Can I Wait And Have My Baby Tested Later
The earlier these treatable disorders are found, the better the outcome for babies with these disorders. It is strongly advised that your baby have a blood sample taken before leaving the hospital. If you decide you do not want your baby to have a blood sample taken before they leave the hospital, you will be asked to sign a form. This form shows you understand the reasons for the test and the possible outcomes for your baby if your baby is tested too late or not at all and has one of these disorders.
What Is Newborn Screening
Newborn screening is a public health service done in each U.S. state. Every newborn is tested for a group of health disorders that aren’t otherwise found at birth.
With a simple blood test, doctors can check for rare genetic, hormone-related, and metabolic conditions that can cause serious health problems. Newborn screening lets doctors diagnose babies quickly and start treatment as soon as possible.
Nichd Newborn Screening Research Goals
NICHD’s research goals related to newborn screening fall into several broad categories.
- Identify, develop, and test the most promising newborn screening technologies.
- Increase the specificity of newborn screening.
- Expand the number of conditions for which screening tests are available.
- Improve and evaluate treatments and disease management strategies for detectable conditions that can currently be treated and for other genetic metabolic, hormonal, and/or functional conditions that can be detected through newborn screening for which treatment is not yet available.
Read Also: How To Get Newborn To Nap In Crib
Which Disorders Does Newborn Screening Test For
Each state determines the disorders included on its newborn screening panel. To guide state health agencies, the Secretary of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services provides the Recommended Uniform Screening Panel . This list includes 35 core conditions and 26 secondary conditions . The conditions fall into four categories:
- Endocrine disorders, which cause hormone levels that are too high or too low
- Hemoglobin disorders, rare blood conditions that affect the blood protein that carries oxygen throughout the body
- Metabolic disorders, conditions that affect how the body processes nutrients or manages enzymes
- Other disorders, such as cystic fibrosis, hearing loss, and spinal muscular atrophy
Each state ultimately chooses which conditions from the RUSP to include in their newborn screening. But states can add conditions to their screening panels that are not part of the RUSP. Screening is available for more than 60 disorders, and all states currently screen for at least 29 conditions. See the conditions included on your states newborn screening panel.
What Are The Most Common Newborn Screening Tests
Congenital Hypothyroidism
Congenital hypothyroidism affects one in about every 4,000 babies. Most children with it who are not identified and treated promptly after birth develop mental retardation and growth failure, deafness, and neurologic abnormalities. Infants with congenital hypothyroidism who start receiving oral thyroid hormone in the first weeks of life perform normally or near-normally on intellectual testing at 4 to 7 years of age.
Phenylketonuria
Babies with PKU lack an enzyme called phenylalanine hydroxylase needed to process phenylalanine, an amino acid in the diet. This defect causes phenylalanine to accumulate in the blood stream and leads to brain damage.
A baby with PKU is given a special formula and later is a diet that is low in phenylalanine. Dietary reatment started in the first few weeks of life can prevent the consequences of the disease and avoid the brain damage and learning disabilities.
Galactosemia
This disease is due to lack of an enzyme needed to handle the sugar galactose. This inability causes failure to thrive, vomiting, cataracts, progressive liver disease, and mental retardation. Death often results from bloodstream infection with the bacteria E. coli .
The elimination of galactose from the child’s diet, by avoiding milk and milk products, leads to dramatic improvement and in time the clinical consequences of the disease decrease or disappear.
Sickle Cell Disease
Also Check: How To Add Newborn To Caresource
Why Are Newborn Screens Done
As soon as a baby is born, a newborn screen identifies if they have one of these conditions. With certain conditions, babies may look healthy right after birth, but then they can quickly become sick.
For babies with metabolic conditions and critical congenital heart disease, finding a condition before symptoms start can be lifesaving. Babies who receive treatment early do much better both early on and throughout their lives. Its important to identify these conditions as soon as possible so babies can start treatment. The CDC estimates that every year newborn screening tests identify 13,000 babies with treatable conditions.
Conditions Detected By Newborn Bloodspot Screening
Some of the conditions that can be detected by newborn bloodspot screening include:
- Phenylketonuria a condition where the body cannot break down phenylalanine . If untreated, PKU can lead to intellectual disability.
