heal. Pumping will help keep up your milk supply and prevent your breast from getting overly full and painful. You can store your milk to give to your baby in a bottle for another feeding. But if parts of your breast pump also touch the sore while pumping, you should throw the milk away.
Recommended Reading: How To Let Newborn Sleep At Night
F: Routine Maternal Health Tests
This section discusses the evidence for offering women a range of tests as part of usual care.
- Listen
This section discusses the evidence for offering women a range of tests as part of usual care.
Recommendations are based on evidence about the diagnostic accuracy of available tests, the effectiveness of interventions to prevent mother-to-child transmission of infection or other effects on the unborn baby, and the availability of treatments.
For notifiable infections , diagnoses are required to be reported to the National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System. This allows analysis of trends in jurisdictions and groups at risk, although data quality varies for the different conditions and reporting of Indigenous status is incomplete in some States and for some conditions. Evidence on the prevalence and incidence of other conditions is generally from observational studies and may not be representative of the Australian population or groups within the population. While incidence or prevalence data are not always available, each chapter includes a brief discussion that aims to give health professionals an indication of the likelihood that women in their community will be affected.
How Do I Tell My Partner I Have An Sti
If you have an STI, it’s important that your sexual partner be tested as well to make sure the infection doesn’t spread further. There are many ways to tell your partner that they need to get tested for STI.
There are programs and tools to help you tell your partner anonymously that they need to get tested.
Contact your local public health department for more information.
Read Also: How To Get Ssn For Newborn
What Should I Be Tested For And When
People often say, Just test for everything. While that might seem to make sense initially, its important to talk to your health care provider about your specific risk factors and lifestyle. There are a few downsides to testing for everything that are important to consider. First of all, tests are expensive, and in a few cases, such as blood testing for herpes, a positive test can be a false positive. False positives may result in unnecessary anxiety when there may be virtually no risk of transmission and no required treatment.
Here are some instances that would prompt a screening test:
- Youre sexually active. Everyone who is sexually active should be screened at some point. We recommend an HIV test for everyone who is sexually active. We also suggest women obtain a test for gonorrhea and chlamydia, because, unlike men, they frequently harbor these infections without developing symptoms. Keep in mind that if youre practicing safe sex and are in a monogamous relationship, you can get tested less frequently.
- Youre having unprotected sex. If youve had or want to start having sex vaginal, anal, or oral with a new partner, without a condom, its a good idea to get tested. Heres how long after exposure we can get a reliable test result:
- 2 weeks: gonorrhea and chlamydia
- 1 week to 3 months: syphilis
- 6 weeks to 3 months: HIV, hepatitis C and B
Still have questions? Make an appointment to talk to your PCP today in our judgment-free office.
What Is Being Tested
Chlamydia is one of the most common bacterial sexually transmitted diseases in the United States and can cause serious complications if not treated. Chlamydia testing identifies the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis as the cause of your infection.
The preferred method for chlamydia testing is the nucleic acid amplification test that detects the genetic material of Chlamydia trachomatis. It is generally more sensitive and specific than other chlamydia tests and can be performed on a vaginal swab on women or urine from both men and women, which eliminates the need for a pelvic exam in women.
Screening for, diagnosing, and treating chlamydia is very important in preventing long-term complications and spread of the infection to others. Chlamydia infections are especially common among people 15 to 24 years of age. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that 2.86 million Americans are infected with chlamydia each year and notes that women are frequently re-infected if their partners don’t get treatment. The actual number of cases may be higher since many people do not experience any symptoms and do not get tested and diagnosed. Still, over one million new cases are reported each year.
Chlamydia is generally spread through sexual contact with an infected partner. Risk factors include having multiple sex partners, infection with another STD at the same time or previous STD infection, and not using a condom correctly and consistently.
Also Check: How Many Diapers Do You Need For Newborn
What Happens If I Dont Get Treated
The initial damage that chlamydia causes often goes unnoticed. However, chlamydia can lead to serious health problems.
If you are a woman, untreated chlamydia can spread to your uterus and fallopian tubes . This can cause pelvic inflammatory disease . PID often has no symptoms, however some women may have abdominal and pelvic pain. Even if it doesnt cause symptoms initially, PID can cause permanent damage to your reproductive system. PID can lead to long-term pelvic pain, inability to get pregnant, and potentially deadly ectopic pregnancy .
