How To Give Vitamin D Drops To Your Breastfed Baby
It isnât possible or safe for your baby to swallow a pill for vitamin D. Instead, your baby will get a liquid version of this nutrient. Your health visitor can give you advice on where to get baby vitamin D drops. Using vitamin D drops for newborn babies is quite simpleâall you need is the liquid supplement and the dropper that comes with it. Hereâs what to do:
Read the directions carefully. Always start by reviewing the amount of vitamin D to give your baby and following the directions on how to measure and administer the appropriate dose. Be sure not to exceed the recommended dose.
Administer the drops. You can drop the liquid onto your breast, on or around the nipple before feeding your baby, or give the drops to your baby with a dropper or on a sterilised spoon with your baby in an upright position. When your baby is older, you can mix the vitamin D drops into their food.
Does My Baby Need A Vitamin C Supplement
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is important for enhancing iron absorption and maintaining a healthy immune system. Its also an antioxidant, meaning it helps prevent cell damage. Infants generally need less vitamin C than adults, and its found in both breast milk and formula. Generally, babies will get enough vitamin C from breastmilk and formula, and its often found in common infant snacks and beginner solid foods Check with your pediatrician, but generally vitamin C supplements arent necessary.
Other Issues With Vitamin D Dosing In Infants
Some families are resistant to providing drops of vitamin D to their breastfed infants or perceive them to be poorly tolerated, especially when given with iron-containing multivitamins. In these cases, there are several alternatives that may be considered . The first is the use of vitamin D drops that can be placed directly on the breast or given as dissolvable filmstrips. For some mothers, this is easier and more acceptable than giving a dropper of vitamins directly to the infant or mixed in their milk .
Fig. 2.
Adequate and inadequate vitamin D metabolism in infants.
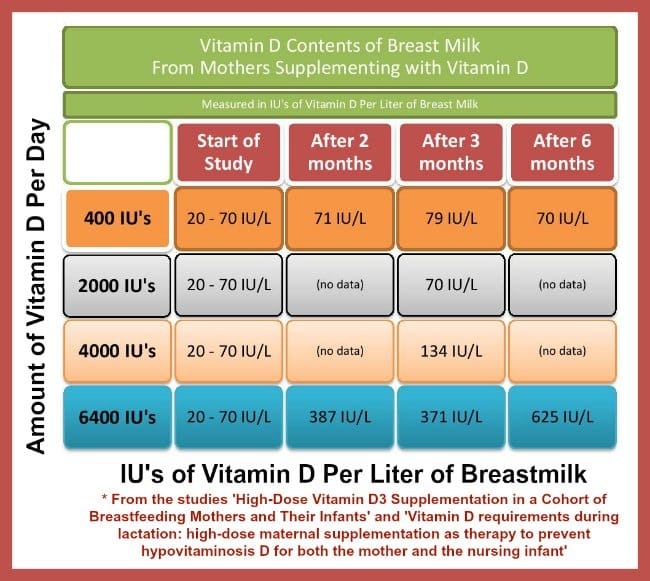
Another approach is to have the lactating mother take a relatively high dose of vitamin D. Studies have shown that a maternal dose of 6,400 IU daily will provide an infant with adequate vitamin D intake from the mothers milk if fully breastfed and if the mother takes the dose every day. Of note is that lower maternal doses, especially those of 4002,000 IU daily, do not provide adequate vitamin D in breast milk. The dose of 6,400 IU daily is slightly above the IOM upper limit of 5,000 IU/day but is highly likely to be safe, and this should not be a concern in recommending this approach if desired by breastfeeding women .
Table 2.
For additional information:
You May Like: How Hard Is It To Adopt A Newborn Baby
Why Babies Need Vitamin D
Vitamin D helps us to build and maintain strong bones and teeth.
Our bodies can make vitamin D from the sun. But babies cannot safely get the vitamin D they need from the sun.
Your baby needs vitamin D because:
- their skin is very sensitive to the sun and should not be in direct sunlight
- their food may not have enough vitamin D in it
- between 0 to 12 months babies grow very quickly and have a greater need for vitamin D to form strong bones
Research shows that vitamin D plays an important role in helping the immune system. It may help prevent diabetes, heart disease, rheumatoid arthritis, MS and some forms of cancer.