- Hypothyroidism a condition where the thyroid gland does not make enough hormones. This can cause severe intellectual disability and growth problems. Early detection and treatment helps children to be healthy.
- Cystic fibrosis a condition where organs such as the lungs and pancreas make abnormal mucus that clogs the organs and stops them working properly.
- Other rare conditions that affect metabolism there are many other rare conditions that make the body unable to break down proteins and fats in the usual way. If these conditions are found and treated early before your baby becomes sick, they will have a better chance of having an improved health outcome.
Read Also: How To Wake Up A Newborn
What Does Screening Mean
The term screening refers to checking people who appear healthy for a specific condition. Screening sorts people into two groups:
- People unlikely to have the condition. Most people fall into this group. Members of this group do not need more testing. Their chance of having the condition, also called their risk for the condition, is low.
- People more likely to have the condition. Fewer people fall into this group. Members of this group need more testing to tell for sure if they have the condition. Their chance of having the condition, also called their risk for the condition, is higher than that for people in the first group.
Common examples of health screening are a mammogram , colonoscopy , and Pap smear . These screens do not tell for sure if someone has breast, colon, or cervical canceronly that they might have it and need more tests to know for sure. Screening helps people with these conditions to find out and get treatment early, when treatment usually works best.
Similarly, NBS checks a baby for certain conditions present at birth that benefit from early treatment or intervention. Newborn screening consists of three parts:
How Many Newborns Are Screened In The United States
Today, all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico have newborn screening programs. This means that nearly every child born in the United States or Puerto Rico is screened shortly after birth.1
- All states currently require newborn screening for at least 29 health conditions. Each state’s public health department decides both the number and types of conditions on its testing panel.2 Most states allow parents to opt out for religious or other reasons.3 Many states also offer supplemental screening programs that screen for disorders beyond those required by the state costs for these supplemental tests are usually covered by insurance.
- About 4 million infants are born each year in the United States,4 and most of them are screened.
- Most states report participation of 99.9% or higher.
- The latest CDC data show that about 12,500 newborns each year are diagnosed with one of the core conditions detected through newborn screening. This means that almost 1 out of every 300 newborns screened is eventually diagnosed.5
- Early diagnosis and treatment in many cases can significantly improve the chances of healthy development and positive outcomes and nearly eliminates death from the conditions.
Read Also: How Much Ounces Should A Newborn Drink
Why Do Newborn Babies Undergo Screening Tests
The purpose of newborn tests is to screen for serious treatable diseases. Most of the disorders are genetic . The tests are usually done before the baby leaves the hospital. If the tests are done earlier than 24 hours after the baby is born, a repeat test is recommended at 1 to 2 weeks of age.
The newborn screening tests which are done in the United States a are decided on a state-by-state basis. The most common newborn screening tests in the US include those for hypothyrodism , PKU , galactosemia, and sickle cell disease. Testing for hypothyroidism and PKU is required in virtually all States. Screening for galactosemia and sickle cell disease is required in most states.
Some states in the US mandate tests for other conditions. These include:
- maple syrup urine disease ,
All these tests are usually done using the same sample of the baby’s blood.
Newborn Screen Blood Test
Ohio law requires that all newborn babies have their blood tested. Even if your baby looks healthy, the Newborn Screen Blood Test will show if they are born with or at risk to have a rare genetic, hormone-related or metabolic disorder. If these disorder are not found early, a child can develop serious health problems or die. Most of these disorders are inherited from parents. Other follow-up tests are often needed to confirm a diagnosis. Many times, the follow-up tests will show that the baby does not have the disorder.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help your baby grow and lead a healthy life.
It is important that the blood sample be collected 24 to 48 hours after birth and before the 5th day of life. The test will be done before your baby goes home.
- If your baby gets tested before 24 hours, the test will need to be done again within 5 days.
- For a premature or sick baby or a baby transferred from another hospital, the health care providers at Nationwide Childrens Hospital will make sure that the Newborn Screen Blood Test and follow-up tests are done.
Read Also: How Many Bottles Do You Need For A Newborn
Parent Options During Screening
States give parents options during NBS. Examples of choices that differ by state include the following:
- Whether and how to refuse NBSAll states require NBS, but most states let parents refuse screening for their baby. Accepted reasons for refusal depend on the laws in a state. For example, some states only let parents refuse NBS for religious reasons. Other states let parents refuse for any reason. A couple of states do not allow parents to refuse NBS at all.
