What To Do If You Have Symptoms
Because the symptoms of lactose intolerance are rather general, it is important to get an accurate diagnosis before removing dairy from your diet .
In fact, many people who think they have lactose intolerance because theyâve experienced the symptoms have been shown to absorb lactose normally.
Health care providers often diagnose lactose intolerance using the hydrogen breath test. This involves ingesting 1.8 ounces of lactose and testing for elevated levels of hydrogen in the breath, which are caused by bacteria fermenting lactose in the colon (
, 8).
This is because not all people with malabsorption have lactose intolerance.
Lactose intolerance is defined by the presence of reported symptoms, and that depends on how sensitive a person is to the effects of malabsorption, as well as the amount of lactose in their diet .
Treatment of lactose intolerance usually involves restriction or avoidance of high-lactose foods such as milk, cheese spread, cream and ice cream . However, people with lactose intolerance can often tolerate up to 1 cup of milk, especially when itâs spread throughout the day. This is equivalent to 0.4â0.5 ounces of lactose (
2 ).
Summary If you have symptoms of lactose intolerance, your doctor may determine your diagnosis by having you perform a hydrogen breath test. Treatment usually involves avoiding high-lactose foods like milk, though you may still tolerate small amounts.
What Is Milk Intolerance And Milk Allergy
Around 1 in 10 young children has a reaction when they drink cow’s milk. This could be because they have a lactose intolerance or a milk allergy. Milk allergy is much more common than lactose intolerance in children under 5.
Lactose intolerance is a problem with the digestive system it means your child doesn’t have the enzyme needed to digest lactose, which is the sugar in milk.
Milk allergy, however, is a problem with the immune system the body reacts to the protein in milk. An allergy usually involves other parts of the body as well as the stomach, and may cause symptoms such as a skin rash or swelling of the face.
Your doctor can confirm whether your child is lactose-intolerant or has a milk allergy by doing some medical tests. Don’t use unproven tests such as Vega, kinesiology, Alcat or allergy elimination tests for children. A milk intolerance is very unlikely to be the cause of mucus or coughing.
Many young children grow out of their intolerance or allergy. But don’t start giving them cow’s milk until your doctor tells you it’s safe to do so.
Symptoms Of Lactose Sensitivity In Infants
Related Articles
If you have a fussy baby or your baby suffers from diarrhea or frequent spitting up, you may suspect lactose intolerance. Before you stop breastfeeding or switch formulas, check with your health care provider about other possible explanations for her symptoms. Lactose intolerance is extremely rare in infants and is usually a result of another condition.
Don’t Miss: Can I Switch My Newborns Formula
What Should I Do If I Think My Baby Is Allergic Or Intolerant To Cows’ Milk
If you think your baby is having a reaction to cows’ milk, see your GP to discuss your concerns.
They will be able to assess if your baby’s symptoms may be caused by a cows’ milk allergy or something else. Make sure you get medical advice before taking cows’ milk out of your child’s diet as it contains important nutrients.
Stay On One Breast Per Feed If Needed

If a mother has a very large storage capacity she may only need to feed from one breast per feed so that her baby can get a good balance of higher fat milk. Jack Newman explains :
Excerpt from
Dr. Jack Newmans Guide to Breastfeeding Jack Newman and Teresa Pitman, 2014, p. 181
In some situations where the baby is colicky from getting too much milk too quickly, and fixing the latch and finishing one side before offering the other breast does not work, it may be worthwhile to try giving one breast at a feeding or even two feedings in a row. The mother needs to be aware that this may cause her milk production to decrease, and that the baby may fuss because hes not getting as much milk as he wantseven if he is still gaining weight well.
Recommended Reading: How To Make Your Newborn Fall Asleep
How Is It Treated
There is no cure for lactose intolerance. But you can treat your symptoms by limiting or avoiding milk products. Some people use milk with reduced lactose, or they substitute soy beverage and soy cheese for milk and milk products. Some people who are lactose-intolerant can eat yogurt without problems, especially yogurt with live cultures. You can also take dietary supplements called lactase products that help digest lactose. In time, most people who have lactose intolerance get to know their bodies well enough to avoid symptoms.
One of the biggest concerns for people who are lactose-intolerant is making sure they get enough of the nutrients found in milk products, especially calcium. Calcium is most important for children, teens, pregnant women, and women after menopause. There are many non-dairy foods that contain calcium, including:
- Broccoli, okra, kale, collards, and turnip greens.
- Fish canned with bones .
- Calcium-fortified juices and cereals.
- Calcium-fortified soy products such as soy beverage and tofu.
- Almonds.
Treatment For Lactose Intolerance
Your GP will help find out if your child is lactose intolerant. Your child may be given a lactose intolerance test, which measures blood sugar levels before and after having a lactose solution drink.
If the test confirms lactose intolerance, your child will likely be referred to a dietitian, who will give you advice on what foods and drinks are suitable. Babies and young children need to get the right nutrients to make sure they grow and develop properly.