African, Afro-Caribbean, Middle-Eastern or Indian parents are more likely to have babies with low levels of vitamin D.
Risks Of Low Vitamin D Levels

In severe cases, low-levels of vitamin D can cause rickets or osteomalacia in children.
Rickets is a condition that leads to soft bones. It can cause severe bone deformities such as bowed legs and spine curves.
Rickets in adults is known as osteomalacia or soft bones. This can cause frequent bone fractures, muscle weakness and bone pain.
Donât Miss: What Do Newborn Babies Wear
Read Also: How To Bathe A Newborn Boy
Zarbees Naturals Baby Vitamin D Supplement
Price: $
Founded by Dr. Zak Zarbock, a pediatrician and dad, Zarbees Naturals creates a vitamin D supplement for babies containing natural ingredients only no drugs, alcohol, artificial sweeteners, flavors, or dyes.
All of their products are gluten-free and pediatrician recommended. This supplement is given in an oral droplet either in breast milk or bottle or mixed with food. Remember, though, that your baby must finish all of what you mix the drop with to get the full dose of 400 IU per 0.25 ml.
Food Sources Rich In Vitamin D
The following food items are good sources of vitamin D:
- Vitamin D fortified food: Infant cereal, crackers for toddlers, formula
- Fatty fish: Salmon, tuna, and mackerel
- Egg: Especially the egg yolk
- Vitamin D fortified milk: Cow or buffalo milk with added vitamin D
Foods like fish, egg, and cow/buffalo milk can be introduced only after the age of 12 months . So how can babies less than one year, who are breastfeeding, get vitamin D?
You May Like: When Is The Best Time To Take Newborn Photos
Study: Many New Moms Babies Deficient
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends vitamin D supplementation of 400 IU for all breastfed babies and those who are drinking less than 1 liter a day of formula.
But pediatrician Frank R. Greer, MD, who headed the committee that came up with the new guidelines, says pediatricians are not selling the message to new parents.
I am frankly surprised that more pediatricians are not recommending supplementation, especially to new moms who are breastfeeding, he says.
The CDC study appears in the April issue of Pediatrics, along with another study, which finds a high rate of vitamin D deficiency among new mothers and their babies living in Boston.
Overall, more than half of the infants and more than a third of the mothers were considered vitamin D deficient. More than a third of the infants and a fifth of the mothers were considered severely deficient.
Study researcher Anne Merewood, MPH, says she was most surprised by the high rate of deficiency among the moms.
Many of these women were taking prenatal vitamins, but this did not ensure that they had adequate vitamin D levels, she says.
Merewood points out that supplementation may be especially important for darker-skinned people who absorb less light from the sun and for lighter skinned people who have little exposure to the sun.
Babies May Get Too Much Vitamin D From Droppers
FDA Says Some Droppers Give Infants Excessive Doses of Liquid Vitamin D
June 15, 2010 — The FDA is warning parents and caregivers of infants that some liquid vitamin D supplement products sold with droppers could allow excessive doses to be given to babies, which could be harmful.
The FDA says some droppers that come with the vitamin D liquid could hold more than the 400 international units a day recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
“It is important that infants not get more than the recommended daily amount of vitamin D,” Linda M. Katz, MD, MPH, of the FDA, says in a news release. “Parents and caregivers should only use the dropper that comes with the vitamin supplement purchased.”
Excessive vitamin D can cause nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, excessive thirst, frequent urination, constipation, abdominal pain, muscle weakness, muscle and joint aches, confusion, and fatigue and even cause serious damage to kidneys, the FDA says.
Vitamin D in proper doses is necessary for infant development, promoting calcium absorption in the gut and strong bone development. Vitamin D supplements are recommended for some infants, especially those who are breastfed, because deficiency can lead to bone problems, such as thinning, soft, and misshapen bones such as seen in the condition known as rickets.