- What happens with your newborns blood spots after NBSSome states give parents choices about what happens to their babys dried blood spots after screening is complete. For example, some states let parents choose whether the blood sample is stored, destroyed, or used for research studies.
You can find out about parent options in your state by contacting your states newborn screening program. Contact information for programs in each state is available on the State pages.
How Screening Is Done
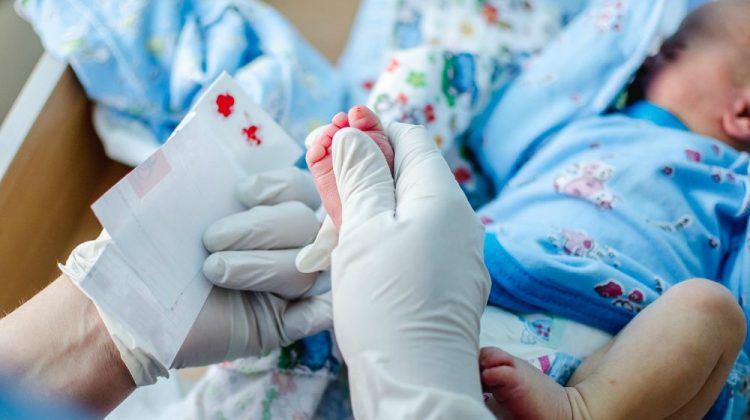
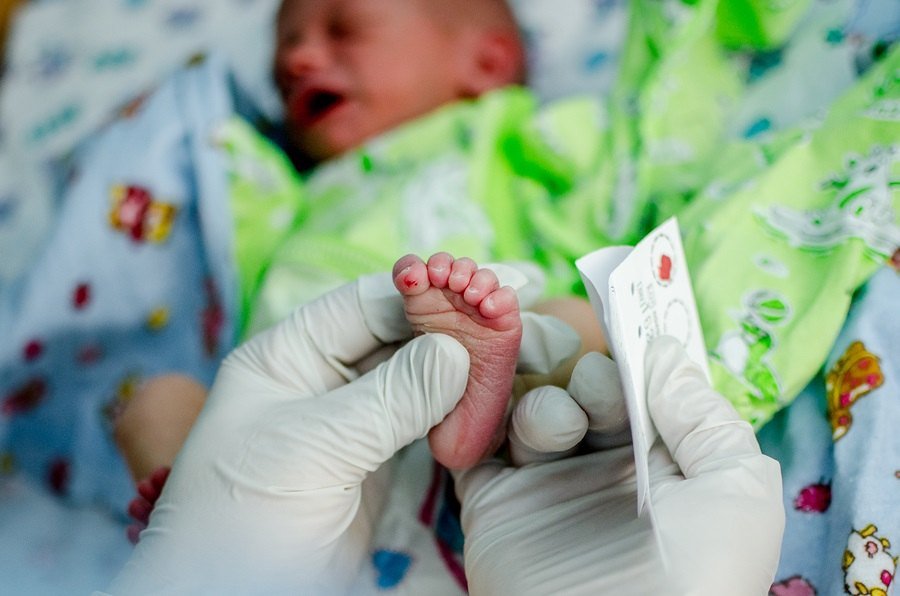
The process of newborn screening is relatively quick and easy. Between 24 hours to seven days after birth, a few drops of blood are taken from an infants heel and placed on a special card. The paper is sent to a specialized laboratory for testing.
The results of the blood tests are sent to the infant’s pediatrician within two to seven days. If any of the tests come back positive, further testing will be done to confirm the diagnosis. Parents do not have to request the tests they should be automatically performed.
In addition to blood-based tests, a hearing test will be performed to check for hearing loss. It is a non-invasive test that only takes around five to 10 minutes to complete.
There are two standard methods of detecting hearing loss in newborns:
- Otoacoustic Emissions : A miniature earphone and microphone can confirm hearing if sounds are reflected back from the ear canal.
- Auditory Brain Stem Response : Electrodes placed on the newborn’s head can detect the presence or absence of brains response to sounds.