Men rarely have health problems linked to chlamydia. Infection sometimes spreads to the tube that carries sperm from the testicles, causing pain and fever. Rarely, chlamydia can prevent a man from being able to have children.
Condoms And Dental Dams
Most STI can be prevented by using a condom or dental dam during vaginal, anal or oral sex. You can buy condoms or dental dams at drug stores or health clinics without a prescription. The use of pre-lubricated condoms or added personal lubricants can help prevent the risk of a condom breaking.
Other things to think about:
- Check the expiry date on a condom before using one and make sure the packaging and the condom itself don’t have any holes or tears.
- Never use a condom more than once, and don’t use 2 condoms at the same time as that can cause breakage.
- It’s recommended to use lubricants with condoms, but be sure to use the right type. Vaseline and other oil-based lubricants destroy latex.
Read Also: How Much Formula Can A Newborn Have
How Can Cs Affect My Baby
CS can have major health impacts on your baby. How CS affects your babys health depends on how long you had syphilis and if or when you got treatment for the infection.
CS can cause:
- Miscarriage ,
- Stillbirth ,
- Prematurity ,
- Low birth weight, or
- Death shortly after birth.
Babies born to women with untreated syphilis may be stillborn, or die from the infection as a newborn.
For babies born with CS, CS can cause:
- Deformed bones,
- Skin rashes.
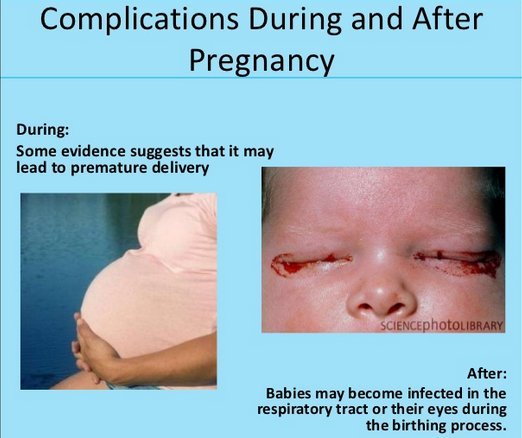
How Do Stis Affect Pregnant Women
STIs can cause many of the same health problems in pregnant women as in women who are not pregnant. But having an STI also can hurt the unborn baby’s health.
Having an STI during pregnancy can cause:
- Premature labor . Early birth is the number one cause of infant death and can lead to long-term developmental and health problems in children.1
- Infection in the uterus after birth
Don’t Miss: What Do I Need To Buy For My Newborn
Stds Can Affect Your Ability To Have Children In The Future
STDs can also affect your ability to have children. If left untreated, even an asymptomatic STD can lead to an episode of pelvic inflammatory disease – one of the leading causes of preventable infertility. Women whove had PID have scarring on their fallopian tubes and other reproductive organs. This can make it difficult for any sperm to reach a womans eggs. It can also lead to ectopic pregnancies, which occurs when a fertilized egg doesnt get to the uterus before implanting. Ectopic pregnancies can be extremely dangerous.
STDs in men can cause infertility. The male reproductive tract, including the epididymis and urethra, can be damaged by the infection. HIV can also reduce a mans semen quality, making it harder for them to get their partner pregnant. STDs in men are usually more likely to cause symptoms than in women, meaning theyre typically more likely to be treated in time, but thats not always the case.
Newborn Blood Spot Test
The newborn blood spot test involves taking a small sample of your baby’s blood to check it for 9 rare but serious health conditions.
When your baby is about 5 days old, a healthcare professional will prick your baby’s heel and collect a few drops of blood on a special card. This is sent off for testing.
The heel prick may be uncomfortable and your baby may cry, but it’s all over very quickly.
You May Like: How Much Vitamin D To Give Newborn
What Should I Think About And Do Before I Have Sex
- Talk about safer sex and STI testing with your partner.
- If you or your partner could get pregnant but aren’t ready to be parents:
- talk about contraception with your partner
- use a tool like It’s a plan to find out the best contraception for you and make an appointment with your health care provider
Text box 6
Hepatitis B and HPV can be prevented by a vaccine.