Continued
For bottle-fed babies with lactose intolerance, your GP will probably advise you to switch to a lactose-free formula milk.
If you are breastfeeding, it may help if your baby has lactase substitute drops, which make it easier for them to digest lactose in breast milk.
Lactose intolerance is often only temporary for many babies and young children. Their symptoms will often get better within a few weeks. At this point, it’s safe to start gradually bringing milk and dairy back into their diet.
Also Check: What All A Newborn Baby Needs
What Happens In My Body If Im Lactose Intolerant
When we drink milk or have a milk-based product, lactase in our small intestines breaks down the milk sugar. It then gets absorbed into the body through the small intestines.
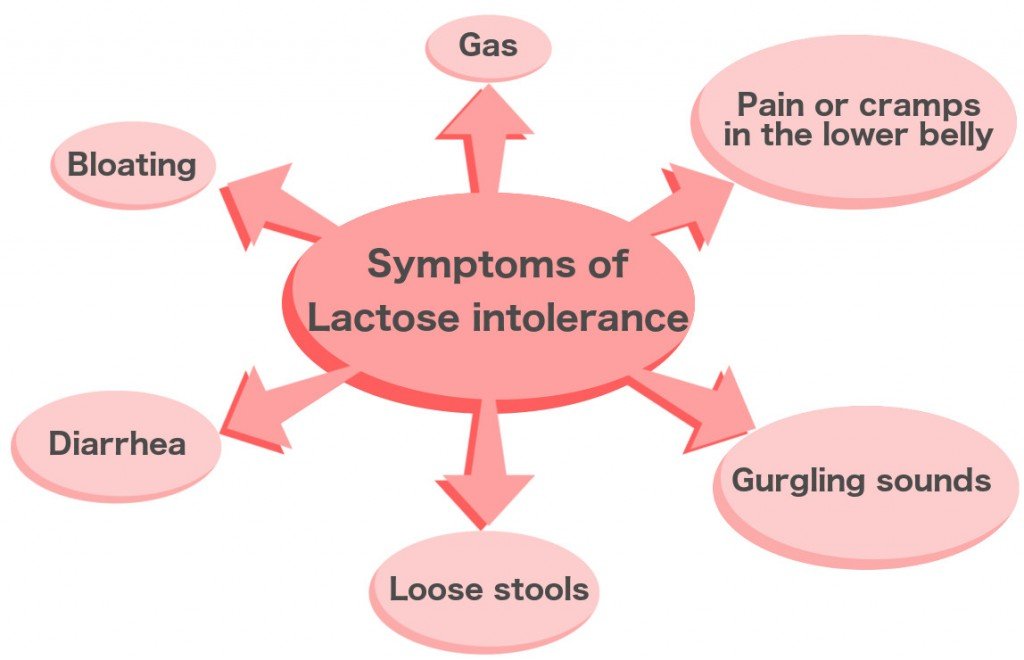
But people who are lactose intolerant donât have it so easy. In them, the lactose doesnât get broken down. Instead, it goes on to the colon, where it mixes with normal bacteria and ferments. It can cause things like gas, bloating and diarrhea.
The symptoms are no fun, but theyâre not dangerous. Most people can manage their symptoms by changing their diet and limiting the amount of lactose they consume. Some people do better by cutting lactose out of their diet altogether.
Your body may be able to handle some lactose without symptoms. Experiment to find out the types and amounts of products with lactose you can eat and drink.
There are some steps you can take to test yourself:
What Are The Symptoms Of Lactose Intolerance
The symptoms of lactose intolerance will always involve your babys digestive system and can include your little one experiencing diarrhoea, wind, bloating and sometimes nappy rash. Lactose intolerant babies often cry a lot and are uncomfortable which is why its sometimes linked with colic. Its important to note that if your baby has mucus or blood in their poo too then its not a lactose intolerance and you should see your GP.
Lactose intolerance is diagnosed by a doctor taking a detailed history and testing your babys poo for acid. Hydrogen breath tests that measure the amount of hydrogen your baby breathes out can also be done but it can be quite difficult to get young babies to do this effectively, so this test tends to be reserved for older children and adults.
You May Like: How To Make A Newborn Baby Stop Crying
What Are The Causes Of Lactose Intolerance
Only 1 in 50 people of European descent have an intolerance to lactose2. In the UK, its more common in people of Asian or African-Caribbean origin3.
There are three main causes of lactose intolerance4:
Primary this is when the bodys natural lactase production decreases by around 10-30%. This could be as a result of age, or in response to reducing the amount of dairy products that you eat. A primary lactose intolerance doesnt usually occur before adulthood, and in most cases is associated with cultural groups where dairy products are not a regular part of the adult diet5.
Secondary this type of intolerance is temporary. It occurs as the result of gut damage, caused by a stomach bug or infection, undiagnosed coeliac disease, or a long course of antibiotics, for example.