Don’t Miss: How To Help Your Newborn Sleep
If One Of Your Children Has A Health Condition Will Another Have It Too
Many of the health conditions found by newborn screening are inherited. Inherited means something that is passed from parent to child through genes. Genes are a part of your bodys cells that store instructions for the way your body grows and works.
When one child in a family has an inherited health condition, the chance of a brother or sister having the same condition is higher than if no child in the family has the condition.
If you have a child with a health condition and you want to have another baby, talk to your health care provider or a genetic counselor. A genetic counselor is a person who is trained to help you understand about genes, birth defects and other medical conditions that run in families, and how they can affect your health and your babys health.
Sometimes hearing loss is not inherited. For example, it can be caused by an infection during pregnancy. In this case, it usually doesnt happen in another pregnancy.
Will My Baby Require Every Test Can I Opt Out Of Newborn Screening Tests
All 50 states and the District of Columbia require a newborn blood screening for at least 21 disorders, with many states screening newborns for the 61 disorders suggested by the HHS and sometimes a few additional ones.
Check with your practitioner or your local board of health to find out what tests are done in your state, or look them up online at Baby’s First Test .
If youre concerned, discuss your fears at a prenatal visit dont wait until delivery day to speak up. You do have the right to opt out of any test or procedure, but you will need to sign paperwork documenting your decision.
In some cases, the hospital might inform the states department of child services that youve decided to forgo the recommended screening.
Keep in mind, although most of these conditions are very rare, they can be life-threatening if they go undetected and untreated. Testing is inexpensive, and in the very unlikely event that your baby tests positive for any condition, the pediatrician can verify the results and begin treatment immediately, making a huge difference in the prognosis.
It’s in your child’s best interest to get all the screenings your pediatrician and hospital recommend.
Read Also: How To Keep A Newborn Awake
Today Every Baby Can Be Screened
Each year, around 12,500 babies are born with one of the conditions included in state newborn screening panels. Most of these infants appear perfectly healthy at birth and come from families with no history of the disorder. Unfortunately, once symptoms appear, they are often irreversible, leading to severe health and developmental problems or even death. Every baby born in the United States is required by law to undergo newborn screening in the first few days after birth. Newborn screening is a quick and simple way to see if a seemingly healthy infant is at increased risk of having these rare, but serious, conditions. Most affected babies identified through newborn screening who receive treatment early grow up healthy with normal development.
For more information regarding the newborn screening procedure and what to expect at the hospital, see the Screening Procedures section.
Why Is Newborn Screening Important
Newborn screening tests for conditions that could be severe or life-threatening to babies and children, according to Dr. Wasserstein. Screening detects some diseases before symptoms occur. With an early diagnosis, children can get timely medical care for these disorders.
When we identify a condition at this stage, we get to monitor the disease, educate the childs family, and begin treatment before symptoms happen, Dr. Wasserstein says. Treating the condition before the disease becomes irreversible gives us the best benefit.
You May Like: What Temperature Water For Newborn Bath
Where Does Nbs Happen
All babies need NBS, regardless of where they are born.
If your baby is born at a hospital, screening will happen before you take your baby home. Usually, a health care provider performs NBS in your room or a newborn/nursery area.
If your baby has an out-of-hospital birth, screening can happen outside of the hospital like at your birth center or home. Many midwives are trained to complete NBS.
If you are planning an out-of-hospital birth, talk to your midwife about NBS before your baby is born. If your midwife cannot perform NBS, make other arrangements. Your babys health care provider can help arrange screening by another midwife, a hospital, clinic, or local health department. It is important that you make a plan so your baby completes screening near the recommended age.
Are Screening And Diagnostic Testing The Same
No, but they are related.
Screening checks whether you might have a condition. Newborn screening cannot determine whether your baby actually has that conditiononly if they are more or less likely to have it.
In contrast, diagnostic testing tells whether your baby actually has a condition.
If screening suggests your baby might have a condition, you will be contacted to schedule follow-up testing. Follow-up testing often includes a diagnostic test to determine whether your baby has the condition or not.
You may need to complete follow-up testing right away to know if your baby needs treatment or intervention. You should follow your health care providers directions about timing and what kind of diagnostic testing your baby needs.
Visit the Newborn Screening Results and Follow-Up page for more information on screening results and follow-up testing.
You May Like: How Often Do You Wash A Newborn