Also Check: How To Get Your Newborn To Sleep In Bassinet
How Do We Get These Babies The Vitamin D They Need
This RCT concluded that giving breastfeeding mothers 6,400 IU vitamin D /day, and no additional supplement for the infant, made sure the mother became sufficient AND infants became sufficient . The infants in this group had equivalent vitamin D status to those who received 400 IU/day . Many other measurements and blood tests were taken, including weight, length and head circumference of the infant, which were similar for both groups.
6400 IU vit D/day = Sufficient mother AND baby
Correlations Between Serum 25d Concentrations And Ca P Ap Albumin Bmi And Age
There was no correlation between serum concentrations of 25D and Ca, P, AP and albumin. There were also no correlations between serum concentrations of 25D and z-scores of BMI . Furthermore, no correlation was found between the age of the infants and the serum concentrations of 25D .
There were no differences in 25D serum levels regarding season of the year, age , sex of the infant, monthly family income, birth weight and nutritional status, as shown in Table 4. Regarding the serum concentrations of phosphorus in the different age groups, it was observed that infants less than 1 year old had serum concentrations higher than the other age groups.
Recommended Reading: How To Become A Newborn Hearing Screener
When To Give Babies Vitamin D Drops
Your baby can start taking vitamin D drops soon after birth. Most likely, your childâs health visitor will recommend the standard amount, which is 8.5 to 10 micrograms daily of vitamin D for babies under 1 year, and 10 micrograms daily for those over 1 year. But once your baby can start getting vitamin D from other food sources , you may be able to reduce the amount they receive by drops.
Every newborn, baby, and child is different, so although there is a recommended dose of vitamin D for babies, itâs always best to check with your childâs midwife or health visitor. Most babies need the standard dose, while others may need more, and some may need to supplement for longer than others.
Vitamin D And Your Baby
Vitamin D helps our bodies use calcium to build and maintain strong bones and teeth.
Low levels of vitamin D in babies/children can cause rickets. Rickets can result in weak bones, delayed walking, bowed legs, and swollen wrists or ankles. If untreated, rickets can lead to failure to grow, deformed or broken bones, pneumonia and seizures.
Every year a number of babies/children in New Zealand are diagnosed with rickets.
Also Check: What Is The Best Formula For Newborns With Gas
You May Like: When To Be Concerned About Newborn Spit Up
How Much Vitamin D Is Necessary For Babies
The American Academy of Pediatrics and the Institute of Medicine recommend a daily intake of 400 IU of vitamin D for babies within the first year. For babies older than 1 year, the amount increases to 600 IU per day. To determine whether your baby is getting enough vitamin D, consider the following:
-
Breastfed babiesand partially breastfed babies will not get enough vitamin D from breast milk alone, so supplementing with liquid vitamin D is necessary and important.
-
Formula-fed babies are likely to get a good amount of vitamin D from their formula, as most brands are fortified with vitamin D. Check the label of your formula and consult your childâs healthcare provider. However, to get the full recommended amount of vitamin D, babies will need to consume 32 ounces of fortified formula a day. Most newborns and many young babies wonât drink this much, so supplementation with vitamin D drops is probably necessary. Check with your provider to be sure.
Itâs also important to keep in mind that every baby is different. Some babies may require more vitamin D, including those with the following conditions:
-
have had recent surgery
-
are taking medications that block the absorption of vitamin D.
To determine the appropriate amount of liquid vitamin D to give your little one, consult the chart below and your childâs healthcare provider.
Not Getting Enough Vitamin D In Your Diet
Good sources of vitamin D include fatty fish and egg yolks. However, its found naturally in very few foods.
For this reason, vitamin D is often added to certain foods and beverages, such as milk. This process is called fortification.
Even with fortified foods, many people still dont get enough vitamin D. Vegans or vegetarians are at a particularly high risk for a deficiency, as their diets may not include any fish, eggs, or milk.
Recommended Reading: Is Zinc Better Than Vitamin C
You May Like: What To Do For Jaundice Newborn At Home
Do Infants Get Enough Vitamin D From Breast Milk
Breast milk alone does not provide infants with an adequate amount of vitamin D. Shortly after birth, most infants will need an additional source of vitamin D.