Congenital an extremely rare, genetic form of the lactose intolerance, where babies are born without, or with very low amounts of lactase.
Lactose intolerance may also occur in babies who are born prematurely. This is because their small intestine is not developed enough at birth, and things usually improve as babies get older.
What Is A Milk Allergy
When a baby is allergic to milk, it means that his or her immune system, which normally fights infections, overreacts to proteins in cow’s milk. Every time the child has milk, the body thinks these proteins are harmful invaders and works hard to fight them. This causes an allergic reaction in which the body releases chemicals like .
Cow’s milk is in most baby formulas. Babies with a milk allergy often show their first symptoms days to weeks after they first get cow milk-based formula. Breastfed infants have a lower risk of having a milk allergy than formula-fed babies.
People of any age can have a milk allergy, but it’s more common in young children. Many kids outgrow it, but some don’t.
If your baby has a milk allergy, keep two epinephrine auto-injectors on hand in case of a severe reaction . An epinephrine auto-injector is an easy-to-use prescription medicine that comes in a container about the size of a large pen. Your doctor will show you how to use it.
You May Like: How To Handle A Newborn
General: Excess Fussiness Sleeplessness Or Colic
Every baby cries, but crying continuously and inconsolably for extended periods is unusual. You might hear someone say a baby who cries a lot has colic. Some doctors find colic controversial, but excess crying comes from somewhere, often with insomnia. Doctors also often downplay fussiness, which can delay diagnosing CMA. We hear this from parents all too often!
When should you suspect that crying is excessive and something serious is happening? The going adage is to talk to the doctor if it happens in threes. That is: if your baby cries for 3+ hours in a day, for 3+ days in a week, for over 3 weeks. That can signal gastrointestinal pain, which could result from CMA.
Extreme fussiness can also come with reflux, a rash, or other factors. Keep this in mind when asking your childs doctor about the possibility of CMA.
Finish The First Breast Offer The Second
The fat content of breast milk increases during a feed and also increases the closer together the feeds are. If a mother is shortening feeds or feeding on a schedule this could lower the fat content in breast milk. Less fat reduces the time spent in the stomach resulting in the lactose passing through the stomach and bowel without being properly digested . Finishing the first breast before offering the second side will help your baby to get the proportion of higher fat milk he needs.
Recommended Reading: When Can You Do A Dna Test On A Newborn
Symptoms Blamed For Lactose Intolerance
Lactose intolerance is often blamed as being a contributory factor for colic, resulting in cessation of breastfeeding and substitution of lactose free formula. Infants with gastrointestinal symptoms on exposure to cows milk are more likely to have cows milk allergy than lactose intolerance
Green and frothy bowel motions may be a sign that the baby is receiving too much lactose, which has a rapid gut transit time. This may be due to an excess of the early less fat-rich milk or switching the baby between breasts before emptying one breast first. Babies may be very unsettled and windy. Mothers may have an overactive letdown reflex.
Assessment by an experienced breastfeeding worker may be beneficial to ensure optimal milk removal by the baby is taking place before considering lactose free formulae. Imbalance of milk transfer can produce similar symptoms i.e. loose bowel motions, which may be green and frothy. This is due to the rapid transit time of large volumes of lower fat milk and consequently an excessive consumption of lactose . Breast compression when the baby is not actively sucking may improve milk transfer.
Babies can exhibit excess wind and gastric discomfort, which may be diagnosed as lactose intolerance, but which in fact is transitory lactase deficiency i.e. too much lactose for the available lactase.
While Relatively Uncommon Some Babies Can Be Lactose Intolerant And The Condition Can Cause Discomfort If Left Untreated
What is lactose intolerance?
Lactose is a sugar found naturally in breast milk, cows milk and most dairy products .
Usually, lactose is broken down in the gut by an enzyme called lactase. Yet some people dont have enough of this enzyme. Without lactase to break it down, the lactose stays in the gut and bacteria eat it instead. This produces large amounts of gas, which in turn produces the symptoms of lactose intolerance.
What causes lactose intolerance?
In babies, lactose intolerance is generally caused by either:
- A congenital condition, where babies are born without lactase
- Premature birth, where the small intestine is not developed enough to produce lactase yet
- A temporary intolerance caused by a stomach bug or infection, undiagnosed coeliac disease or antibiotics
Lactose intolerance can also develop in older children whose diets are low in lactose. This is often the case in cultural groups where dairy isnt part of the everyday diet.
How do I know if my baby is lactose intolerant?
It can be tricky to diagnose lactose intolerance, as the symptoms are similar to other conditions. Things to look out for include:
- Stomach pain
- Excessive wind
These symptoms usually appear within three hours of the feed.
If your baby is showing any of these symptoms or you think he is having trouble digesting a feed, you should consult your doctor or health professional. They will be able to advise on the best way to address the condition.
Will my baby grow out of lactose intolerance?
Recommended Reading: What Items Do You Need For A Newborn Baby