To avoid developing a vitamin D deficiency, the Dietary Guidelines for Americans and American Academy of Pediatrics recommend breastfed and partially breastfed infants be supplemented with 400 IU per day of vitamin D beginning in the first few days of life. Families who do not wish to provide a supplement directly to their infant should discuss with a healthcare provider the risks and benefits of maternal high dose supplementation options.
Guidelines For Vitamin D Intake
In 2003, the American Academy of Pediatrics published a guideline recommending that all children older than two months receive 200 IU of supplemental vitamin D daily.10 This expert consensus statement was supported by studies of breastfed infants in the United States, Norway, and China and suggested that infants who ingest 100 or 200 IU of supplemental vitamin D daily were less likely to develop rickets.11 Since then, there have been concerns that these dosages may be insufficient. These concerns are supported by studies showing that vitamin D deficiency can occur early in life12 that serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations tend to be lower in breastfed infants13 and that 400 IU of vitamin D supplementation in these infants maintains higher concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D.14 In addition, studies have shown that adolescents consume insufficient levels of dietary vitamin D 15,16 and that supplementation increases 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and bone mineral density.17
| Clinical recommendation |
|---|
Read Also: What To Do When Your Newborn Is Constipated
Vitamin D Supplementation In Infants Children And Adolescents
CATHERINE F. CASEY, MD DAVID C. SLAWSON, MD and LINDSEY R. NEAL, MD, University of Virginia Medical Center, Charlottesville, Virginia
Am Fam Physician. 2010 Mar 15 81:745-748.
Vitamin D deficiency in children can have adverse health consequences, such as growth failure and rickets. In 2008, the American Academy of Pediatrics increased its recommended daily intake of vitamin D in infants, children, and adolescents to 400 IU. Infants who are breastfed and children and adolescents who consume less than 1 L of vitamin Dfortified milk per day will likely need supplementation to reach 400 IU of vitamin D per day. This recommendation is based on expert opinion and recent clinical trials measuring biomarkers of vitamin D status. It is also based on the precedent of preventing and treating rickets with 400 IU of vitamin D. In addition to dietary sources, exposure to ultraviolet B sunlight provides children and adults with additional vitamin D. Although the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends keeping infants out of direct sunlight, decreased sunlight exposure may increase childrenâs risk of vitamin D deficiency. No randomized controlled trials assessing patient-oriented outcomes have been performed on universal vitamin D supplementation. However, vitamin D may reduce the risk of certain infections and chronic diseases. Physicians should help parents choose the appropriate vitamin D supplement for their child.
Also Check: Why Is My Newborn Constantly Crying
Description Of Clinical Trial
This randomized controlled trial divided the breastfeeding women/infant pairs, at 4-6 weeks post-partum, into one of three groups:
Previous research found that if the breastfeeding mother was only taking the recommended daily allowance of 400 IU per day, then an infant, solely fed on breast milk, would get the equivalent of 33 68 IU vitamin D / liter, which would provide the infant with far less than the recommended 400 IU/day. Hollis was a co-author in a study that reported infants breastfed by mothers taking only 400 IU/day typically had vitamin D levels < 5 ng/ml .
Recommended Reading: How Do I Add Newborn To Medicaid
S Is For Skimpy Sun Exposure
The other source of vitamin D isnt food at allits the sun. Ultraviolet rays stimulate the skin to produce vitamin D. This creates a conundrum, of course, since its known that direct exposure to sunlight without sun protection can drive up a childs risk of developing skin cancer. Thats why the AAP says infants under 6 months should never have direct sun exposure. Older children should be slathered with a generous amount of a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a sun protection factor of 15 to 30 before going outside.
Increased use of sunscreen may be another reason vitamin D deficiency has become more common in kids, so is there really any harm in allowing a child to soak up a few rays in the name of bone health? Thats a tough call, because no one really knows how much sun exposure is enough to get the benefits.
Some vitamin D researchers estimate that just five to 30 minutes of sun exposure to the face, arms, legs, or back between 10 a.m. and 3 p.m., twice a week, is plenty, but you should check with your pediatrician about whether it would be a good idea to let your child go out in the sun unprotected for even short periods of time.
Dont Miss: Is There Vitamin C In Orange Juice
